Abstract
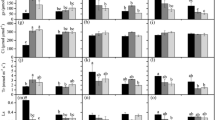
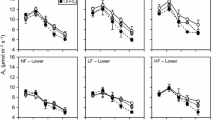
Ground-level ozone (O3) pollution has affected carbon metabolism in tree species, which becomes one of the top environmental issues in China. In this paper, 1-year-old seedlings of Phoebe bournei and Pinus massoniana Lamb. were grown under field conditions at a rural site near the city of Taihe (Jiangxi Province). The plants were exposed in open-top chambers either to charcoal-filtered air or nonfiltered ambient air for 145 days. At the end of the growth season, the plants were harvested and the major nonstructural carbohydrates in leaves and roots were determined. Exposure to nonfiltered ambient air compared with filtered air controls caused an increase of sucrose, glucose, fructose, starch, and total nonstructural carbohydrates (TNCs) in fine roots of Ph. bournei, while there is no change in carbohydrate contents in Pi. massoniana roots. Compared with filtered air, in Ph. Bournei, starch and TNCs in leaves were reduced by 48 and 7 %, respectively, in ambient O3. While, ambient O3 just increased TNC content by 8.9 % in Pi. massoniana needles compared to filtered air. In summary, ambient O3 affected carbohydrate metabolism of these two subtropical tree species in China, and Pi. massoniana was less sensitive than Ph. bournei. O3 induced much greater changes in the amounts of carbohydrates in roots than in leaves.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alscher, R. G., Amundson, R. G., & Cummin, J. R. (1989). Seasonal changes in the pigments, carbohydrates and growth of red spruce as affected by ozone. New Phytologist, 113, 211–223.
Amundson, R. G., Alscher, R. G., Fellows, S., Rubin, G., Fincher, J., Leuken, P. V., & Weinstein, L. H. (1991). Seasonal changes in the pigments, carbohydrates and growth of red spruce as affected by exposure to ozone for two growing seasons. New Phytologist, 118, 127–137.
Andersen, C. P. (2003). Source-sink balance and carbon allocation below ground in plants exposed to ozone. New Phytologist, 157, 213–228.
Andersen, C. P., & Scagel, C. F. (1997). Nutrient availability alters below-ground respiratory responses of Ponderosa Pine to ozone. Tree Physiology, 17, 377–387.
Andersen, C., Wilson, R., Plocher, M., & Hogsett, W. E. (1997). Carry-over effects of ozone on root growth and carbohydrate concentrations of ponderosa pine seedlings. Tree Physiology, 17, 805–811.
Anttonen, S., Kittilä, M., & Kärenlampi, L. (1998). Impacts of ozone on Aleppo pine needles: visible symptoms, starch concentrations and stomatal responses. Chemosphere, 36(4–5), 663–668.
Ashmore, M. R. (2005). Assessing the future global impacts of ozone on vegetation. Plant, Cell and Environment, 28, 949–964.
Barnes, J. D., Eamus, D., & Arown, K. A. (1990). The influence of ozone, acid mist and soil nutrient status on Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. New Phytologist, 115, 149–156.
Braun, S., & Fluckiger, W. (1995). Effects of ambient ozone on seedlings of Fagus sylvatica L. and Picea abies (L.) Karst. New Phytologist, 129, 33–44.
Braun, S., Zugmaier, U., Thomas, V., & Fluckiger, W. (2004). Carbohydrate concentrations in different plant parts of young beech and spruce along a gradient of ozone pollution. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 2399–2407.
Calvo, E., Martin, C., & Sanz, M. J. (2007). Ozone sensitivity differences in five tomato cultivars: visible injury and effects on biomass and fruits. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 186, 167–181.
Chapin, F. S., III, Schulze, E., & Mooney, H. A. (1990). The ecology and economics of storage in plants. Annual Review of Ecology Systematics, 21, 423–447.
Chen, Z., Wang, X., Feng, Z., Xiao, Q., & Duan, X. (2009). Impact of elevated O3 on soil microbial community function under wheat crop. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 198, 189–198.
Chen, Z., Wang, X., Yao, F., Zheng, F., & Feng, Z. (2010). Elevated ozone changed soil microbial community in a rice paddy. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 74(3), 829–837.
Chen, Z., Wang, X. K., & Shang, H. (2014). Using 13C isotope to investigate O3 effects on C fixation and translocation of rice. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(7), 1983–1988.
Darrall, N. M. (1989). The effect of air pollutants on physiological processes in plants. Plant, Cell & Environment, 12, 1–30.
Degl’Innocenti, E., Guidi, L., & Soldatini, G. F. (2002). Characterisation of the photosynthetic response of tobacco leaves to ozone: CO2 assimilation and chlorophyll fluorescence. Journal of Plant Physiology, 159, 845–853.
Feng, Z. Z., Zheng, H. Q., Wang, X. K., Zheng, Q. W., & Feng, Z. Z. (2008). Sensitivity of Metasequoia glyptostroboides to ozone stress. Photosynthetica, 46(3), 463–465.
