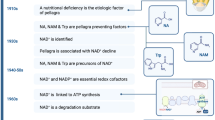
Abstract
Background
Nicotinamide (NAM) is a form of vitamin B3 that, when administered at near-gram doses, has been shown or suggested to be therapeutically effective against many diseases and conditions. The target conditions are incredibly diverse ranging from skin disorders such as bullous pemphigoid to schizophrenia and depression and even AIDS. Similar diversity is expected for the underlying mechanisms. In a large portion of the conditions, NAM conversion to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) may be a major factor in its efficacy. The augmentation of cellular NAD+ level not only modulates mitochondrial production of ATP and superoxide, but also activates many enzymes. Activated sirtuin proteins, a family of NAD+-dependent deacetylases, play important roles in many of NAM’s effects such as an increase in mitochondrial quality and cell viability countering neuronal damages and metabolic diseases. Meanwhile, certain observed effects are mediated by NAM itself. However, our understanding on the mechanisms of NAM’s effects is limited to those involving certain key proteins and may even be inaccurate in some proposed cases.
Aim of review
This review details the conditions that NAM has been shown to or is expected to effectively treat in humans and animals and evaluates the proposed underlying molecular mechanisms, with the intention of promoting wider, safe therapeutic application of NAM.
Key scientific concepts of review
NAM, by itself or through altering metabolic balance of NAD+ and tryptophan, modulates mitochondrial function and activities of many molecules and thereby positively affects cell viability and metabolic functions. And, NAM administration appears to be quite safe with limited possibility of side effects which are related to NAM’s metabolites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, B. H., et al. (2008). A role for the mitochondrial deacetylase Sirt3 in regulating energy homeostasis. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 14447–14452. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803790105.
Anderson, D. W., Bradbury, K. A., & Schneider, J. S. (2008). Broad neuroprotective profile of nicotinamide in different mouse models of MPTP-induced parkinsonism. European Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 610–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06356.x.
Aoyagi, S., & Archer, T. K. (2008). Nicotinamide uncouples hormone-dependent chromatin remodeling from transcription complex assembly. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01158-07.
Arauz, J., Rivera-Espinoza, Y., Shibayama, M., Favari, L., Flores-Beltran, R. E., & Muriel, P. (2015). Nicotinic acid prevents experimental liver fibrosis by attenuating the prooxidant process. International Immunopharmacology, 28, 244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.045.
Avalos, J. L., Bever, K. M., & Wolberger, C. (2005). Mechanism of sirtuin inhibition by nicotinamide: Altering the NAD(+) cosubstrate specificity of a Sir2 enzyme. Molecular Cell, 17, 855–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.022.
Backesjo, C. M., Li, Y., Lindgren, U., & Haldosen, L. A. (2006). Activation of Sirt1 decreases adipocyte formation during osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 21, 993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.060415.
Badawy, A. A. (2017). Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: regulatory and functional aspects. International Journal of Tryptophan Research, 10, 1178646917691938. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646917691938.
Badawy, A. A., & Evans, M. (1976). The role of free serum tryptophan in the biphasic effect of acute ethanol administration on the concentrations of rat brain tryptophan, 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindol-3-ylacetic acid. Biochemical Journal, 160, 315–324. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1600315.
Banasik, M., Stedeford, T., Strosznajder, R. P., Persad, A. S., Tanaka, S., & Ueda, K. (2004). The effects of organic solvents on poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activity: Implications for neurotoxicity. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis (Wars), 64, 467–473.
Banfi, A., Muraglia, A., Dozin, B., Mastrogiacomo, M., Cancedda, R., & Quarto, R. (2000). Proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells: Implications for their use in cell therapy. Experimental Hematology, 28, 707–715.
Baohua, Y., & Li, L. (2012). Effects of SIRT6 silencing on collagen metabolism in human dermal fibroblasts. Cell Biology International, 36, 105–108. https://doi.org/10.1042/cbi20110268.
Belenky, P., Bogan, K. L., & Brenner, C. (2007). NAD + metabolism in health and disease. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 32, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2006.11.006.
Benavente, C. A., & Jacobson, E. L. (2008). Niacin restriction upregulates NADPH oxidase and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in human keratinocytes. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 44, 527–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.10.006.
Benavente, C. A., Jacobson, M. K., & Jacobson, E. L. (2009). NAD in skin: Therapeutic approaches for niacin. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 15, 29–38.
Benyo, Z., et al. (2005). GPR109A (PUMA-G/HM74A) mediates nicotinic acid-induced flushing. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115, 3634–3640. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci23626.
Berger, N. A. (1985). Poly(ADP-ribose) in the cellular response to DNA damage. Radiation Research, 101, 4–15.
Berger, N. A., & Petzold, S. J. (1985). Identification of minimal size requirements of DNA for activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochemistry, 24, 4352–4355.
Bitterman, K. J., Anderson, R. M., Cohen, H. Y., Latorre-Esteves, M., & Sinclair, D. A. (2002). Inhibition of silencing and accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of yeast sir2 and human SIRT1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 45099–45107. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205670200.
Bogan, K. L., & Brenner, C. (2008). Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: A molecular evaluation of NAD + precursor vitamins in human nutrition. Annual Review of Nutrition, 28, 115–130. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155443.
Bold, J. M., Gardner, C. R., & Walker, R. J. (1985). Central effects of nicotinamide and inosine which are not mediated through benzodiazepine receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 84, 689–696.
Bordone, L., et al. (2006). Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in pancreatic beta cells. PLoS Biology, 4, e31. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040031.
Bosch-Presegue, L., & Vaquero, A. (2011). The dual role of sirtuins in cancer. Genes Cancer, 2, 648–662. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911417862.
Braidy, N., Guillemin, G. J., Mansour, H., Chan-Ling, T., Poljak, A., & Grant, R. (2011). Age related changes in NAD + metabolism oxidative stress and Sirt1 activity in wistar rats. PLoS ONE, 6, e19194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019194.
Brenmoehl, J., & Hoeflich, A. (2013). Dual control of mitochondrial biogenesis by sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3. Mitochondrion, 13, 755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2013.04.002.
Brown, K. D., et al. (2014). Activation of SIRT3 by the NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide riboside protects from noise-induced hearing loss. Cell Metabolism, 20, 1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.11.003.
Bruder, S. P., Jaiswal, N., & Haynesworth, S. E. (1997). Growth kinetics, self-renewal, and the osteogenic potential of purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive subcultivation and following cryopreservation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 64, 278–294.
Brune, B. (2003). Nitric oxide: NO apoptosis or turning it ON? Cell Death and Differentiation, 10, 864–869. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401261.
Brunet, A., et al. (2004). Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science, 303, 2011–2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094637.
Busch, F., Mobasheri, A., Shayan, P., Stahlmann, R., & Shakibaei, M. (2012). Sirt-1 is required for the inhibition of apoptosis and inflammatory responses in human tenocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 25770–25781. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.355420.
Cai, A. L., Zipfel, G. J., & Sheline, C. T. (2006). Zinc neurotoxicity is dependent on intracellular NAD levels and the sirtuin pathway. European Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 2169–2176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05110.x.
Caito, S., et al. (2010). SIRT1 is a redox-sensitive deacetylase that is post-translationally modified by oxidants and carbonyl stress. The FASEB Journal, 24, 3145–3159. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-151308.
Campbell, P. I., Abraham, M. I., & Kempson, S. A. (1989). Increased cAMP in proximal tubules is acute effect of nicotinamide analogues. American Journal of Physiology, 257, F1021–F1026. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F1021.
Canto, C., et al. (2012). The NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metabolism, 15, 838–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.022.
Carafa, V., et al. (2016). Sirtuin functions and modulation: From chemistry to the clinic. Clinical Epigenetics, 8, 61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0224-3.
Carter, C. S., et al. (2012). Usefulness of preclinical models for assessing the efficacy of late-life interventions for sarcopenia. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 67, 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glr042.
Chang, H. C., & Guarente, L. (2014). SIRT1 and other sirtuins in metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 25, 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2013.12.001.
Chen, A. C., et al. (2015a). A phase 3 randomized trial of nicotinamide for skin-cancer chemoprevention. New England Journal of Medicine, 373, 1618–1626. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1506197.
Chen, J., et al. (2005). SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-beta toxicity through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 40364–40374. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509329200.
