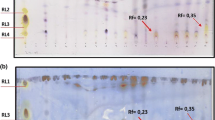
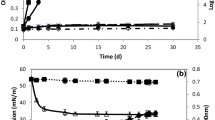
Abstract
Aquaculture wastewaters, with oleic acid (C18:1 ω9) as the most representative contaminant fatty acid, were used as inoculum to perform enrichment cultures in mineral medium in the presence of oleic acid as the sole carbon and energy source, allowing isolation of four bacterial strains named DG1a, DG2a, DG1b and DG2b. 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis assigned the four isolates to the species Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Among the isolates, P. aeruginosa strain DG2a showed degradation of fatty acids, including oleic acid (C18:1 ω9). The hydrophobicity features were investigated in strain DG2a, and a constitutive hydrophobicity in the bacterial cells was highlighted. The capability to produce biosurfactants by cells of the bacterial strain P. aeruginosa strain DG2a was evidenced both in the presence of oleic acid and of aquaculture wastewaters by revealing emulsifying activity, oil spreading tests, haemolytic and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide agar tests. Bacterial cultures containing raw biosurfactant were added to native wastewaters, showing a depletion of the oleic acid content. The use of the isolated bacterial strain P. aeruginosa strain DG2a and of the produced biosurfactant in bioremediation of aquaculture wastewaters is proposed, and the valorization of aquaculture wastewaters as raw material for biosurfactant production by using the isolate is moreover suggested.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-Blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Baldi, F., Ivošević, N., Minacci, A., Pepi, M., Fani, R., Svetličić, V., et al. (1999). Adhesion of Acinetobacter venetianus to diesel fuel droplets studied with in situ electrochemical and molecular probes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 2041–2048.
Banat, I. (1993). The isolation of a thermophilic biosurfactant-producing Bacillus species. Biotechnology Letters, 15, 591–594.
Bligh, E. G., & Dyer, W. J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37, 911–917.
Bodour, A. A., Drees, K. P., & Maier, M. R. (2003). Distribution of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms in undisturbed and contaminated arid southwestern soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 3280–3287.
Bofill, C., Prim, N., Mormeneo, M., Manresa, A., Pastor, F. J., & Diaz, P. (2010). Differential behaviour of Pseudomonas sp. 42A2 LipC, a lipase showing greater versatility than its counterpart LipA. Biochimie, 92, 307–316.
Cameotra, S. S., & Makkar, R. S. (1998). Synthesis of biosurfactants in extreme conditions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 50, 520–529.
Chipasa, K. B., & Mędrzycka, K. (2006). Behaviour of lipids in biological wastewater treatment processes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 33, 635–645.
Cole, J. R., Wang, Q., Cardenas, E., Fish, J., Chai, B., Farris, R. J., et al. (2009). The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 37(Database issue), D141–D145. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn879.
Cooper, D. G., & Goldenberg, B. G. (1987). Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Environmental Microbiology, 53, 224–229.
de Lima, C. J. B., Ribeiro, E. J., Sérvulo, E. F. C., Resende, M. M., & Cardoso, V. L. (2009). Biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in residual soybean oil. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 152, 156–168.
Franzetti, A., Bestetti, G., Caredda, P., La Colla, P., & Tamburini, E. (2008). Surface-active compounds and their role in the access to hydrocarbons in Gordonia strains. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 63, 238–248.
Heipieper, H. J., Cornelissen, S., & Pepi, M. (2010). Surface properties and cellular energetics of bacteria in response to the presence of hydrocarbons. In K. N. Timmis (Ed.), Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology (Vol. 2, pp. 1615–1624). Berlin: Springer. Part 9.
Henkel, M., Müller, M. M., Kügler, J. H., Lovaglio, R. B., Contiero, J., Syldatk, C., et al. (2012). Rhamnolipids as biosurfactants from renewable resources: concepts for next-generation rhamnolipid production. Process Biochemistry, 47, 1207–1219.
Keenan, D., & Sabelnikov, A. (2000). Biological augmentation eliminates grease and oil in bakery wastewater. Water Environ Research, 72, 141–146.
Kimura, M. (1980). A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16, 111–120.
Kumar, S., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Tamura, K. (2008). MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9, 299–306.
Li, Z. K., Brian, A., & Wrenn, C. A. (2004). Effects of ferric hydroxide on the anaerobic biodegradation kinetics and toxicity of vegetable oil in freshwater sediments. Water Research, 38, 3859–3868.
Liu, V. I., Nakhla, G., & Bassi, A. (2004). Treatability and kinetics studies of mesophilic aerobic biodegradation of high oil and grease pet food wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 112, 87–94.
Lyczak, J. B., Cannon, C. L., & Pier, G. B. (2002). Lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 15, 194–222.