Feng, Z. Z., Niu, J. F., Zhang, W. W., Wang, X. K., Yao, F. F., & Tian, Y. (2011). Effects of ozone exposure on sub-tropical evergreen Cinnamomum camphora seedlings grown in different nitrogen loads. Trees, 25, 617–625.
Feng, Z. Z., Sun, J. S., Wan, W. X., Hu, E. Z., & Calatayud, V. (2014). Evidence of widespread ozone-induced visible injury on plants in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 193, 296–301.
Frey, B. R., Lieffers, V. J., Landhäusser, S. M., Comeau, P. G., & Greenway, K. J. (2003). An analysis of sucker regeneration of trembling aspen. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 33, 1169–1179.
Galvez, D. A., Landhäusser, S. M., & Tyree, M. T. (2011). Root carbon reserve dynamics in aspen seedlings: does simulated drought induce reserve limitation? Tree Physiology, 31, 250–257.
Gelang, J., Selldén, G., Younis, S., & Pleijel, H. (2001). Effects of ozone on biomass, non-structural carbohydrates and nitrogen in spring wheat with artificially manipulated source/sink ratio. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 46, 155–169.
Grantz, D. A., Silva, V., Toyota, M., & Ott, N. (2003). Ozone increases root respiration but decreases leaf CO2 assimilation in cotton and melon. Journal of Experimental Botany, 54, 2375–2384.
Grossnickle, S. C. (2005). Importance of root growth in overcoming planting stress. New Forests, 30, 273–294.
Grulke, N. W., Andersen, C. P., & Hogsett, W. E. (2001). Seasonal changes in above- and belowground carbohydrate concentrations of Ponderosa pine along a pollution gradient. Tree Physiology, 21, 173–181.
Günthardt-Goerg, M., Matyssek, R., Scheidegger, C., & Keller, T. (1993). Differentiation and structural decline in the leaves and bark of birch (Betula pendula) under low ozone concentrations. Trees, 7, 104–114.
Körner, C. H. (1991). Some often overlooked plant characteristics as determinants of plant growth: a reconsideration. Functional Ecology, 5, 162–173.
Kozlowski, T. T., & Pallardy, S. G. (2002). Acclimation and adaptive responses of woody plants to environmental stresses. Botanical Review, 68, 270–334.
Landhäusser, S. M. (2011). Aspen shoots are carbon autonomous during bud break. Trees, 25, 531–536.
Landhäusser, S. M., Pinno, B. D., Lieffers, V. J., & Chow, P. S. (2012). Partitioning of carbon allocation to reserves or growth determines future performance of aspen seedlings. Forest Ecology and Management, 275, 43–51.
Landolt, W., Giinthardt-Goerg, M. S., Pfenninger, I., Einig, W., Hampp, R., & Matyssek, R. (1997). Effect of fertilization on ozone induced changes in the metabolism of birch leaves (Betula pendula). New Phytologist, 137, 389–397.
Lux, D., Leonardi, S., Muller, J., Wiemken, A., & Fluckiger, W. (1997). Effects of ambient ozone concentrations on contents of non-structural carbohydrates in young Picea abies and Fagus sylvatica. New Phytologist, 137, 399–409.
Manes, F., Incerti, G., Salvatori, E., Vitale, M., Riotta, C., & Costanza, R. (2012). Urban ecosystem services: tree diversity and stability of tropospheric ozone removal. Ecological Application, 22(1), 349–360.
Martens, L. A., Landhäusser, S. M., & Lieffers, V. J. (2007). First-year growth response of cold-stored, nursery-grown aspen planting stock. New Forests, 33, 281–295.
Matyssek, R., & Innes, J. L. (1999). Ozone—a risk factor for trees and forests in Europe. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 116, 199–226.
Matyssek, R., & Sandermann, H. (2003). Impact of ozone on trees: an ecophysiological perspective. Progress in Botany, 64, 349–404.
Matyssek, R., Reich, P. B., Oren, R., & Winner, W. E. (1995). Response mechanisms of conifers to air pollutants. In W. K. Smith & T. H. Hinckley (Eds.), Physiological ecology of coniferous forests (pp. 255–308). New York: Academic.
Miller, J. E., Shafer, S. R., Schoeneberger, M. M., Pursley, W. A., Horton, S. J., & Davey, C. B. (1997). Influence of a mycorrhizal fungus and/or Rhizobium on growth and biomass partitioning of subterranean clover exposed to ozone. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 96, 233–248.
Mortensen, L. M. (1998). Growth responses of seedlings of six Betula pubescens Ehrh. provenances to six ozone exposure regimes. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 13, 189–196.
Neufeld, H. S., Peoples, S. J., Davison, A. W., Chappelka, A. H., Somers, G. L., Thomley, J. E., & Booker, F. L. (2012). Ambient ozone effects on gas exchange and total non-structural carbohydrate levels in cutleaf condflower (Rudbeckia laciniata L.) growing in Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Environmental Pollution, 160, 74–81.
