Abstract
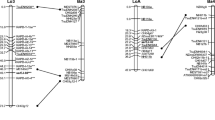
One hundred and sixty microsatellite (simple sequence repeat (SSR)) and six gene-specific markers revealing 174 loci were scored in 94 seedlings from the inter-specific cross of Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’ × Prunus nipponica accession F1292. The co-segregation data from these markers were used to construct a linkage map for cherry which spanned 680 cM over eight linkage groups with an average marker spacing of 3.9 cM per marker and just six gaps longer than 15 cM. Markers previously mapped in Prunus dulcis ‘Texas’ × Prunus persica ‘Earlygold’ allowed the cherry map to be anchored to the peach × almond map and showed the high level of synteny between the species. Eighty-four loci segregated in P. avium ‘Napoleon’ versus 159 in P. nipponica. The segregations of 32 isoenzyme loci in a subset of 47 seedlings from the progeny were scored, using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and/or isoelectric focusing separation followed by activity staining, and the co-segregation data were analysed along with those for 39 isoenzymes reported previously and for the 174 sequence-tagged site loci plus an additional two SSR loci. The second map incorporates 233 loci and spans 736 cM over eight linkage groups with an average marker spacing of 3.2 cM per marker and just two gaps greater than 15 cM. The microsatellite map will provide a useful tool for cherry breeding and marker-assisted selection and for synteny studies within Prunus; the gene-specific markers and isoenzymes will be useful for comparisons with maps of other rosaceous fruit crops.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranzana MJ, Garcia-Mas J, Carbo J, Arus P (2002) Development and variability analysis of microsatellite markers in peach. Plant Breed 121:87–92
Aranzana MJ, Pineda A, Cosson P, Dirlewanger E, Ascasibar J, Cipriani G, Ryder CD, Testolin R, Abbott A, King GJ, Iezzoni AF, Arus P (2003) A set of simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor Appl Genet 106:819–825
Ballester J, Boskovic R, Batlle I, Arus P, Vargas F, de Vicente MC (1998) Location of the self-incompatibility gene on the almond linkage map. Plant Breed 117:69–72
Blenda AV, Verde I, Georgi LL, Reighard GL, Forrest SD, Muñoz-Torres M, Baird WV, Abbott AG (2007) Construction of a genetic linkage map and identification of molecular markers in peach rootstocks for response to peach tree short life syndrome. Tree Genet Gen 3:341–350
Bošković R, Tobutt KR (1996) Correlation of stylar ribonuclease zymograms with incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry. Euphytica 90:245–250
Bošković R, Tobutt KR (1998) Inheritance and linkage relationships of isoenzymes in two interspecific cherry progenies. Euphytica 103:273–286
Bošković R, Tobutt KR, Arus P, Messeguer R (1994) Isoenzymes. In: Messeguer R (ed) Methods of molecular marker analysis in Prunus. IRTA, Barcelona, pp 4–25
Bošković R, Tobutt KR, Nicoll FJ (1997) Inheritance of isoenzymes and their linkage relationships in two interspecific cherry progenies. Euphytica 93:129–143
Cantini C, Iezzoni AF, Lamboy WF, Boritzki M, Struss D (2001) DNA fingerprinting of tetraploid cherry germplasm using simple sequence repeats. J Amer Soc Hortic Sci 126:205–209
Cheliak WM, Pitel JA (1984) Techniques for starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes from forest tree species. In: Information report PI-X-42 of Petawawa National Forestry Institute. Agriculture Canada, pp 1–49
Chevreau E, Leuliette S, Gallet M (1997) Inheritance and linkage of isoenzyme loci in pear (Pyrus communis L.). Theor Appl Genet 94:498–506
Cipriani G, Lot G, Huang WG, Marrazzo MT, Peterlunger E, Testolin R (1999) AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch): isolation, characterization and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 99:65–72
Clarke JB, Tobutt KR (2003) Development and characterisation of polymorphic microsatellites Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’. Mol Ecol Notes 3:578–580
Davis TM, Yu H (1997) A linkage map of the diploid strawberry, Fragaria vesca. J Hered 88:215–221
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana MJ, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Arus P, Laigret F (2002) Development of microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:127–138
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Calderé F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. PNAS 101:9891–9896