Chen, L., So, W. Y., Li, S. Y., Cheng, Q., Boucher, B. J., & Leung, P. S. (2015b). Niacin-induced hyperglycemia is partially mediated via niacin receptor GPR109a in pancreatic islets. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 404, 56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.029.
Chlopicki, S., et al. (2007). 1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA), a primary metabolite of nicotinamide, exerts anti-thrombotic activity mediated by a cyclooxygenase-2/prostacyclin pathway. British Journal of Pharmacology, 152, 230–239. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707383.
Chong, Z. Z., Lin, S. H., Li, F., & Maiese, K. (2005). The sirtuin inhibitor nicotinamide enhances neuronal cell survival during acute anoxic injury through AKT, BAD, PARP, and mitochondrial associated “anti-apoptotic” pathways. Current Neurovascular Research, 2, 271–285.
Chong, Z. Z., Lin, S. H., & Maiese, K. (2002). Nicotinamide modulates mitochondrial membrane potential and cysteine protease activity during cerebral vascular endothelial cell injury. Journal of Vascular Research, 39, 131–147. https://doi.org/10.1159/000057762.
Chong, Z. Z., Lin, S. H., & Maiese, K. (2004). The NAD + precursor nicotinamide governs neuronal survival during oxidative stress through protein kinase B coupled to FOXO3a and mitochondrial membrane potential. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 24, 728–743. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.WCB.0000122746.72175.0E.
Cipriani, G., Rapizzi, E., Vannacci, A., Rizzuto, R., Moroni, F., & Chiarugi, A. (2005). Nuclear poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 rapidly triggers mitochondrial dysfunction. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 17227–17234. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M414526200.
Clark, J. B., & Pinder, S. (1969). Control of the steady-state concentrations of the nicotinamide nucleotides in rat liver. Biochemical Journal, 114, 321–330.
Cohen, H. Y., et al. (2004). Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science, 305, 390–392. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1099196.
Coleman, M. P., et al. (1998). An 85-kb tandem triplication in the slow Wallerian degeneration (Wlds) mouse. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 9985–9990.
Collins, T. M., et al. (1991). The effects of nicotinamide and hyperbaric oxygen on skin flap survival. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery, 25, 5–7.
Colman, R. J., Beasley, T. M., Allison, D. B., & Weindruch, R. (2008). Attenuation of sarcopenia by dietary restriction in rhesus monkeys. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 63, 556–559.
Cowen, P., & Sherwood, A. C. (2013). The role of serotonin in cognitive function: Evidence from recent studies and implications for understanding depression. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 27, 575–583. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881113482531.
Cramer, T., et al. (2003). HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell, 112, 645–657.
Crino, A., et al. (2005). A two year observational study of nicotinamide and intensive insulin therapy in patients with recent onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism, 18, 749–754.
Crino, A., et al. (2004). A randomized trial of nicotinamide and vitamin E in children with recent onset type 1 diabetes (IMDIAB IX). European Journal of Endocrinology, 150, 719–724.
Damian, D. L., Patterson, C. R., Stapelberg, M., Park, J., Barnetson, R. S., & Halliday, G. M. (2008). UV radiation-induced immunosuppression is greater in men and prevented by topical nicotinamide. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 128, 447–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701058.
Daniel, J., Marechal, Y., Van Gool, F., Andris, F., & Leo, O. (2007). Nicotinamide inhibits B lymphocyte activation by disrupting MAPK signal transduction. Biochemical Pharmacology, 73, 831–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2006.11.024.
Delmez, J. A., & Slatopolsky, E. (1992). Hyperphosphatemia: Its consequences and treatment in patients with chronic renal disease. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 19, 303–317.
Deng, C. X. (2009). SIRT1, is it a tumor promoter or tumor suppressor? International Journal of Biological Sciences, 5, 147–152.
Dong, Y. J., et al. (2014). Renal protective effect of sirtuin 1. Journal of Diabetes Research, 2014, 843786. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/843786.
Dou, X., Shen, C., Wang, Z., Li, S., Zhang, X., & Song, Z. (2013). Protection of nicotinic acid against oxidative stress-induced cell death in hepatocytes contributes to its beneficial effect on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 24, 1520–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.12.012.
Drummond, G. R., Selemidis, S., Griendling, K. K., & Sobey, C. G. (2011). Combating oxidative stress in vascular disease: NADPH oxidases as therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 10, 453–471. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3403.
Du, H., et al. (2008). Cyclophilin D deficiency attenuates mitochondrial and neuronal perturbation and ameliorates learning and memory in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine, 14, 1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1868.
Elhassan, Y. S., Philp, A. A., & Lavery, G. G. (2017). Targeting NAD + in metabolic disease: New insights into an old molecule. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 1, 816–835. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2017-00092.
Elliott, R. B., Pilcher, C. C., Fergusson, D. M., & Stewart, A. W. (1996). A population based strategy to prevent insulin-dependent diabetes using nicotinamide. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism, 9, 501–509.
Elvehjem, C. A., Madden, R. J., Strong, F. M., & Wolley, D. W. (1938). The isolation and identification of the anti-black tongue factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 123, 137–149.
Eto, N., Miyata, Y., Ohno, H., & Yamashita, T. (2005). Nicotinamide prevents the development of hyperphosphataemia by suppressing intestinal sodium-dependent phosphate transporter in rats with adenine-induced renal failure. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 20, 1378–1384. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfh781.
Feldman, J. L., et al. (2015). Kinetic and structural basis for acyl-group selectivity and NAD(+) dependence in sirtuin-catalyzed deacylation. Biochemistry, 54, 3037–3050. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00150.
Ferreira, R. G., et al. (2012). Neutrophil recruitment is inhibited by nicotinamide in experimental pleurisy in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 685, 198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.04.014.
Fivenson, D. P., Breneman, D. L., Rosen, G. B., Hersh, C. S., Cardone, S., & Mutasim, D. (1994). Nicotinamide and tetracycline therapy of bullous pemphigoid. Archives of Dermatology, 130, 753–758.
Fontana, L. (2008). Calorie restriction and cardiometabolic health. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation, 15, 3–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJR.0b013e3282f17bd4.
Fontana, L., Meyer, T. E., Klein, S., & Holloszy, J. O. (2004). Long-term calorie restriction is highly effective in reducing the risk for atherosclerosis in humans. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 6659–6663. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308291101.
Frederick, D. W., et al. (2016). Loss of NAD homeostasis leads to progressive and reversible degeneration of skeletal muscle. Cell Metabolism, 24, 269–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.07.005.
Fricker, R. A., Green, E. L., Jenkins, S. I., & Griffin, S. M. (2018). The influence of nicotinamide on health and disease in the central nervous system. International Journal of Tryptophan Research, 11, 1178646918776658. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646918776658.
Fu, M., et al. (2006). Hormonal control of androgen receptor function through SIRT1. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 26, 8122–8135. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00289-06.
Fu, X., Lawson, M. A., Kelley, K. W., & Dantzer, R. (2011). HIV-1 Tat activates indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase in murine organotypic hippocampal slice cultures in a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent manner. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 8, 88. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-88.
Fujimura, M., Tominaga, T., & Yoshimoto, T. (1997). Nicotinamide inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in primary rat glial cells. Neuroscience Letters, 228, 107–110.
Fukushima, T. (2005). Niacin metabolism and Parkinson’s disease. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 10, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1265/ehpm.10.3.
Gale, E. A., Bingley, P. J., Emmett, C. L., Collier, T., & G. European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial. (2004). European nicotinamide diabetes intervention trial (ENDIT): A randomised controlled trial of intervention before the onset of type 1 diabetes. Lancet, 363, 925–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15786-3.
Galione, A., Lee, H. C., & Busa, W. B. (1991). Ca(2 +)-induced Ca2 + release in sea urchin egg homogenates: modulation by cyclic ADP-ribose. Science, 253, 1143–1146.
Gan, L., & Mucke, L. (2008). Paths of convergence: Sirtuins in aging and neurodegeneration. Neuron, 58, 10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.03.015.
Garavaglia, S., et al. (2012). The high-resolution crystal structure of periplasmic Haemophilus influenzae NAD nucleotidase reveals a novel enzymatic function of human CD73 related to NAD metabolism. Biochemical Journal, 441, 131–141. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20111263.
