Abstract
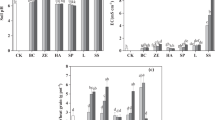
As an extremely toxic metal, cadmium (Cd) is readily taken up by most plants. In situ Cd passivation is of great importance to reduce Cd availability in soil. In this experiment, two alkaline amendments, lime (L) (at a dosage of 0.02%, 0.04%, or 0.08%) and biochar (B) (at a dosage of 0.5%, 1%, or 2%), were used to improve Cd passivation by spent mushroom substrate (SMS) in a simulating Cd-contaminated soil (0.6 mg kg−1). Results showed that the application of SMS alone reduced Cd bioavailability by 44.80% and EC by 9.71% and increased soil pH by 0.61 units, CEC by 25.32%, and soil enzymes activities by 17.11% to 21.10% compared with non-amendment Cd-contaminated soil. Biochar combination enhanced the efficiency of SMS on Cd reduction by 48.32–66.58% and pH increased by 0.17 to 0.59 units and enzymes activities elevation by 5.74% to 47.29% in a dose-dependent manner. Lime also facilitated SMS to passivate Cd by decreasing bioavailable Cd by 63.10%–66.47% and increasing soil pH by 0.25–0.72 units and enzymes activities by 3.28% to 37.86% compared to those of SMS. Among six combined amendments, SMSB3 (0.5% SMS + 2% B) performed best in reducing bioavailable Cd (39.46% higher than SMS), increasing organic matter content (28.54% higher than SMS) and soil enzyme activities (25.82%, 47.29%, and 26.23% higher than that of SMS for catalase, urease, and invertase, respectively). Both biochar and lime can assist SMS to passivate Cd and improve soil property, and biochar is more efficient than lime in reducing cadmium content and increasing enzyme activity and organic matter.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Lee SE, Al-Wabel MI, Tsang DC, Ok YS (2017) Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metalloids in contaminated soils. J Soils Sediments 17(3):717–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1339-4
Ball AS, Jackson AM (1995) The recovery of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from spent mushroom compost. Bioresour Technol 54(3):311–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(95)00153-0
Behnke GD, Zuber SM, Pittelkow CM, Nafziger ED, Villamil MB (2018) Long-term crop rotation and tillage effects on soil greenhouse gas emissions and crop production in Illinois, USA. Agric Ecosyst Environ 261:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.03.007
Bomhard E, Maruhn D, Paar D, Wehling K (1984) Urinary enzyme measurements as sensitive indicators of chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity. Contrib Nephrol 42:142–147. https://doi.org/10.1159/000409974
Cao X, Ma L, Gao B, Harris W (2009) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43(9):3285–3291. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803092k
Chen G, Yu Y, Wu X, Wang G, Gu G, Wang F, Ren J, Zhang H, Zhao Y (2019a) Microfluidic electrospray niacin metal-organic frameworks encapsulated microcapsules for wound healing. Research 2019:6175398. https://doi.org/10.34133/2019/6175398
Chen H, Li W, Wang J, Xu H, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhang Y (2019b) Adsorption of cadmium and lead ions by phosphoric acid-modified biochar generated from chicken feather: selective adsorption and influence of dissolved organic matter. Bioresour Technol 292:121948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121948
Dong LY, Jin Y, Song T, Liang JS, Bai X, Yu SM, Teng CY, Wang X, Qu JJ, Huang XM (2017) Removal of Cr (VI) by surfactant modified Auricularia auricula spent substrate: biosorption condition and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17626–17641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9326-5
García-Delgado C, Jiménez-Ayuso N, Frutos I, Gárate A, Eymar E (2013) Cadmium and lead bioavailability and their effects on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons biodegradation by spent mushroom substrate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):8690–8699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1829-0
Georgescu AA, Eliescu A, Nicolescu CM, Bumbac M, Cioateră N, Mureșeanu M, Buruleanu LC (2019) Performance of Pleurotus ostreatus mushrooms and spent substrate for the biosorption of cd (II) from aqueous solution. Anal Lett 52(13):2007–2027. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1590380
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B, Usman M, Gurajala HK, Rashid MS, He Z, Yang X (2019a) Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ Pollut 257:113609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113609
