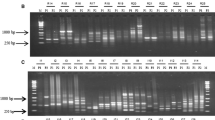
Abstract
White pine blister rust (WPBR), caused by Cronartium ribicola, is a devastating disease in Pinus monticola and other five-needle pines. Pyramiding a major resistance gene (Cr2) with other resistance genes is an important component of integrated strategies to control WPBR in P. monticola. To facilitate this strategy, the objective of the present study was to identify leucine-rich repeat (LRR) polymorphisms, amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLPs), and sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers linked to the western white pine Cr2 (BSA) gene for precise gene mapping. Bulked segregant analysis and haploid segregation analysis allowed the identification of 11 LRR polymorphisms and five AFLP markers in the Cr2 linkage. The closest LRR markers were 0.53 Kosambi cM from Cr2 at either end. After marker cloning and sequencing, AFLP marker EacccMccgat-365 and random polymorphic DNA marker U570–843 were converted successfully into SCAR markers. For a potential application in marker-assisted selection (MAS), these two SCAR markers were verified in two western white pine families. This study represents the first report of LRR-related DNA markers linked to C. ribicola resistance in five-needle pines. These findings may help further candidate gene identification for disease resistance in a conifer species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Backes G, Madsen LH, Jaiser H, Stougaard J, Herz M, Mohler V, Jahoor A (2003) Localisation of genes for resistance against Blumeria graminis sp. hordei and Puccinia graminis in a cross between a barley cultivar and a wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) line. Theor Appl Genet 106:353–362
Benet H, Guries RP, Boury S, Samalley EB (1995) Identification of RAPD markers linked to a black leaf spot resistance gene in Chinese elm. Theor Appl Genet 90:1068–1073
Cervera M-T, Gusmao J, Steenackers M, Peleman J, Storme V, Vanden Broeck A, Van Montagu M, Boerjan W (1996) Identification of AFLP molecular markers for resistance against Melampsora larici-populina in Populus. Theor Appl Genet 93:733–737
Chen XM, Line RF, Leung H (1998) Genome scanning for resistance-gene analogs in rice, barley, and wheat by high-resolution electrophoresis. Theor Appl Genet 97:345–355
Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Devey ME, Mix AD, Kinloch BB Jr, Neale DB (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA markers tightly linked to a gene for resistance to white pine blister rust in sugar pine. Proc Natl Acad USA 92:2066–2070
Fourmann M, Chariot F, Froger N, Delourme R, Brunel D (2001) Expression, mapping, and genetic variability of Brassica napus disease resistance gene analogues. Genome 44(6):1083–1099
Friesen N, Brandes A, Heslop-Harrison JS (2001) Diversity, origin, and distribution of retrotransposons (gypsy and copia) in conifers. Mol Biol Evol 18:1176–1188
Geffroy V, Sevignac M, De Oliveira JC, Fouilloux G, Skroch P, Thoquet P, Gepts P, Langin T, Dron M (2000) Inheritance of partial resistance against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Phaseolus vulgaris and co-localization of quantitative trait loci with genes involved in specific resistance. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:287–296
Harkins DM, Johnson GN, Skaggs PA, Mix AD, Dupper GE, Devey ME, Kinloch BB Jr, Neale DB (1998) Saturation mapping of a major gene for resistance to white pine blister rust in sugar pine. Theor Appl Genet 97:1355–1360
Hayes AJ, Maroof MAS (2000) Targeted resistance gene mapping in soybean using modified AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 100:1279–1283
Hunt RS (1997) Relative value of slow canker growth and bark reaction as resistance responses to white pine blister rust. Can J Plant Pathol 19:352–357
Hunt RS, Jensen GD, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2004) Confirmation of dominant gene resistance (Cr2) in US white pine selection to white pine blister rust growing in British Columbia. In: Sniezko RA, Samman S, Schlarbaum SE (eds) Kriebel HB Breeding and genetic resources of five-needle pines: growth, adaptability, and pest resistance; 2001 July 23–27; Medford, OR, USA. IUFRO Working Party, pp 227–229
Kajava AV (1998) Structural diversity of leucine-rich repeat proteins. J Mol Biol 277:519–527
Kinloch BB Jr, Sniezko RA, Barnes GD, Greathouse TE (1999) A major gene for resistance to white pine blister rust in western white pine from the western Cascade Range. Phytopathol 89:861–867
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:725–732
Jermstad KD, Sheppard LA, Kinloch BB, Delfino-Mix A, Ersoz ES, Krutovsky KV, Neale DB (2006) Isolation of a full-length CC–NBS–LRR resistance gene analog candidate from sugar pine showing low nucleotide diversity. Tree Genet Genomes 2:76–85
Johnk N, Hietala AM, Fossdal CG, Collinge DB, Newman MA (2005) Defense-related genes expressed in Norway spruce roots after infection with the root rot pathogen Ceratobasidium bicorne (anamorph: Rhizoctonia sp.). Tree Physiol 25:1533–1543
Jones DA, Thomas CM, Hammond-Kosack KE, Balint-Kurti PJ, Jones JD (1994) Isolation of the tomato Cf-9 gene for resistance to Cladosporium fulvum by transposon tagging. Science 266(5186):789–793