George, E. B., Glass, J. D., & Griffin, J. W. (1995). Axotomy-induced axonal degeneration is mediated by calcium influx through ion-specific channels. Journal of Neuroscience, 15, 6445–6452.
Ghosh, D., LeVault, K. R., Barnett, A. J., & Brewer, G. J. (2012). A reversible early oxidized redox state that precedes macromolecular ROS damage in aging nontransgenic and 3xTg-AD mouse neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 5821–5832. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6192-11.2012.
Gimble, J. M., Duh, E., Ostrove, J. M., Gendelman, H. E., Max, E. E., & Rabson, A. B. (1988). Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by herpes simplex virus type 1 is associated with induction of a nuclear factor that binds to the NF-kappa B/core enhancer sequence. Journal of Virology, 62, 4104–4112.
Ginsberg, C., & Ix, J. H. (2016). Nicotinamide and phosphate homeostasis in chronic kidney disease. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 25, 285–291. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0000000000000236.
Goenka, S., & Boothby, M. (2006). Selective potentiation of Stat-dependent gene expression by collaborator of Stat6 (CoaSt6), a transcriptional cofactor. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 4210–4215. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506981103.
Goldie, C., Taylor, A. J., Nguyen, P., McCoy, C., Zhao, X. Q., & Preiss, D. (2016). Niacin therapy and the risk of new-onset diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Heart, 102, 198–203. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2015-308055.
Golestaneh, N., Chu, Y., Cheng, S. K., Cao, H., Poliakov, E., & Berinstein, D. M. (2016). Repressed SIRT1/PGC-1alpha pathway and mitochondrial disintegration in iPSC-derived RPE disease model of age-related macular degeneration. Journal of Translational Medicine, 14, 344. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-1101-8.
Goodwin, P. M., Lewis, P. J., Davies, M. I., Skidmore, C. J., & Shall, S. (1978). The effect of gamma radiation and neocarzinostatin on NAD and ATP levels in mouse leukaemia cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 543, 576–582.
Green, K. N., et al. (2008). Nicotinamide restores cognition in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice via a mechanism involving sirtuin inhibition and selective reduction of Thr231-phosphotau. Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 11500–11510. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3203-08.2008.
Greenbaum, C. J., Kahn, S. E., & Palmer, J. P. (1996). Nicotinamide’s effects on glucose metabolism in subjects at risk for IDDM. Diabetes, 45, 1631–1634.
Greengard, P., Quinn, G. P., & Reid, M. B. (1964). Pituitary influence of pyridine nucleotide metabolism of rat liver. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 239, 1887–1892.
Griffin, S. M., Pickard, M. R., Orme, R. P., Hawkins, C. P., & Fricker, R. A. (2013). Nicotinamide promotes neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells in vitro. NeuroReport, 24, 1041–1046. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000000071.
Guan, X., Lin, P., Knoll, E., & Chakrabarti, R. (2014). Mechanism of inhibition of the human sirtuin enzyme SIRT3 by nicotinamide: Computational and experimental studies. PLoS ONE, 9, e107729. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107729.
Guarente, L. (2013). Calorie restriction and sirtuins revisited. Genes & Development, 27, 2072–2085. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.227439.113.
Gurujeyalakshmi, G., Iyer, S. N., Hollinger, M. A., & Giri, S. N. (1996). Procollagen gene expression is down-regulated by taurine and niacin at the transcriptional level in the bleomycin hamster model of lung fibrosis. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 277, 1152–1157.
Guy, A. P., & Gardner, C. R. (1985). Pharmacological characterisation of a modified social interaction model of anxiety in the rat. Neuropsychobiology, 13, 194–200. https://doi.org/10.1159/000118187.
Ha, H. C., Juluri, K., Zhou, Y., Leung, S., Hermankova, M., & Snyder, S. H. (2001). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is required for efficient HIV-1 integration. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 3364–3368. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.051633498.
Hafner, A. V., et al. (2010). Regulation of the mPTP by SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of CypD at lysine 166 suppresses age-related cardiac hypertrophy. Aging (Albany NY), 2, 914–923. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100252.
Hakozaki, T., et al. (2002). The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. British Journal of Dermatology, 147, 20–31.
Harrison, I. F., Powell, N. M., & Dexter, D. T. (2019). The histone deacetylase inhibitor nicotinamide exacerbates neurodegeneration in the lactacystin rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 148, 136–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14599.
Harrison, L. B., Chadha, M., Hill, R. J., Hu, K., & Shasha, D. (2002). Impact of tumor hypoxia and anemia on radiation therapy outcomes. Oncologist, 7, 492–508.
Hasmann, M., & Schemainda, I. (2003). FK866, a highly specific noncompetitive inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, represents a novel mechanism for induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Research, 63, 7436–7442.
Hassa, P. O., Covic, M., Hasan, S., Imhof, R., & Hottiger, M. O. (2001). The enzymatic and DNA binding activity of PARP-1 are not required for NF-kappa B coactivator function. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 45588–45597. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106528200.
Hassa, P. O., & Hottiger, M. O. (1999). A role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in NF-kappaB transcriptional activation. Biological Chemistry, 380, 953–959. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.1999.118.
Hathorn, T., Snyder-Keller, A., & Messer, A. (2011). Nicotinamide improves motor deficits and upregulates PGC-1alpha and BDNF gene expression in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiology of Diseases, 41, 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.08.017.
Hiromatsu, Y., Sato, M., Tanaka, K., Ishisaka, N., Kamachi, J., & Nonaka, K. (1993). Inhibitory effects of nicotinamide on intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on cultured human thyroid cells. Immunology, 80, 330–332.
Hiromatsu, Y., Sato, M., Yamada, K., & Nonaka, K. (1992). Inhibitory effects of nicotinamide on recombinant human interferon-gamma-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and HLA-DR antigen expression on cultured human endothelial cells. Immunology Letters, 31, 35–39.
Hoffer, A. (1959). Treatment of arthritis by nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 81, 235–238.
Hoffer, A. (1967). Biochemistry of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. Psychosomatics, 8, 95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0033-3182(67)72029-0.
Hoffer, A. (1970). Pellagra and schizophrenia. Psychosomatics, 11, 522–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(70)71623-X.
Holleran, W. M., Williams, M. L., Gao, W. N., & Elias, P. M. (1990). Serine-palmitoyl transferase activity in cultured human keratinocytes. Journal of Lipid Research, 31, 1655–1661.
Hollis, F., van der Kooij, M. A., Zanoletti, O., Lozano, L., Canto, C., & Sandi, C. (2015). Mitochondrial function in the brain links anxiety with social subordination. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, 15486–15491. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512653112.
Hsu, C. P., et al. (2010). Silent information regulator 1 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation, 122, 2170–2182. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958033.
Hua, S. Y., et al. (1994). Cyclic ADP-ribose modulates Ca2 + release channels for activation by physiological Ca2 + entry in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron, 12, 1073–1079.
Huang, J., et al. (2008). SIRT1 overexpression antagonizes cellular senescence with activated ERK/S6k1 signaling in human diploid fibroblasts. PLoS ONE, 3, e1710. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001710.
Huang, R., et al. (2015). Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under starvation. Molecular Cell, 57, 456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.013.
Hwang, E. S., Ok, J. S., & Song, S. (2016). Chemical and physical approaches to extend the replicative and differentiation potential of stem cells. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports, 12, 315–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-016-9652-x.
Hwang, E. S., & Song, S. B. (2017). Nicotinamide is an inhibitor of SIRT1 in vitro, but can be a stimulator in cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 74, 3347–3362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2527-8.
Imai, S., & Guarente, L. (2014). NAD + and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends in Cell Biology, 24, 464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2014.04.002.
Institute of Medicine. (1998). Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline. Washington, DC: The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health.
Jang, S. Y., Kang, H. T., & Hwang, E. S. (2012). Nicotinamide-induced mitophagy: Event mediated by high NAD +/NADH ratio and SIRT1 protein activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 19304–19314. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.363747.
Jeong, H., et al. (2011). Sirt1 mediates neuroprotection from mutant huntingtin by activation of the TORC1 and CREB transcriptional pathway. Nature Medicine, 18, 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2559.
Jeong, J., et al. (2007). SIRT1 promotes DNA repair activity and deacetylation of Ku70. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 39, 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.2.
