Abstract
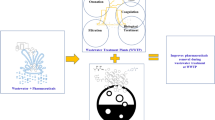
The combined coagulation and adsorption of targeted acetaminophen and naproxen using activated biochar and aluminum sulfate were studied under various synthetic “combined sewer overflow” (CSO) conditions. The biochar demonstrated better adsorption performance for both acetaminophen and naproxen (removal, 94.1 and 97.7 %, respectively) than that of commercially available powdered activated carbon (removal, 81.6 and 94.1 %, respectively) due to superior carbonaceous structure and surface properties examined by nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. The adsorption of naproxen was more favorable, occupying active adsorption sites on the adsorbents by naproxen due to its higher adsorption affinity compared to acetaminophen. Three classified CSO components (i.e., representing hydrophobic organics, hydrophilic organics, and inorganics) played different roles in the adsorption of both adsorbates, resulted in inhibition by humic acid complexation or metal ligands and negative electrostatic repulsion under adsorption and coagulation combined system. Adsorption alone with biochar was determined to be the most effective adsorptive condition for the removal of both acetaminophen and naproxen under various CSO conditions, while both coagulation alone and combined adsorption and coagulation failed to remove the acetaminophen and naproxen adequately due to an increase in ionic strength in the presence of spiked aluminum species derived from the coagulant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar MI, Sáez J, Lloréns M, Soler A, Ortuño JF, Meseguer V, Fuentes A (2005) Improvement of coagulation–flocculation process using anionic polyacrylamide as coagulant aid. Chemosphere 58:47–56
Alvárez PM, Beltrán FJ, Masa FJ, Pocostales JP (2009) A comparison between catalytic ozonation and activated carbon adsorption/ozone-regeneration processes for wastewater treatment. Appl Catal B-Environ 92:393–400
Anslyn EV, Dougherty DA (2006) Modern physical organic chemistry. University Science Books
Ávila C, Salas JJ, Martin I, Aragón C, García J (2013) Integrated treatment of combined sewer wastewater and stormwater in a hybrid constructed wetland system in southern Spain and its further reuse. Ecol Eng 50:13–20
Benotti MJ, Brownawell BJ (2007) Distributions of pharmaceuticals in an urban estuary during both dry-and wet-weather conditions. Environ Sci Technol 41:5795–5802
Brewer CE, Schmidt‐Rohr K, Satrio JA, Brown RC (2009) Characterization of biochar from fast pyrolysis and gasification systems. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 28:386–396
Broadhead AT, Horn R, Lerner DN (2013) Captured streams and springs in combined sewers: a review of the evidence, consequences and opportunities. Water Res 47:4752–4766
Buerge IJ, Poiger T, Müller MD, Buser H-R (2006) Combined sewer overflows to surface waters detected by the anthropogenic marker caffeine. Environ Sci Technol 40:4096–4102
Castet S, Dandurand J-L, Schott J, Gout R (1993) Boehmite solubility and aqueous aluminum speciation in hydrothermal solutions (90–350 °C): experimental study and modeling. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 57:4869–4884
Chen B, Zhou D, Zhu L (2008a) Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ Sci Technol 42:5137–5143
Chen J, Chen W, Zhu D (2008b) Adsorption of nonionic aromatic compounds to single-walled carbon nanotubes: effects of aqueous solution chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 42:7225–7230
Cho H-H, Smith BA, Wnuk JD, Fairbrother DH, Ball WP (2008) Influence of surface oxides on the adsorption of naphthalene onto multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 42:2899–2905
Ghosh K, Schnitzer M (1980) Macromolecular structures of humic substances. Soil Sci 129:266–276
Hyung H, Kim J-H (2008) Natural organic matter (NOM) adsorption to multi-walled carbon nanotubes: effect of NOM characteristics and water quality parameters. Environ Sci Technol 42:4416–4421