Junghans DT, Alfenas AC, Brommonschenkel SH, Oda S, Mello EJ, Grattapaglia D (2003) Resistance to rust (Puccinia psidii Winter) in eucalyptus: mode of inheritance and mapping of a major gene with RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:175–180
Liu J-J, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2003) Isolation, genetic variation and expression of TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs from western white pine (Pinus monticola Dougl. ex. D. Don.). Mol Genet Genom 270:432–441
Liu J-J, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2007) The CC-NBS-LRR subfamily in western white pine (Pinus monticola D. Don.): targeted identification, gene expression and genetic linkage with disease resistance against Cronartium ribicola. Phytopathol 97:728–736
Liu J-J, Ekramoddoullah AKM, Hunt RS, Zamani A (2006) Identification and characterization of RAPD markers tightly linked to a major gene (Cr2) for resistance to Cronartium ribicola (Fish.) in Pinus monticola (D. Don). Phytopathol 96(4):395–399
McDonald G, Zambino P, Sniezko R (2004) Breeding rust-resistant five-needle pines in the western United States: lessons from the past and a look to the future. In: Sniezko RA, Samman S, Schlarbaum SE, Kriebel HB (eds) Breeding and genetic resources of five-needle pines: Growth, adaptability, and pest resistance; 2001 July 23–27; Medford, OR, USA. IUFRO Working Party, pp 28–50
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Davis JW, Chen H, Bassil NV, Smith DC, Kubisiak TL (2004) RAPD markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in Corylus avellana. Theor Appl Genet 108:651–656
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Sobral BW, Young ND (1999) Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J 20:317–332
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Pan Q, Wendel J, Fluhr R (2000) Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J Mol Evol 50:203–213
Sicard D, Woo S-S, Arroyo-Garcia R, Ochoa O, Nguyen D, Korol A, Nevo ER, Michelmore R (1999) Molecular diversity at the major cluster of disease resistance genes in cultivated and wild Lactuca spp. Theor Appl Genet 99:405–418
Smith JA, Blanchette RA, Burnes TA, Jacobs JJ, Higgins L, Witthuhn BA, David AJ, Gillman JH (2006) Proteomic comparison of needles from blister rust-resistant and susceptible Pinus strobus seedlings reveals upregulation of putative disease resistance proteins. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19(2):150–160
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL, Kim HS, Pi LY, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C, Ronald P (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21 Science. 270(5243):1804–1806
Soriano JM, Vilanova S, Romero C, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2005) Characterization and mapping of NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Theor Appl Genet 110(5):980–989
Tabor GM, Kubisiak TL, Klopfenstein NB, Mcabb HS Jr (2000) Bulked segregant analysis identifies molecular markers linked to Melampsora medusae resistance in Populus deltoides. Phytopathol 90:1039–1042
Ujino-Ihara T, Yoshimura K, Ugawa Y, Yoshimaru H, Nagasaka K, Tsumura Y (2000) Expression analysis of ESTs derived from the inner bark of Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Mol Biol 43:451–457
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JOINMAP 3.0, Software for the calculation of the genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, The Netherlands
van der Linden CG, Wouters DC, Mihalka V, Kochieva EZ, Smulders MJ, Vosman B (2004) Efficient targeting of plant disease resistance loci using NBS profiling. Theor Appl Genet 109(2):384–393
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wilcox PL, Amerson HV, Kuhlman EG, Liu B-H, O’Malley DM (1996) Detection of a major gene for resistance to fusiform rust disease in loblolly pine by genomic mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3859–3864
Yousef GG, Juvik JA (2001) Comparison of phenotypic and marker-assisted selection for quantitative traits in sweet corn. Crop Sci 41:645–655
Zhang Z, Xu J, Xu Q, Larkin P, Xin Z (2004) Development of novel PCR markers linked to the BYDV resistance gene Bdv2 useful in wheat for marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 109(2):433–439
Zhang J, Yuan Y, Niu C, Hinchliffe DJ, Lu Y, Yu S, Percy RG, Ulloa M, Cantrell RG (2007) AFLP-RGA markers in comparison with RGA and AFLP in cultivated tetraploid cotton. Crop Sci 47:180–187
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the forest genomics funding from the Canadian Forest Service of Natural Resources Canada. We thank Dr. J. Eades and Miss P. Rajkumar for technical assistance with AFLP gel electrophoresis and SCAR marker tests, and Dr. P. Dale, H. Williams, and J. Stone for thoughtful comments on the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Aitken
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JJ., Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. Development of leucine-rich repeat polymorphism, amplified fragment length polymorphism, and sequence characterized amplified region markers to the Cronartium ribicola resistance gene Cr2 in western white pine (Pinus monticola). Tree Genetics & Genomes 4, 601–610 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0135-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0135-3