Dondini L, Costa E, Tataranni G, Tartarini S, Sansavini S (2006) Cloning of apricot RGAs (resistance gene analogs) and development of molecular markers associated with Sharka (PPV) resistance. J Hort Sci Biotech 79:729–734
Downey SL, Iezzoni AF (2000) Polymorphic DNA markers in black cherry (Prunus serotina) are identified using sequences from sweet cherry, peach, and sour cherry. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 125:76–80
Etienne C, Rothan C, Moing A, Plomion C, Bodénès C, Svanella-Dumas L, Cosson P, Pronier V, Monet R, Dirlewanger E (2002) Candidate genes and QTLs for sugar and organic acid content in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Theor Appl Genet 105:145–159
Fishman L, Kelly AJ, Morgan E, Willis JH (2001) A genetic map in the Mimulus guttatus species complex reveals transmission ratio distortion due to heterospecific interactions. Genetics 159:1701–1716
Foulongne M, Pascal T, Arus P, Kervella J (2003) The potential of Prunus davidiana for introgression into peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] assessed by comparative mapping. Theor Appl Genet 107:227–238
Fukatsu E, Isoda K, Hirao T, Takahashi M, Watanabe A (2005) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat DNA markers for Zelkova serrata. Mol Ecol Notes 5:378–380
Hagen LS, Chaib J, Fady B, Decroocq V, bouchet JP, Lambert P, Audergon JM (2004) Genomic and cDNA microsatellites from apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Mol Ecol Notes 4:742–745
Hemmat M, Weeden NF, Manganaris AG, Lawson DM (1994) Molecular marker linkage map of apple. Heredity 85:4–11
Howad W, Yamamoto T, Dirlewanger E, Testolin R, Cosson P, Cipriani G, Monforte A, Georgi L, Abbott A, Arus P (2005) Mapping with a few plants: using selective mapping for microsatellite saturation of the Prunus reference map (2005). Genetics 171:1305–1309
Jaaska V (1978) NADP-dependent aromatic alcohol dehydrogenase in polyploid wheats and their diploid relatives. On the origin and phylogeny of polyploid wheats. Theor Appl Genet 53:209–217
James CM, Wilson F, Hadonou AM, Tobutt KR (2003) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in diploid strawberry (Fragaria vesca L.) for mapping, diversity studies and clone identification. Mol Ecol Notes 3:171–173
Joobeur T, Viruel MA, de Vicente MC, Jauregui B, Ballester J, Dettori MT, Verde I, Truco MJ, Messeguer R, Battle I, Quarta R, Dirlewanger E, Arus P (1998) Construction of a saturated linkage map for Prunus using an almond × peach F2 progeny. Theor Appl Genet 97:1034–1041
Joobeur T, Periam N, Vicente MC, King GJ, Arus P (2000) Development of a second generation linkage map for almond using RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 43:649–655
Kobayashi N, Horikoshi T, Katsuyama H, Handa T, Takayanagi K (1998) A simple and efficient DNA extraction method for plants, especially woody plants. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 4:76–80
Lee S, Wen J (2001) A phylogenetic analysis of Prunus and the Amygdaloideae (Rosaceae) using ITS sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Amer J Botany 88:150–160
Lopes MS, Sefc KM, Laimer M, Da Camaro Machado A (2002) Identification of microsatellite loci in apricot. Mol Ecol Notes 2:24–26
Messina R, Lain O, Marrazzo T, Cipriani G, Testolin R (2004) New set of microsatellite loci isolated in apricot. Mol Ecol Notes 4:432–434
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Howad W, Badenes ML, Arus P (2004) Simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) are highly polymorphic and transferable to peach and almond. Mol Ecol Notes 4:163–166
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Howad W, Arus P (2005) Development and transportability across Prunus species of 42 polymorphic almond microsatellites. Mol Ecol Notes 5:531–535
Pashkoulov DT, Tobutt KR, Bošković R (2000) Comparison of isoenzymes in Prunus avium separated by two different electrophoretic techniques. Plant Breeding 119:153–156
Santi F, Lemoine M (1990) Genetic markers for Prunus avium L.: inheritance and linkage of isoenzyme loci. Ann Forest Sci 47:131–139
Sargent DJ, Rys A, Nier S, Simpson DW, Tobutt KR (2007) The development and mapping of functional markers in Fragaria and their transferability and potential for mapping in other genera. Theor Appl Genet 114:373–384
Schuster M, Tobutt KR (2004) Screening of cherries for resistance to leaf spot, Blumeriella jaapii. Acta Hort 663:239–243