Jiang, H. Y., Koike, T., Li, P., Wang, Z. H., Kawata, Y., & Oshida, Y. (2010). Combined effects of short-term calorie restriction and exercise on insulin action in normal rats. Hormone and Metabolic Research, 42, 950–954. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1267174.
Jin, J., Lee, K. B., Park, S. Y., & Jang, J.-J. (2011). Nicotinamide inhibits hepatic fibrosis by suppressing DNA synthesis and enhancing apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells. Virchows Archiv, 458, 689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1071-4.
Kaanders, J. H., Bussink, J., & van der Kogel, A. J. (2002). ARCON: A novel biology-based approach in radiotherapy. The lancet Oncology, 3, 728–737.
Kalckar, H. M., Maxwell, E. S., & Strominger, J. L. (1956). Some properties of uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 65, 2–10.
Kang, H. T., & Hwang, E. S. (2009). Nicotinamide enhances mitochondria quality through autophagy activation in human cells. Aging Cell, 8, 426–438. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00487.x.
Kang, H. T., Lee, H. I., & Hwang, E. S. (2006). Nicotinamide extends replicative lifespan of human cells. Aging Cell, 5, 423–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00234.x.
Kaufman, W. (1949). The common form of joint dysfunction: its incidence and treatment. Brattleboro: E.L. Hildreth & Co.
Kauppinen, A., Suuronen, T., Ojala, J., Kaarniranta, K., & Salminen, A. (2013). Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-kappaB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cellular Signalling, 25, 1939–1948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007.
Kawahara, T. L., et al. (2009). SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell, 136, 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.052.
Keenan, J. M. (2018). The role of niacin in the management of dyslipidemia. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.81725.
Kempson, S. A., Colon-Otero, G., Ou, S. Y., Turner, S. T., & Dousa, T. P. (1981). Possible role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide as an intracellular regulator of renal transport of phosphate in the rat. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 67, 1347–1360.
Kim, M. Y., Mauro, S., Gevry, N., Lis, J. T., & Kraus, W. L. (2004). NAD + -dependent modulation of chromatin structure and transcription by nucleosome binding properties of PARP-1. Cell, 119, 803–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.002.
Kim, M. Y., Woo, E. M., Chong, Y. T., Homenko, D. R., & Kraus, W. L. (2006). Acetylation of estrogen receptor alpha by p300 at lysines 266 and 268 enhances the deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transactivation activities of the receptor. Molecular Endocrinology, 20, 1479–1493. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2005-0531.
Kim, M. Y., Zhang, T., & Kraus, W. L. (2005). Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP-1: ‘PAR-laying’ NAD + into a nuclear signal. Genes & Development, 19, 1951–1967. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1331805.
Kim, S. K., Yun, S. J., Kim, J., Lee, O. J., Bae, S. C., & Kim, W. J. (2011a). Identification of gene expression signature modulated by nicotinamide in a mouse bladder cancer model. PLoS ONE, 6, e26131. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026131.
Kim, S. Y., et al. (2017). Redox dysregulation in schizophrenia revealed by in vivo NAD +/NADH measurement. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43, 197–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbw129.
Kim, W. J., Lee, J. W., Quan, C., Youn, H. J., Kim, H. M., & Bae, S. C. (2011b). Nicotinamide inhibits growth of carcinogen induced mouse bladder tumor and human bladder tumor xenograft through up-regulation of RUNX3 and p300. Journal of Urology, 185, 2366–2375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.02.017.
Kirsch, M., & De Groot, H. (2001). NAD(P)H, a directly operating antioxidant? The FASEB Journal, 15, 1569–1574.
Kitada, M., & Koya, D. (2013). Renal protective effects of resveratrol. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2013, 568093. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/568093.
Kitada, M., Takeda, A., Nagai, T., Ito, H., Kanasaki, K., & Koya, D. (2011). Dietary restriction ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through anti-inflammatory effects and regulation of the autophagy via restoration of Sirt1 in diabetic Wistar fatty (fa/fa) rats: A model of type 2 diabetes. Experimental Diabetes Research, 2011, 908185. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/908185.
Klaidman, L., Morales, M., Kem, S., Yang, J., Chang, M. L., & Adams, J. D., Jr. (2003). Nicotinamide offers multiple protective mechanisms in stroke as a precursor for NAD + , as a PARP inhibitor and by partial restoration of mitochondrial function. Pharmacology, 69, 150–157. https://doi.org/10.1159/000072668.
Knip, M., et al. (2000a). Safety of high-dose nicotinamide: A review. Diabetologia, 43, 1337–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250051536.
Knip, M., et al. (2000b). Safety of high-dose nicotinamide: A review. Diabetologia, 43, 1337–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250051536.
Koh, P. O. (2011). Nicotinamide attenuates the ischemic brain injury-induced decrease of Akt activation and Bad phosphorylation. Neuroscience Letters, 498, 105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.05.003.
Kroger, H., Miesel, R., Dietrich, A., Ohde, M., Rajnavolgyi, E., & Ockenfels, H. (1996). Synergistic effects of thalidomide and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition on type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Inflammation, 20, 203–215.
Lader, M. (1975). The psychophysiology of mental illness. Oxford: Routledge.
Lappas, M. (2012). Anti-inflammatory properties of sirtuin 6 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mediators of Inflammation, 2012, 597514. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/597514.
Le Page, C., Sanceau, J., Drapier, J. C., & Wietzerbin, J. (1998). Inhibitors of ADP-ribosylation impair inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription through inhibition of NF kappa B activation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 243, 451–457.
LeClaire, R. D., Kell, W., Bavari, S., Smith, T. J., & Hunt, R. E. (1996). Protective effects of niacinamide in staphylococcal enterotoxin-B-induced toxicity. Toxicology, 107, 69–81.
Lee, D. H., Oh, J.-H., & Chung, J. H. (2016). Glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan in skin aging. Journal of Dermatological Science, 83, 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.05.016.
Lee, H. I., Jang, S. Y., Kang, H. T., & Hwang, E. S. (2008a). p53-, SIRT1-, and PARP-1-independent downregulation of p21WAF1 expression in nicotinamide-treated cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 368, 298–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.082.
Lee, H. R., et al. (2014a). Attenuation of beta-amyloid-induced tauopathy via activation of CK2alpha/SIRT1: Targeting for cilostazol. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 92, 206–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23310.
Lee, H. R., et al. (2014b). Cilostazol suppresses beta-amyloid production by activating a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10 via the upregulation of SIRT1-coupled retinoic acid receptor-beta. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 92, 1581–1590. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23421.
Lee, I. H., et al. (2008b). A role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 3374–3379. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0712145105.
Lewis, C. M., Canafax, D. M., Sprafka, J. M., & Barbosa, J. J. (1992). Double-blind randomized trial of nicotinamide on early-onset diabetes. Diabetes Care, 15, 121–123.
Li, D., et al. (2013a). Nicotinamide supplementation induces detrimental metabolic and epigenetic changes in developing rats. British Journal of Nutrition, 110, 2156–2164. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513001815.
Li, F., Chong, Z. Z., & Maiese, K. (2006). Cell life versus cell longevity: The mysteries surrounding the NAD + precursor nicotinamide. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 13, 883–895.
Li, J., et al. (2008). Insulin inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion: Role of Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation. Critical Care Medicine, 36, 1551–1558. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181782335.
Li, L., Yuan, L., Luo, J., Gao, J., Guo, J., & Xie, X. (2013b). MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 13, 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-012-0186-5.
Li, P., et al. (2012). Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) disrupts energy expenditure and metabolic homeostasis by suppressing SIRT1 transcription. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 1609–1620. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr984.
Li, W. J., Shin, M. K., & Oh, S. J. (2011). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is involved in the development of diabetic cystopathy via regulation of nuclear factor kappa B. Urology, 77(1265), e1–e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2011.01.022.
Li, Y., et al. (2017). Negative regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome by SIRT1 in vascular endothelial cells. Immunobiology, 222, 552–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2016.11.002.
Liaudet, L., et al. (2002). Activation of poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase-1 is a central mechanism of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung inflammation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 165, 372–377. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.3.2106050.
Limagne, E., et al. (2017). Sirtuin-1 activation controls tumor growth by impeding Th17 differentiation via STAT3 deacetylation. Cell Reports, 19, 746–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.004.