Pregitzer, K. S., Burton, A. J., King, J. S., & Zak, D. R. (2008). Soil respiration, root biomass, and root turnover following long-term exposure of northern forests to elevated atmospheric CO2 and tropospheric O3. New Phytologist, 180, 153–161.
Samuelson, L., & Kelly, J. M. (2001). Scaling ozone effects from seedlings to forest trees. New Phytologist, 149, 21–41.
Sild, E., Pleijel, H., & Selldén, G. (2002). Elevated ozone (O3) alters carbohydrate metabolism during grain filling in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agriculture. Ecosystems and Environment, 92, 71–81.
Sprugel, D. G. (2002). When branch autonomy fails: Milton’s Law of resource availability and allocation. Tree Physiology, 22, 1119–1124.
Thomas, V. F. D., Hiltbrunner, E., Braun, S., & Flückiger, W. (2002). Changes in root starch contents of mature beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) along an ozone and nitrogen gradient in Switzerland. Phyton, 42, 223–228.
Thomas, V. F. D., Braun, S., & Flückiger, W. (2005). Effects of simultaneous ozone exposure and nitrogen loads on carbohydrate concentrations, biomass, and growth of young spruce trees (Picea abies). Environmental Pollution, 137, 507–516.
Thomas, V. F. D., Braun, S., & Flückiger, W. (2006). Effects of simultaneous ozone exposure and nitrogen loads on carbohydrate concentrations, biomass, growth, and nutrient concentrations of young beech trees (Fagus sylvatica). Environmental Pollution, 143, 341–354.
Topa, M. A., Vanderklein, D. W., & Corbin, A. (2001). Effects of elevated ozone and low light on diurnal and seasonal carbon gain in sugar maple. Plant, Cell and Environment, 24, 663–677.
Topa, M. A., McDermitt, D. J., Yun, S. C., & King, P. S. (2004). Do elevated ozone and variable light alter carbon transport to roots in sugar maple? New Phytologist, 162, 173–186.
Vollsnes, A. V., Kruse, O. M. O., Eriksen, A. B., Oxaal, U., & Futsaether, C. M. (2010). In vivo root growth dynamics of ozone exposed Trifolium subterraneum. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 69, 183–188.
Wang, X. K., Manning, W., Feng, Z. W., & Zhu, Y. G. (2007). Ground level ozone in China: distribution and effects on crop yields. Environmental Pollution, 147, 394–400.
Wellburn, F. A. M., & Wellburn, A. R. (1994). Atmospheric ozone affects carbohydrate allocation and winter hardiness of Pinus halepensis Mill. Journal of Experimental Botany, 45, 607–614.
Wonisch, A., Müller, M., Tausz, M., Soja, G., & Grill, D. (1999). Simultaneous analysis of chromosomes in root meristems and of the biochemical status of needle tissues of three different clones of Norwayspruce trees challenged with moderate ozone levels. European Journal Forest Pathology, 29, 281–294.
Wyka, T. (2000). Effect of nutrients on growth rate and carbohydrate storage in Oxytropis sericea: a test of the carbon accumulation hypothesis. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 161, 381–386.
Yao, F. F., Wang, X. K., Chen, Z., Feng, Z. Z., Zheng, Q. W., Duan, X. N., Ouyang, Z. Y., & Feng, Z. Z. (2008). Response of photosynthesis, growth and yield of field-grown winter wheat to ozone exposure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32(1), 212–219.
Zhang, W. W., Niu, J. F., Wang, X. K., Tian, Y., Yao, F. F., & Feng, Z. Z. (2011). Effects of ozone exposure on growth and photosynthesis of the seedlings of Liriodendron chinense (Hemsl.) Sarg, a native tree species of subtropical China. Photosynthetica, 49(1), 29–36.
Zhang, W. W., Feng, Z. Z., Wang, X. K., & Niu, J. F. (2012). Responses of native broadleaved woody species to elevated ozone in subtropical China. Environmental Pollution, 163, 149–157.
Zhang, W. W., Feng, Z. Z., Wang, X. K., & Niu, J. F. (2014). Impacts of elevated ozone on growth and photosynthesis of Metasequoia glyptostroboides Hu et Cheng. Plant Science, 226, 182–188.
Zouzoulas, D., Koutroubas, S. D., Vassiliou, G., & Vardavakis, E. (2009). Effects of ozone fumigation on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) morphology, anatomy, physiology, yield and qualitative characteristics of fibers. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 67, 293–303.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Special Fund for Forest Scientific Research in the Public Welfare (201304313) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31370606) and The Lecture and Study Program for Outstanding Scholars from Home and Abroad (CAFYBB2011007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Shang, H., Cao, J. et al. Effects of Ambient Ozone Concentrations on Contents of Nonstructural Carbohydrates in Phoebe bournei and Pinus massoniana Seedlings in Subtropical China. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 310 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2555-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2555-7