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Tobutt KR (2006) Improved discrimination of self-incompatibility S-RNase alleles in cherry and high throughput genotyping by automated sizing of first intron polymerase chain reaction products. Plant Breed 125:305–307
Sosinski B, Gannavarapu M, Hager LD, Beck LE, King GJ, Ryder CD, Rajapakse S, Baird WV, Ballard RE, Abbott AG (2000) Characterization of microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 101:421–428
Struss D, Boritzki M, Karle R, Iezzoni AF (2002) Microsatellite markers differentiate eight Giessen cherry rootstocks. HortScience 37:191–193
Struss D, Ahmad R, Southwick SM (2003) Analysis of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR and AFLP markers. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 128:904–909
Testolin R, Marrazzo T, Cipriani G, Quarta R, Verde I, Dettori MT, Pancaldi M, Sansavini S (2000) Microsatellite DNA in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 43:512–520
Testolin R, Messina R, Lain O, Marrazzo MT, Huang W-G, Cipriani G (2004) Microsatellites isolated in almond from an AC-repeat enriched library. Mol Ecol Notes 4:459–461
Tobutt KR (1985) New approaches to breeding sweet cherry scion varieties at East Malling with particular reference to small tree size. Acta Hort 160:43–50
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Vaughan SP, Russell K (2004) Characterization of novel microsatellites and development of multiplex PCR for large-scale population studies in wild cherry, Prunus avium. Mol Ecol Notes 4:429–431
Verde I, Lauria M, Dettori M, Vendramin E, Balconi C, Micali S, Wang Y, Marrazzo MT, Cipriani G, Hartings H, Testolin R, Abbott AG, Motto M, Quarta R (2005) Microsatellite and AFLP markers in the Prunus persica [L. (Batsch)] x P. ferganensis BC1 linkage map: saturation and coverage improvement. Theor Appl Genet 111:1013–1021
Viruel MA, Messeguer R, de Vicente MC, Garcia-Mas J, Puigdomènech P, Vargas F, Arus P (1995) A linkage map with RFLP and isoenzyme markers for almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:964–971
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wendel JF, Weeden NF (1989) Visualisation and interpretation of plant isozymes. In: Soltis DE, Soltis PS (eds) Isozymes in plant biology. Dioscorides, Oregon, pp 5–45
Yamamoto T, Mochida K, Imai T, Shi YZ, Ogiwara I, Hayashi T (2002) Microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] derived from an enriched genomic and cDNA libraries. Mol Ecol Notes 2:298–301
Yamamoto T, Yamaguchi M, Hayashi T (2005) An integrated genetic linkage map of peach by SSR, STS, AFLP and RAPD. J Japan Soc Hort Sci 74:204–213
Acknowledgements
Stone fruit genetics at East Malling Research is funded by Defra. A. Belaj acknowledges a grant from Instituto Andaluz de Investigación y Formación Agraria y Pesquera, Conserjería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa, Andalucía, Spain and R. Bošković a grant from the Mount Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Morgante.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Table S1
Monogenic segregation ratios and chi-squared values for goodness of fit to expected Mendelian segregation ratios for 174 loci (160 SSR and six gene-specific markers) scored in PA × PN including their linkage group location. The suffixes A, B and C distinguish multiple loci revealed by particular primers. Segregation ratios deviating significantly from the expected ratios (P ≤ 0.05, 0.01, 0.001) are indicated with one, two or three asterisks, respectively (DOC 264 KB)
Table S2
Monogenic segregation ratios and chi-squared values for goodness of fit to expected Mendelian segregation ratios for 32 isoenzyme and two SSR loci scored in a 47 seedling subset of the PA × PN progeny including their linkage group location. The suffixes -1, -2, -3, etc. distinguish multiple isoenzyme loci detected with PAGE and -a, -b, -c for cathodal and -z, -y, -x, etc. for anodal loading with IEF. Segregation ratios deviating significantly from the expected ratios (P ≤ 0.05, 0.01, 0.001) are indicated with one, two or three asterisks, respectively (DOC 79.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clarke, J.B., Sargent, D.J., Bošković, R.I. et al. A cherry map from the inter-specific cross Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’ × P. nipponica based on microsatellite, gene-specific and isoenzyme markers. Tree Genetics & Genomes 5, 41–51 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0166-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0166-9