Hamid Y, Tang L, Yaseen M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Aziz MZ, He ZL, Yang X (2019b) Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat cropping system. Chemosphere 214:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.113
Han XQ, Xiao XY, Guo ZH, Xie YH, Zhu HW, Peng C, Liang YQ (2018) Release of cadmium in contaminated paddy soil amended with NPK fertilizer and lime under water management. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 159:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.049
He L, Zhong H, Liu G, Dai Z, Brookes PC, Xu J (2019) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.151
Hoult EH, McGarity JW (1986) The measurement and distribution of urease activity in a pasture system. Plant Soil 93(3):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02374286
Hu B, Liang D, Liu J, Lei L, Yu D (2014) Transformation of heavy metal fractions on soil urease and nitrate reductase activities in copper and selenium co-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.08.007
Hu T, Wang X, Zhen L, Gu J, Zhang K, Wang Q, Ma J, Peng H, Lei L, Zhao W (2019) Effects of inoculating with lignocellulose-degrading consortium on cellulose-degrading genes and fungal community during co-composting of spent mushroom substrate with swine manure. Bioresour Technol 291:121876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121876
Jiang H, Li T, Han X, Yang X, He Z (2012) Effects of pH and low molecular weight organic acids on competitive adsorption and desorption of cadmium and lead in paddy soils. Environ Monit Assess 184(10):6325–6335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2422-y
Langer U, GuÈnther T (2001) Effects of alkaline dust deposits from phosphate fertilizer production on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in grassland soils. Environ Pollut 112(3):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00148-2
Lee SH, Kim EY, Park H, Yun J, Kim JG (2011) In situ stabilization of arsenic and metal-contaminated agricultural soil using industrial by-products. Geoderma 161(1–2):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.11.008
Li YT, Rouland C, Benedetti M, Li FB, Pando A, Lavelle P, Dai J (2009) Microbial biomass, enzyme and mineralization activity in relation to soil organic C, N and P turnover influenced by acid metal stress. Soil Biol Biochem 41(5):969–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.01.021
Lim JE, Ahmad M, Usman AR, Lee SS, Jeon WT, Oh SE, Yang JE, Ok YS (2013) Effects of natural and calcined poultry waste on Cd, Pb and As mobility in contaminated soil. Environ Earth Sci 69(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1929-z
Liu D, Huang Y, An S, Sun H, Bhople P, Chen Z (2018) Soil physicochemical and microbial characteristics of contrasting land-use types along soil depth gradients. Catena 162:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.028
Ma L, Liu M (2018) Effect of exogenous cd pollution on red soil and wheat. In IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (Vol. 394, no. 5, p. 052043). IOP publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/394/5/052043
Marković J, Jović M, Smičiklas I, Šljivić-Ivanović M, Onjia A, Trivunac K, Popović A (2019) Cadmium retention and distribution in contaminated soil: effects and interactions of soil properties, contamination level, aging time and in situ immobilization agents. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.001
Meimaroglou N, Mouzakis C (2019) Cation exchange capacity (CEC), texture, consistency and organic matter in soil assessment for earth construction: the case of earth mortars. Constr Build Mater 221:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.036
Mohamed I, Zhang GS, Li ZG, Liu Y, Chen F, Dai K (2015) Ecological restoration of an acidic Cd contaminated soil using bamboo biochar application. Ecol Eng 84:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.07.009
Nirola R, Biswas B, Megharaj M, Subramanian A, Thavamani P, Aryal R, Saint C (2018) Assessment of chromium hyper-accumulative behaviour using biochemical analytical techniques of greenhouse cultivated Sonchus asper on tannery waste dump site soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(27):26992–26999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2740-5
Ono K, Yasutaka T, Hayashi TI, Kamo M, Iwasaki Y, Nakamori T, Fujii Y, Kamitani T (2019) Model construction for estimating potential vulnerability of Japanese soils to cadmium pollution based on intact soil properties. PLoS One 14(6):e0218377. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218377