Lin, S. H., Chong, Z. Z., & Maiese, K. (2001). Nicotinamide: A nutritional supplement that provides protection against neuronal and vascular injury. Journal of Medicinal Food, 4, 27–38. https://doi.org/10.1089/10966200152053686.
Lin, S. H., Vincent, A., Shaw, T., Maynard, K. I., & Maiese, K. (2000). Prevention of nitric oxide-induced neuronal injury through the modulation of independent pathways of programmed cell death. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 20, 1380–1391. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200009000-00013.
Liu, D., et al. (2013). Nicotinamide forestalls pathology and cognitive decline in Alzheimer mice: Evidence for improved neuronal bioenergetics and autophagy procession. Neurobiology of Aging, 34, 1564–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.020.
Liu, T. F., & McCall, C. E. (2013). Deacetylation by SIRT1 reprograms inflammation and cancer. Genes Cancer, 4, 135–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601913476948.
Macallan, D. C., et al. (1995). Energy expenditure and wasting in human immunodeficiency virus infection. New England Journal of Medicine, 333, 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199507133330202.
Madsen, A. S., et al. (2016). Investigating the sensitivity of NAD + -dependent sirtuin deacylation activities to NADH. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291, 7128–7141. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.668699.
Maes, M., Galecki, P., Chang, Y. S., & Berk, M. (2011). A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro)degenerative processes in that illness. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 35, 676–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.05.004.
Maiese, K., Chong, Z. Z., Hou, J., & Shang, Y. C. (2009). The vitamin nicotinamide: Translating nutrition into clinical care. Molecules, 14, 3446–3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14093446.
Manna, R., et al. (1992). Nicotinamide treatment in subjects at high risk of developing IDDM improves insulin secretion. British Journal of Clinical Practice, 46, 177–179.
Martens, C. R., et al. (2018). Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD(+) in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nature Communications, 9, 1286. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03421-7.
Martens, K. M., Vonder Haar, C., Hutsell, B. A., & Hoane, M. R. (2013). The dig task: A simple scent discrimination reveals deficits following frontal brain damage. Journal of Visualized Experiments. https://doi.org/10.3791/50033.
Massudi, H., Grant, R., Braidy, N., Guest, J., Farnsworth, B., & Guillemin, G. J. (2012). Age-associated changes in oxidative stress and NAD + metabolism in human tissue. PLoS ONE, 7, e42357. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042357.
Matsubara, K., Aoyama, K., Suno, M., & Awaya, T. (2002). N-methylation underlying Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 24, 593–598.
Mayoral, R., et al. (2015). Adipocyte SIRT1 knockout promotes PPARgamma activity, adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity in chronic-HFD and obesity. Molecular Metabolism, 4, 378–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.02.007.
McCarty, M. F. (2000). High-dose pyridoxine as an ‘anti-stress’ strategy. Medical Hypotheses, 54, 803–807. https://doi.org/10.1054/mehy.1999.0955.
McIntire, C. R., Yeretssian, G., & Saleh, M. (2009). Inflammasomes in infection and inflammation. Apoptosis, 14, 522–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0312-3.
McKenney, J. (2003). Niacin for dyslipidemia: Considerations in product selection. American Journal of Health System Pharmacy, 60, 995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/60.10.995.
Mehrotra, P., Riley, J. P., Patel, R., Li, F., Voss, L., & Goenka, S. (2011). PARP-14 functions as a transcriptional switch for Stat6-dependent gene activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 1767–1776. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.157768.
Mendoza-Alvarez, H., & Alvarez-Gonzalez, R. (1993). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is a catalytic dimer and the automodification reaction is intermolecular. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 22575–22580.
Miesel, R., Kurpisz, M., & Kroger, H. (1995). Modulation of inflammatory arthritis by inhibition of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase. Inflammation, 19, 379–387.
Mills, K. F., et al. (2016). Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metabolism, 24, 795–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013.
Min, S. W., et al. (2010). Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron, 67, 953–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044.
Miura, Y. (2016). Human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: Current clinical applications and potential for hematology. International Journal of Hematology, 103, 122–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1920-z.
Moding, E. J., Kastan, M. B., & Kirsch, D. G. (2013). Strategies for optimizing the response of cancer and normal tissues to radiation. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 12, 526–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4003.
Mohler, H., Polc, P., Cumin, R., Pieri, L., & Kettler, R. (1979). Nicotinamide is a brain constituent with benzodiazepine-like actions. Nature, 278, 563–565.
Mokudai, T., Ayoub, I. A., Sakakibara, Y., Lee, E. J., Ogilvy, C. S., & Maynard, K. I. (2000). Delayed treatment with nicotinamide (Vitamin B(3)) improves neurological outcome and reduces infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in Wistar rats. Stroke, 31, 1679–1685.
Monfrecola, G., Gaudiello, F., Cirillo, T., Fabbrocini, G., Balato, A., & Lembo, S. (2013). Nicotinamide downregulates gene expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in HaCaT keratinocytes after ultraviolet B irradiation. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology, 38, 185–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.12018.
Mouchiroud, L., Houtkooper, R. H., & Auwerx, J. (2013a). NAD(+) metabolism: A therapeutic target for age-related metabolic disease. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 48, 397–408. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2013.789479.
Mouchiroud, L., et al. (2013b). The NAD(+)/sirtuin pathway modulates longevity through activation of mitochondrial UPR and FOXO signaling. Cell, 154, 430–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.016.
Moynihan, K. A., et al. (2005). Increased dosage of mammalian Sir2 in pancreatic beta cells enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. Cell Metabolism, 2, 105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2005.07.001.
Murray, M. F. (2003a). Nicotinamide: An oral antimicrobial agent with activity against both Mycobacterium tuberculosis and human immunodeficiency virus. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 36, 453–460. https://doi.org/10.1086/367544.
Murray, M. F. (2003b). Tryptophan depletion and HIV infection: A metabolic link to pathogenesis. Lancet Infect Dis, 3, 644–652.
Murray, M. F., Nghiem, M., & Srinivasan, A. (1995). HIV infection decreases intracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide [NAD]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 212, 126–131. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1995.1945.
Murray, M. F., & Srinivasan, A. (1995). Nicotinamide inhibits HIV-1 in both acute and chronic in vitro infection. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 210, 954–959. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1995.1749.
Nagai, A., Matsumiya, H., Hayashi, M., Yasui, S., Okamoto, H., & Konno, K. (1994). Effects of nicotinamide and niacin on bleomycin-induced acute injury and subsequent fibrosis in hamster lungs. Experimental Lung Research, 20, 263–281.
Naia, L., et al. (2017). Comparative mitochondrial-based protective effects of resveratrol and nicotinamide in Huntington’s Disease models. Molecular Neurobiology, 54, 5385–5399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0048-3.
Nakajima, H., et al. (1986). Elevated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and its inhibition by nicotinamide in the diabetic NOD mouse. Immunology Letters, 12, 91–94.
Namazi, M. R. (2003). Nicotinamide: A potential addition to the anti-psoriatic weaponry. The FASEB Journal, 17, 1377–1379. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0002hyp.
Navarrete-Solis, J., et al. (2011). A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of niacinamide 4% versus hydroquinone 4% in the treatment of melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice, 2011, 379173. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/379173.
North, B. J., & Verdin, E. (2004). Sirtuins: Sir2-related NAD-dependent protein deacetylases. Genome Biology, 5, 224. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-5-224.
O’Brien, B. A., Harmon, B. V., Cameron, D. P., & Allan, D. J. (2000). Nicotinamide prevents the development of diabetes in the cyclophosphamide-induced NOD mouse model by reducing beta-cell apoptosis. The Journal of Pathology, 191, 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200005)191:1%3c86:AID-PATH573%3e3.0.CO;2-0.
O’Brien, T., Silverberg, J. D., & Nguyen, T. T. (1992). Nicotinic acid-induced toxicity associated with cytopenia and decreased levels of thyroxine-binding globulin. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 67, 465–468.
O’Callaghan, C., & Vassilopoulos, A. (2017). Sirtuins at the crossroads of stemness, aging, and cancer. Aging Cell, 16, 1208–1218. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12685.
Oblong, J. E. (2014). The evolving role of the NAD +/nicotinamide metabolome in skin homeostasis, cellular bioenergetics, and aging. DNA Repair (Amst), 23, 59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.04.005.