Mahjaubi, M., Jaouani, A., Guesmi, A., Ben Amor, S., Jouini, A., Cherif, H., et al. (2013). Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria isolated from petroleum contaminated sites in Tunisia: isolation, identification and characterization of the biotechnological potential. New Biotechnology. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2013.03.004.
Makkar, R. S., & Cameotra, S. S. (2002). An update on the use of unconventional substrates for the biosurfactant production and their new applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 58, 428–434.
Makkar, R. S., Cameotra, S. S., & Banat, I. M. (2011). Advances in utilization of renewable substrates for biosurfactant production. Applied Microbiology and Biothechnology Express, 1, 5.
Maldonando, M., Carmona, M. C., Echeverría, Y., & Riesgo, A. (2005). The environmental impact of Mediterranean cage fish farms at semi-exposed locations: does it need a re-assessment? Helgoland Marine Research, 59, 121–135.
Matsumiya, Y., Wakita, D., Kimura, A., Sanpa, S., & Kubo, M. (2007). Isolation and characterization of a lipid-degrading bacterium and its application to lipid-containing wastewater treatment. Journal of Bioscience Bioengineering, 103, 325–330.
Morikawa, M. (2006). Beneficial biofilm formation by industrial bacteria Bacillus subtilis and related species. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 101, 1–8.
Morrison, W. R., & Smith, L. M. (1964). Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethylacetals from lipids with boron fluoride-methanol. Journal of Lipid Research, 5, 600–608.
Mulligan, C. N. (2005). Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environmental Pollution, 133, 183–198.
Pepi, M., Cesàro, A., Liut, G., & Baldi, F. (2005). An Antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium Halomonas sp. ANT-3b, growing on n-hexadecane, produces a new emulsifying glycolipid. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 53, 157–166.
Perfumo, A., Banat, I., Canganella, F., & Marchant, R. (2006). Rhamnolipid production by a thermophilic hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa AP02-1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72, 132–138.
Reis, F. A., Servulo, E. F., & De Franca, F. P. (2004). Lipopeptide surfactant production by Bacillus subtilis grown on low-cost raw materials. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 115, 899–912.
Ron, E. Z., & Rosenberg, E. (2001). Natural roles of biosurfactants. Environmental Microbiology, 3, 229–236.
Rosenberg, M., Gutnick, D., & Rosenberg, E. (1980). Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 9, 29–33.
Saatci, Y., Arslan, E. I., & Konar, V. (2003). Removal of total lipids and fatty acids from sunflower oil factory effluent by UASB bioreactor. Bioresource Technology, 87, 269–272.
Saitou, N., & Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406–425.
Siegmund, I., & Wagner, F. (1991). New method for detecting rhamnolipids excreted by Pseudomonas species during growth on mineral agar. Biotechnology Techniques, 5, 265–268.
Smibert, R. M., & Krieg, N. R. (1981). General characterization. In P. Gerhardt, R. G. E. Murray, R. N. Costilow, E. W. Nester, W. A. Wood, N. R. Krieg, & G. B. Philips (Eds.), Manual of methods for general bacteriology (pp. 411–442). Washington: American Society for Microbiology.
Sousa, D. Z., Smidt, H., Alves, M. M., & Stams, A. J. (2009). Ecophysiology of syntrophic communities that degrade saturated and unsaturated long-chain fatty acids. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 68, 257–272.
Stickland, H. G., Davenport, P. W., Lilley, K. S., Griffin, J. L., & Welch, M. (2010). Mutation of nfxB causes global changes in the physiology and metabolism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 2957–2967.
Thavasi, R., Jayalakshmi, S., Balasubramanian, T., & Banat, I. M. (2007). Biosurfactant production by Corynebacterium kutscheri from waste motor lubricant oil and peanut oil cake. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 45, 686–691.
Watanabe, K. (2001). Microorganisms relevant to bioremediation. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 12, 237–241.
Zhang, H., Xiang, H., Zhang, G., Cao, X., & Meng, Q. (2009). Enhance treatment of waste frying oil in an activated sludge system by addition of crude rhamnolipid solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 217–223.
Zhu, Y., Gan, J. J., Zhang, G. L., Yao, B., Zhu, W. J., & Meng, Q. (2007). Reuse of waste frying oil for production of rhamnolipids using Pseudomonas aeruginosa zju.u1M. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 8, 1514–1520.
Zouboulis, A. J., & Avranas, A. (2000). Treatment of oil-in-water emulsion by coagulation and dissolved-air flotation. Colloids and Surfaces A, 172, 153–161.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank E. Bertelli for image study of bacterial cells, S. Gasperini for his technical support and E. Franchi for information on the aquaculture plant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pepi, M., Focardi, S., Lobianco, A. et al. Degradation of Fatty Acids and Production of Biosurfactant as an Added Value, by a Bacterial Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa DG2a Isolated from Aquaculture Wastewaters. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1772 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1772-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1772-1