Qin L, Huang X, Xue Q, Liu L, Wan Y (2019) In-situ biodegradation of harmful pollutants in landfill by sludge modified biochar used as biocover. Environ Pollut 258:113710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113710
Ramtahal G, Umaharan P, Hanuman A, Davis C, Ali L (2019) The effectiveness of soil amendments, biochar and lime, in mitigating cadmium bioaccumulation in Theobroma cacao L. Sci Total Environ 693:133563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.369
Schinner F, Von Mersi W (1990) Xylanase-, CM-cellulase-and invertase activity in soil: an improved method. Soil Biol Biochem 22(4):511–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(90)90187-5
Schwertfeger DM, Hendershot WH (2009) Determination of effective cation exchange capacity and exchange acidity by a one-step BaCl 2 method. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73(3):737–743. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2008.0009
Shi W, Ma X (2017) Effects of heavy metal cd pollution on microbial activities in soil. Ann Agric Environ Med 24(4):722–725. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/80920
Sun Y, Wen C, Liang X, He C (2018) Determination of the phytoremediation efficiency of Ricinus communis L. and methane uptake from cadmium and nickel-contaminated soil using spent mushroom substrate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(32):32603–32616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3128-2
Tapia Y, Cala V, Eymar E, Frutos I, Gárate A, Masaguer A (2010) Chemical characterization and evaluation of composts as organic amendments for immobilizing cadmium. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5437–5443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.034
Van Zwieten L, Kimber S, Morris S, Chan KY, Downie A, Rust J, Joseph S, Cowie A (2010) Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 327(1–2):235–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0050-x
Wei YN, Jin ZH, Zhang M, Li Y, Huang SQ, Liu XS, Jin Y, Wang HM, Qu JJ (2019) Impact of spent mushroom substrate on cd immobilization and soil property. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07138-y
Xu C, Chen HX, Xiang Q, Zhu HH, Wang S, Zhu QH, Huang DY, Zhang YZ (2018) Effect of peanut shell and wheat straw biochar on the availability of Cd and Pb in a soil–rice (Oryza sativa L.) system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0495-z
Xu H, Liu L, Teng F, Lu N (2019) Emission enhancement of fluorescent molecules by antireflective arrays. Research 2019:3495841. https://doi.org/10.34133/2019/3495841
Yan-bing H, Dao-You H, Qi-Hong Z, Shuai W, Shou-Long L, Hai-Bo H, Han-Hua Z, Chao X (2017) A three-season field study on the in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil using lime, two industrial by-products, and a low-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.005
Yang Y, Chen J, Huang Q, Tang S, Wang J, Hu P, Shao G (2018) Can liming reduce cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa) in slightly acidic soils? A contradictory dynamic equilibrium between Cd uptake capacity of roots and Cd immobilisation in soils. Chemosphere 193:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.061
Yang X, Zhou HL, He CT, Mo ZW, Ye JW, Chen XM, Zhang JP (2019) Flexibility of metal-organic framework tunable by crystal size at the micrometer to submillimeter scale for efficient xylene isomer separation. Research 2019:9463719. https://doi.org/10.34133/2019/9463719
Yousefi Z, Kolahi M, Majd A, Jonoubi P (2018) Effect of cadmium on morphometric traits, antioxidant enzyme activity and phytochelatin synthase gene expression (SoPCS) of Saccharum officinarum var. cp48-103 in vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:472–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.076
Zhang X, Sun F, He J, Xu H, Cui F, Wang W (2017) Robust phosphate capture over inorganic adsorbents derived from lanthanum metal organic frameworks. Chem Eng J 326:1086–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.052
Zhu X, Chen B, Zhu L, Xing B (2017) Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: a review. Environ Pollut 227:98–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.032
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Key Research Project of China (Grant no.: 2017YFD0801104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Zhang, M., Li, R. et al. Spent mushroom substrate combined with alkaline amendment passivates cadmium and improves soil property. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 16317–16325 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08099-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08099-3