Odegaard, J. I., & Chawla, A. (2008). Mechanisms of macrophage activation in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology & Metabolism, 4, 619–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0976.
Ohguchi, K., Itoh, T., Akao, Y., Inoue, H., Nozawa, Y., & Ito, M. (2010). SIRT1 modulates expression of matrix metalloproteinases in human dermal fibroblasts. British Journal of Dermatology, 163, 689–694. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09825.x.
Ok, J. S., Song, S. B., & Hwang, E. S. (2018). Enhancement of replication and differentiation potential of human bone marrow stem cells by nicotinamide treatment. International Journal of Stem Cells, 11, 13–25. https://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc18033.
Oliver, F. J., et al. (1999). Resistance to endotoxic shock as a consequence of defective NF-kappaB activation in poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 deficient mice. EMBO Journal, 18, 4446–4454. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.16.4446.
Olkkola, K. T., & Ahonen, J. (2008). Midazolam and other benzodiazepines. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74806-9_16.
Olmos, P. R., et al. (2006). Nicotinamide protected first-phase insulin response (FPIR) and prevented clinical disease in first-degree relatives of type-1 diabetics. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 71, 320–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2005.07.009.
Olmos, Y., et al. (2013). SirT1 regulation of antioxidant genes is dependent on the formation of a FoxO3a/PGC-1alpha complex. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 19, 1507–1521. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4713.
Omidian, M., et al. (2013). Therapeutic effect of oral nicotinamide on refractory uremic pruritus: A randomized, double-blind study. Saudi Journal of Kidney Disease and Transplantation, 24, 995–999.
Orioli, D., & Dellambra, E. (2018). Epigenetic regulation of skin cells in natural aging and premature aging diseases cells. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120268.
Pandya, C. D., Howell, K. R., & Pillai, A. (2013). Antioxidants as potential therapeutics for neuropsychiatric disorders. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 46, 214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.10.017.
Park, S. Y., Lee, K. B., Lee, M. J., Bae, S. C., & Jang, J. J. (2012). Nicotinamide inhibits the early stage of carcinogen-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in mice and suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 227, 899–908. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22799.
Parodi-Rullan, R. M., Chapa-Dubocq, X. R., & Javadov, S. (2018). Acetylation of mitochondrial proteins in the heart: The role of SIRT3. Frontiers in Physiology, 9, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01094.
Parsons, R. B., Smith, S. W., Waring, R. H., Williams, A. C., & Ramsden, D. B. (2003). High expression of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience Letters, 342, 13–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(03)00218-0.
Peek, C. B., et al. (2013). Circadian clock NAD + cycle drives mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in mice. Science, 342, 1243417. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1243417.
Pellat-Deceunynck, C., Wietzerbin, J., & Drapier, J. C. (1994). Nicotinamide inhibits nitric oxide synthase mRNA induction in activated macrophages. Biochemical Journal, 297(Pt 1), 53–58.
Peng, C. H., et al. (2010). SirT1—A sensor for monitoring self-renewal and aging process in retinal stem cells. Sensors (Basel), 10, 6172–6194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100606172.
Picard, F., et al. (2004). Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature, 429, 771–776. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02583.
Pinzone, M. R., Cacopardo, B., Condorelli, F., Di Rosa, M., & Nunnari, G. (2013). Sirtuin-1 and HIV-1: An overview. Current Drug Targets, 14, 648–652.
Pirot, P., Cardozo, A. K., & Eizirik, D. L. (2008). Mediators and mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 diabetes. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia, 52, 156–165. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0004-27302008000200003.
Pittelli, M., et al. (2010). Inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase: Cellular bioenergetics reveals a mitochondrial insensitive NAD pool. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 34106–34114. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.136739.
Pleschke, J. M., Kleczkowska, H. E., Strohm, M., & Althaus, F. R. (2000). Poly(ADP-ribose) binds to specific domains in DNA damage checkpoint proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 40974–40980. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006520200.
Pozzilli, P., Browne, P. D., & Kolb, H. (1996). Meta-analysis of nicotinamide treatment in patients with recent-onset IDDM. The Nicotinamide Trialists. Diabetes Care, 19, 1357–1363.
Pozzilli, P., et al. (1998). Metabolic and immune parameters at clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes: A population-based study. IMDIAB Study Group. Immunotherapy Diabetes. Metabolism, 47, 1205–1210.
Prousky, J. (2010). Vitamin B3 for depression: Case report and review of the literature. Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine, 25, 137–147.
Prousky, J., & Seely, D. (2005). The treatment of migraines and tension-type headaches with intravenous and oral niacin (nicotinic acid): Systematic review of the literature. Nutrition Journal, 4, 3.
Qiu, X., Brown, K., Hirschey, M. D., Verdin, E., & Chen, D. (2010). Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metabolism, 12, 662–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.015.
Rajendrasozhan, S., Yang, S. R., Edirisinghe, I., Yao, H., Adenuga, D., & Rahman, I. (2008a). Deacetylases and NF-kappaB in redox regulation of cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation: epigenetics in pathogenesis of COPD. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 10, 799–811. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1938.
Rajendrasozhan, S., Yang, S. R., Kinnula, V. L., & Rahman, I. (2008b). SIRT1, an antiinflammatory and antiaging protein, is decreased in lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 177, 861–870. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200708-1269OC.
Ramsey, K. M., Mills, K. F., Satoh, A., & Imai, S. (2008). Age-associated loss of Sirt1-mediated enhancement of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in beta cell-specific Sirt1-overexpressing (BESTO) mice. Aging Cell, 7, 78–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00355.x.
Ramsey, K. M., et al. (2009). Circadian clock feedback cycle through NAMPT-mediated NAD + biosynthesis. Science, 324, 651–654. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1171641.
Rankin, P. W., Jacobson, E. L., Benjamin, R. C., Moss, J., & Jacobson, M. K. (1989). Quantitative studies of inhibitors of ADP-ribosylation in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 264, 4312–4317.
Ratajczak, J., et al. (2016). NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells. Nature Communication, 7, 13103. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13103.
Rennie, G., Chen, A. C., Dhillon, H., Vardy, J., & Damian, D. L. (2015). Nicotinamide and neurocognitive function. Nutritional Neuroscience, 18, 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000112.
Revollo, J. R., et al. (2007). Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metabolism, 6, 363–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.09.003.
Rojas, A. (1992). ARCON: Accelerated radiotherapy with carbogen and nicotinamide. BJR Supplement, 24, 174–178.
Rojas, J., & Bermudez, V. (2018). Pancreatic beta cell death: Novel potential mechanisms in diabetes therapy. Journal of Diabetes Research, 2018, 9601801. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9601801.
Rom, S., Reichenbach, N. L., Dykstra, H., & Persidsky, Y. (2015a). The dual action of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase -1 (PARP-1) inhibition in HIV-1 infection: HIV-1 LTR inhibition and diminution in Rho GTPase activity. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 878. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00878.
Rom, S., Zuluaga-Ramirez, V., Dykstra, H., Reichenbach, N. L., Ramirez, S. H., & Persidsky, Y. (2015b). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition in brain endothelium protects the blood-brain barrier under physiologic and neuroinflammatory conditions. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 35, 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.167.
Rosen, E. D., et al. (2002). C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: A unified pathway. Genes & Development, 16, 22–26. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.948702.
Rothgiesser, K. M., Erener, S., Waibel, S., Luscher, B., & Hottiger, M. O. (2010). SIRT2 regulates NF-kappaB dependent gene expression through deacetylation of p65 Lys310. Journal of Cell Science, 123, 4251–4258. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.073783.
Rye, P. T., Frick, L. E., Ozbal, C. C., & Lamarr, W. A. (2011). Advances in label-free screening approaches for studying histone acetyltransferases. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 16, 1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057111418653.
Saini, J. S., et al. (2017). Nicotinamide ameliorates disease phenotypes in a human iPSC model of age-related macular degeneration. Cell Stem Cell, 20, 635–647.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.12.015.
Sama, D. M., & Norris, C. M. (2013). Calcium dysregulation and neuroinflammation: Discrete and integrated mechanisms for age-related synaptic dysfunction. Ageing Research Reviews, 12, 982–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2013.05.008.