Jelic A, Gros M, Ginebreda A, Cespedes-Sánchez R, Ventura F, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2011) Occurrence, partition and removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage water and sludge during wastewater treatment. Water Res 45:1165–1176
Joseph L, Heo J, Park Y-G, Flora JR, Yoon Y (2011) Adsorption of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on single walled carbon nanotubes from seawater and brackish water. Desalination 281:68–74
Joseph L, Boateng LK, Flora JR, Park Y-G, Son A, Badawy M, Yoon Y (2013) Removal of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials and powdered activated carbon. Sep Purif Technol 107:37–47
Jung C, Park J, Lim KH, Park S, Heo J, Her N, Oh J, Yun S, Yoon Y (2013) Adsorption of selected endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals on activated biochars. J Hazard Mater 263:702–710
Karanfil T, Kilduff JE (1999) Role of granular activated carbon surface chemistry on the adsorption of organic compounds. 1. Priority pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 33:3217–3224
Kitis M (2004) Disinfection of wastewater with peracetic acid: a review. Environ Int 30:47–55
Laird DA, Brown RC, Amonette JE, Lehmann J (2009) Review of the pyrolysis platform for coproducing bio‐oil and biochar. Biofuels Bioprod Bior 3:547–562
Li Q, Snoeyink VL, Mariñas BJ, Campos C (2003) Pore blockage effect of NOM on atrazine adsorption kinetics of PAC: the roles of PAC pore size distribution and NOM molecular weight. Water Res 37:4863–4872
Lorphensri O, Sabatini DA, Kibbey TCG, Osathaphan K, Saiwan C (2007) Sorption and transport of acetaminophen, 17α-ethynyl estradiol, nalidixic acid with low organic content aquifer sand. Water Res 41:2180–2188
Lü J, Liu J, Wei Y, Jiang K, Fan S, Liu J, Jiang G (2007) Preparation of single‐walled carbon nanotube fiber coating for solid‐phase microextraction of organochlorine pesticides in lake water and wastewater. J Sep Sci 30:2138–2143
Manabe K, Kobayashi S (1999) Mannich-type reactions of aldehydes, amines, and ketones in a colloidal dispersion system created by a Brønsted acid − surfactant-combined catalyst in water. Org Lett 1:1965–1967
Mikhailova SS, Mykhaylyk OM, Dorfman AM, Povstugar VI (2000) XPS study of finely dispersed iron powders modified by radiation-grafted acrylamide. Surf Interface Anal 29:519–523
Moussas PA, Zouboulis AI (2009) A new inorganic–organic composite coagulant, consisting of polyferric sulphate (PFS) and polyacrylamide (PAA). Water Res 43:3511–3524
OECD (1994) OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Organization for Economic
Pan B, Xing B (2008) Adsorption mechanisms of organic chemicals on carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 42:9005–9013
Papić S, Koprivanac N, Lončarić Božić A, Meteš A (2004) Removal of some reactive dyes from synthetic wastewater by combined Al(III) coagulation/carbon adsorption process. Dyes Pigments 62:291–298
Park J, Meng J, Lim KH, Rojas OJ, Park S (2013) Transformation of lignocellulosic biomass during torrefaction. J Anal Appl Pyrol 100:199–206
Passerat J, Ouattara NK, Mouchel J-M, Rocher V, Servais P (2011) Impact of an intense combined sewer overflow event on the microbiological water quality of the Seine River. Water Res 45:893–903
Phillips P, Chalmers A, Gray J, Kolpin D, Foreman W, Wall G (2012) Combined sewer overflows: an environmental source of hormones and wastewater micropollutants. Environ Sci Technol 46:5336–5343
Quiñonero D, Garau C, Rotger C, Frontera A, Ballester P, Costa A, Deyà PM (2002) Anion–π interactions: do they exist? Angew Chem 114:3539–3542
Rebhun M, Meir S, Laor Y (1998) Using dissolved humic acid to remove hydrophobic contaminants from water by complexation − flocculation process. Environ Sci Technol 32:981–986
Reemtsma T, Gnirß R, Jekel M (2000) Infiltration of combined sewer overflow and tertiary municipal wastewater: an integrated laboratory and field study on nutrients and dissolved organics. Water Res 34:1179–1186