Santidrian, A. F., et al. (2013). Mitochondrial complex I activity and NAD +/NADH balance regulate breast cancer progression. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 123, 1068–1081. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64264.
Sato, S., et al. (2017). Circadian reprogramming in the liver identifies metabolic pathways of aging. Cell, 170, 664–677.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.042.
Satoh, A., Stein, L., & Imai, S. (2011). The role of mammalian sirtuins in the regulation of metabolism, aging, and longevity. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 206, 125–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21631-2_7.
Scarpulla, R. C. (2012). Nucleus-encoded regulators of mitochondrial function: Integration of respiratory chain expression, nutrient sensing and metabolic stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1819, 1088–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.011.
Schiavone, S., & Trabace, L. (2016). Pharmacological targeting of redox regulation systems as new therapeutic approach for psychiatric disorders: A literature overview. Pharmacological Research, 107, 195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.019.
Scialo, F., Fernandez-Ayala, D. J., & Sanz, A. (2017). Role of mitochondrial reverse electron transport in ROS signaling: Potential roles in health and disease. Frontiers in Physiology, 8, 428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00428.
Sethi, J. K., Empson, R. M., & Galione, A. (1996). Nicotinamide inhibits cyclic ADP-ribose-mediated calcium signalling in sea urchin eggs. Biochemical Journal, 319(Pt 2), 613–617.
Sgarbanti, M., et al. (2008). IRF-1 is required for full NF-kappaB transcriptional activity at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat enhancer. Journal of Virology, 82, 3632–3641. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00599-07.
Shalita, A. R., Smith, J. G., Parish, L. C., Sofman, M. S., & Chalker, D. K. (1995). Topical nicotinamide compared with clindamycin gel in the treatment of inflammatory acne vulgaris. International Journal of Dermatology, 34, 434–437.
Sheline, C. T., Behrens, M. M., & Choi, D. W. (2000). Zinc-induced cortical neuronal death: Contribution of energy failure attributable to loss of NAD(+) and inhibition of glycolysis. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 3139–3146.
Sheline, C. T., Cai, A. L., Zhu, J., & Shi, C. (2010a). Serum or target deprivation-induced neuronal death causes oxidative neuronal accumulation of Zn2 + and loss of NAD+. European Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 894–904. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07372.x.
Sheline, C. T., Zhou, Y., & Bai, S. (2010b). Light-induced photoreceptor and RPE degeneration involve zinc toxicity and are attenuated by pyruvate, nicotinamide, or cyclic light. Molecular Vision, 16, 2639–2652.
Shen, A., et al. (2017). NAD(+) augmentation ameliorates acute pancreatitis through regulation of inflammasome signalling. Scientific Reports, 7, 3006. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03418-0.
Shimazu, T., et al. (2010). SIRT3 deacetylates mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase 2 and regulates ketone body production. Cell Metabolism, 12, 654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.003.
Singh, I. (1983). Ceramide synthesis from free fatty acids in rat brain: Function of NADPH and substrate specificity. Journal of Neurochemistry, 40, 1565–1570.
Skidmore, C. J., et al. (1979). The involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the degradation of NAD caused by gamma-radiation and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. European Journal of Biochemistry, 101, 135–142.
Skyler, J. S. (2007). Prediction and prevention of type 1 diabetes: Progress, problems, and prospects. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 81, 768–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.clpt.6100179.
Slominski, A., Semak, I., Pisarchik, A., Sweatman, T., Szczesniewski, A., & Wortsman, J. (2002). Conversion of l-tryptophan to serotonin and melatonin in human melanoma cells. FEBS Letters, 511, 102–106.
Smit, E., Graham, N. M., Tang, A., Flynn, C., Solomon, L., & Vlahov, D. (1996). Dietary intake of community-based HIV-1 seropositive and seronegative injecting drug users. Nutrition, 12, 496–501.
Sol, E. M., et al. (2012). Proteomic investigations of lysine acetylation identify diverse substrates of mitochondrial deacetylase sirt3. PLoS ONE, 7, e50545. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050545.
Soma, Y., Kashima, M., Imaizumi, A., Takahama, H., Kawakami, T., & Mizoguchi, M. (2005). Moisturizing effects of topical nicotinamide on atopic dry skin. International Journal of Dermatology, 44, 197–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02375.x.
Sonee, M., Martens, J. R., & Mukherjee, S. K. (2002). Nicotinamide protects HCN2 cells from the free radical generating toxin, tertiary butylhydroperoxide (t-BuOOH). Neurotoxicity Research, 4, 595–599. https://doi.org/10.1080/1029842021000045480.
Song, H. S., et al. (2017a). Increase in furfural tolerance by combinatorial overexpression of NAD salvage pathway enzymes in engineered isobutanol-producing E. coli. Bioresource Technology, 245, 1430–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.197.
Song, S. B., & Hwang, E. S. (2018). A rise in ATP, ROS, and mitochondrial content upon glucose withdrawal correlates with a dysregulated mitochondria turnover mediated by the activation of the protein deacetylase SIRT1. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010011.
Song, S. B., et al. (2017b). Modulation of mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS generation by nicotinamide in a manner independent of SIRT1 and mitophagy. Molecules and Cells, 40, 503–514. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0081.
Staeva-Vieira, T., Peakman, M., & von Herrath, M. (2007). Translational mini-review series on type 1 diabetes: Immune-based therapeutic approaches for type 1 diabetes. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 148, 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03328.x.
Strom, K., et al. (2018). N(1)-methylnicotinamide is a signalling molecule produced in skeletal muscle coordinating energy metabolism. Scientific Reports, 8, 3016. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21099-1.
Sun, L., et al. (2013). PIASy mediates hypoxia-induced SIRT1 transcriptional repression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells. Journal of Cell Science, 126, 3939–3947. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.127381.
Sun, W. P., et al. (2012). Excess nicotinamide inhibits methylation-mediated degradation of catecholamines in normotensives and hypertensives. Hypertension Research, 35, 180–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2011.151.
Sundaresan, N. R., et al. (2015). SIRT3 blocks aging-associated tissue fibrosis in mice by deacetylating and activating glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 36, 678–692. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00586-15.
Sundaresan, N. R., Samant, S. A., Pillai, V. B., Rajamohan, S. B., & Gupta, M. P. (2008). SIRT3 is a stress-responsive deacetylase in cardiomyocytes that protects cells from stress-mediated cell death by deacetylation of Ku70. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 6384–6401. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00426-08.
Takahashi, Y., et al. (2004). Nicotinamide suppresses hyperphosphatemia in hemodialysis patients. Kidney International, 65, 1099–1104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00482.x.
Takayama, K., et al. (2009). SIRT1 regulation of apoptosis of human chondrocytes. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 60, 2731–2740. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24864.
Tanno, M., et al. (2010). Induction of manganese superoxide dismutase by nuclear translocation and activation of SIRT1 promotes cell survival in chronic heart failure. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 8375–8382. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.090266.
Tanno, O., Ota, Y., Kitamura, N., Katsube, T., & Inoue, S. (2000). Nicotinamide increases biosynthesis of ceramides as well as other stratum corneum lipids to improve the epidermal permeability barrier. British Journal of Dermatology, 143, 524–531.
Tao, R., et al. (2010). Sirt3-mediated deacetylation of evolutionarily conserved lysine 122 regulates MnSOD activity in response to stress. Molecular Cell, 40, 893–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.013.
Tao, Y., et al. (2015). SIRT4 suppresses inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 15, 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-014-9287-6.
Tarantini, S., et al. (2019). Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function in aged mice. Redox Biology, 24, 101192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192.
Tian, Y. J., et al. (2013). Excess nicotinamide increases plasma serotonin and histamine levels. Sheng Li Xue Bao, 65, 33–38.
Tippmann, F., Hundt, J., Schneider, A., Endres, K., & Fahrenholz, F. (2009). Up-regulation of the alpha-secretase ADAM10 by retinoic acid receptors and acitretin. The FASEB Journal, 23, 1643–1654. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-121392.
Traba, J., et al. (2015). Fasting and refeeding differentially regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human subjects. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 125, 4592–4600. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci83260.
Traister, A., et al. (2005). Nicotinamide induces apoptosis and reduces collagen I and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in rat hepatic stellate cells. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 40, 1226–1234. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520510023341.