Reum N, Fink-Straube C, Klein T, Hartmann RW, Lehr C-M, Schneider M (2010) Multilayer coating of gold nanoparticles with drug − polymer coadsorbates. Langmuir 26:16901–16908
Richardson SD, Ternes TA (2005) Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 77:3807–3838
Samsuri A, Sadegh-Zadeh F, Seh-Bardan B (2014) Characterization of biochars produced from oil palm and rice husks and their adsorption capacities for heavy metals. Int J Environ Sci Tech 11:967–976
Schottel BL, Chifotides HT, Dunbar KR (2008) Anion-π interactions. Chem Soc Rev 37:68–83
Shak KPY, Wu TY (2014) Coagulation–flocculation treatment of high-strength agro-industrial wastewater using natural Cassia obtusifolia seed gum: treatment efficiencies and flocs characterization. Chem Eng J 256:293–305
Stephenson RJ, Duff SJ (1996) Coagulation and precipitation of a mechanical pulping effluent—I. Removal of carbon, colour and turbidity. Water Res 30:781–792
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai S-P (2014) A comprehensive study on coagulant performance and floc characterization of natural Cassia obtusifolia seed gum in treatment of raw pulp and paper mill effluent. Ind Crop Prod 61:317–324
Teh CY, Wu TY, Juan JC (2014) Potential use of rice starch in coagulation–flocculation process of agro-industrial wastewater: treatment performance and flocs characterization. Ecol Eng 71:509–519
Timur S, Kantarli IC, Ikizoglu E, Yanik J (2006) Preparation of activated carbons from Oreganum stalks by chemical activation. Energ Fuel 20:2636–2641
Van de Moortel AM, Rousseau DP, Tack FM, De Pauw N (2009) A comparative study of surface and subsurface flow constructed wetlands for treatment of combined sewer overflows: a greenhouse experiment. Ecol Eng 35:175–183
Vinke P, Van der Eijk M, Verbree M, Voskamp A, Van Bekkum H (1994) Modification of the surfaces of a gas activated carbon and a chemically activated carbon with nitric acid, hypochlorite, and ammonia. Carbon 32:675–686
Vinu A, Hossain K, Satish Kumar G, Ariga K (2006) Adsorption of l-histidine over mesoporous carbon molecular sieves. Carbon 44:530–536
Wesolowski DJ, Palmer DA (1994) Aluminum speciation and equilibria in aqueous solution: V. Gibbsite solubility at 50 °C and pH 3–9 in 0.1 molal NaCl solutions (a general model for aluminum speciation; analytical methods). Geochim Cosmochim Ac 58:2947–2969
Westerhoff P, Yoon Y, Snyder S, Wert E (2005) Fate of endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical, and personal care product chemicals during simulated drinking water treatment processes. Environ Sci Technol 39:6649–6663
Weyrauch P, Matzinger A, Pawlowsky-Reusing E, Plume S, von Seggern D, Heinzmann B, Schroeder K, Rouault P (2010) Contribution of combined sewer overflows to trace contaminant loads in urban streams. Water Res 44:4451–4462
Yang Y, Lin X, Wei B, Zhao Y, Wang J (2014) Evaluation of adsorption potential of bamboo biochar for metal-complex dye: equilibrium, kinetics and artificial neural network modeling. Int J Environ Sci Tech 11:1093–1100
Zhang S, Shao T, Bekaroglu SSK, Karanfil T (2009) The impacts of aggregation and surface chemistry of carbon nanotubes on the adsorption of synthetic organic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 43:5719–5725
Zhang S, Shao T, Bekaroglu SSK, Karanfil T (2010) Adsorption of synthetic organic chemicals by carbon nanotubes: effects of background solution chemistry. Water Res 44:2067–2074
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment, “Project, 414-111-006.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 3595 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, C., Oh, J. & Yoon, Y. Removal of acetaminophen and naproxen by combined coagulation and adsorption using biochar: influence of combined sewer overflow components. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 10058–10069 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4191-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4191-6