Trammell, S. A., et al. (2016). Nicotinamide riboside is uniquely and orally bioavailable in mice and humans. Nature Communications, 7, 12948. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12948.
Turunc Bayrakdar, E., et al. (2013). Kainic acid-induced seizure activity alters the mRNA expression and G-protein activation of the opioid/nociceptin receptors in the rat brain cortex. Epilepsy Research, 105, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.12.008.
van der Horst, A., Tertoolen, L. G., de Vries-Smits, L. M., Frye, R. A., Medema, R. H., & Burgering, B. M. (2004). FOXO4 is acetylated upon peroxide stress and deacetylated by the longevity protein hSir2(SIRT1). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 28873–28879. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401138200.
Vaziri, H., et al. (1997). ATM-dependent telomere loss in aging human diploid fibroblasts and DNA damage lead to the post-translational activation of p53 protein involving poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. EMBO Journal, 16, 6018–6033. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.19.6018.
Virag, L., & Szabo, C. (2002). The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacological Reviews, 54, 375–429.
Vonder Haar, C., Anderson, G. D., & Hoane, M. R. (2011). Continuous nicotinamide administration improves behavioral recovery and reduces lesion size following bilateral frontal controlled cortical impact injury. Behavioural Brain Research, 224, 311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.06.009.
Wahlberg, G., Carlson, L. A., Wasserman, J., & Ljungqvist, A. (1985). Protective effect of nicotinamide against nephropathy in diabetic rats. Diabetes Research, 2, 307–312.
Wahlberg, G., Walldius, G., & Efendic, S. (1992). Effects of nicotinic acid on glucose tolerance and glucose incorporation into adipose tissue in hypertriglyceridaemia. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 52, 537–545.
Wang, F., et al. (2017). SIRT5 desuccinylates and activates pyruvate kinase M2 to block macrophage IL-1beta production and to prevent DSS-induced colitis in mice. Cell Reports, 19, 2331–2344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.065.
Wang, P., & Miao, C. Y. (2015). NAMPT as a therapeutic target against stroke. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 36, 891–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2015.08.012.
Wang, T., Cui, H., Ma, N., & Jiang, Y. (2013). Nicotinamide-mediated inhibition of SIRT1 deacetylase is associated with the viability of cancer cells exposed to antitumor agents and apoptosis. Oncology Letters, 6, 600–604. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2013.1400.
Wang, Y., Dawson, V. L., & Dawson, T. M. (2009). Poly(ADP-ribose) signals to mitochondrial AIF: A key event in parthanatos. Experimental Neurology, 218, 193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.03.020.
Webster, B. R., Lu, Z., Sack, M. N., & Scott, I. (2012). The role of sirtuins in modulating redox stressors. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 52, 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.10.484.
Weiss, E. P., & Fontana, L. (2011). Caloric restriction: Powerful protection for the aging heart and vasculature. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 301, H1205–H1219. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00685.2011.
Weiss, R., et al. (2015). Nicotinamide: A vitamin able to shift macrophage differentiation toward macrophages with restricted inflammatory features. Innate Immunity, 21, 813–826. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425915602545.
Willets, J. M., Lunec, J., Williams, A. C., & Griffiths, H. R. (1993). Neurotoxicity of nicotinamide derivatives: Their role in the aetiology of Parkinson’s disease. Biochemical Society Transactions, 21(Pt 3), 299S.
Williams, A. C., & Ramsden, D. B. (2005). Autotoxicity, methylation and a road to the prevention of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 12, 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2004.10.002.
Williams, P. A., & Harder, J. M. (2017). Vitamin B3 modulates mitochondrial vulnerability and prevents glaucoma in aged mice. Science, 355, 756–760. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal0092.
Williams, P. A., Harder, J. M., Foxworth, N. E., Cardozo, B. H., Cochran, K. E., & John, S. W. M. (2017a). Nicotinamide and WLD(S) act together to prevent neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 11, 232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00232.
Williams, P. A., Harder, J. M., & John, S. W. M. (2017b). Glaucoma as a metabolic optic neuropathy: Making the case for nicotinamide treatment in glaucoma. Journal of Glaucoma, 26, 1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000000767.
Winter, S. L., & Boyer, J. L. (1973). Hepatic toxicity from large doses of vitamin B3 (nicotinamide). New England Journal of Medicine, 289, 1180–1182. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197311292892208.
Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Ma, X., Zhang, N., & Qin, G. (2012). The effect of resveratrol on FoxO1 expression in kidneys of diabetic nephropathy rats. Molecular Biology Reports, 39, 9085–9093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1780-z.
Wu, Y., et al. (2015). Overexpression of Sirtuin 6 suppresses cellular senescence and NF-kappaB mediated inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis development. Scientific Reports, 5, 17602. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17602.
Xu, J., Xu, S. Q., Liang, J., Lu, Y., Luo, J. H., & Jin, J. H. (2012). Protective effect of nicotinamide in a mouse Parkinson’s disease model. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 41, 146–152.
Yamagoe, S., Kohda, T., & Oishi, M. (1991). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors suppress UV-induced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 11, 3522–3527.
Yamakuchi, M., Ferlito, M., & Lowenstein, C. J. (2008). miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 13421–13426. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801613105.
Yang, H., Lavu, S., & Sinclair, D. A. (2006a). Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin: A regulator of mammalian health and longevity? Experimental Gerontology, 41, 718–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2006.06.003.
Yang, H., et al. (2007). Nutrient-sensitive mitochondrial NAD + levels dictate cell survival. Cell, 130, 1095–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.035.
Yang, J., et al. (2002). The effects of nicotinamide on energy metabolism following transient focal cerebral ischemia in Wistar rats. Neuroscience Letters, 333, 91–94.
Yang, T., Fu, M., Pestell, R., & Sauve, A. A. (2006b). SIRT1 and endocrine signaling. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 17, 186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2006.04.002.
Yeung, F., et al. (2004). Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO Journal, 23, 2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600244.
Yoshino, J., Mills, K. F., Yoon, M. J., & Imai, S. (2011). Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell Metabolism, 14, 528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.014.
Yuan, H. F., et al. (2012). SIRT1 is required for long-term growth of human mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Molecular Medicine (Berl), 90, 389–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0825-4.
Zee, R. S., et al. (2010). Redox regulation of sirtuin-1 by S-glutathiolation. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 13, 1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3251.
Zerfaoui, M., et al. (2009). Effects of PARP-1 deficiency on airway inflammatory cell recruitment in response to LPS or TNF: Differential effects on CXCR332 ligands and Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 86, 1385–1392. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0309183.
Zhang, C. Y., et al. (2001). Uncoupling protein-2 negatively regulates insulin secretion and is a major link between obesity, beta cell dysfunction, and type 2 diabetes. Cell, 105, 745–755.
Zhang, R., et al. (2010). SIRT1 suppresses activator protein-1 transcriptional activity and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 7097–7110. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.038604.
Zhang, X., Tang, N., Hadden, T. J., & Rishi, A. K. (2011). Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1813, 1978–1986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.010.
Zhou, S. S., et al. (2009). Nicotinamide overload may play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 5674–5684.
Zhu, Y., et al. (2016). Exogenous NAD(+) decreases oxidative stress and protects H2O2-treated RPE cells against necrotic death through the up-regulation of autophagy. Scientific Reports, 6, 26322. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26322.
Zocchi, L., & Sassone-Corsi, P. (2012). SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of MeCP2 contributes to BDNF expression. Epigenetics, 7, 695–700. https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.20733.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the 2018 Research Fund of University of Seoul to ES Hwang, and by grants from the Korean National Research Foundation (Grant Nos. NRF-2016R1D1A1B04934603, NRF-2014R1A1A3051320, and NRF-2014M3A9D8034459) to IH Lee.
Funding
The 2018 Research Fund of University of Seoul to ES Hwang, and the grants of Korean National Research Foundation to IH Lee (Grant Nos. NRF-2016R1D1A1B04934603, NRF-2014R1A1A3051320, and NRF-2014M3A9D8034459).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SBS, JSP, GJC, IHL searched and analyzed literature and made Tables, and approved the manuscript. ESH conceived study, analyzed literature, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S.B., Park, J.S., Chung, G.J. et al. Diverse therapeutic efficacies and more diverse mechanisms of nicotinamide. Metabolomics 15, 137 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1604-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1604-4