Abstract
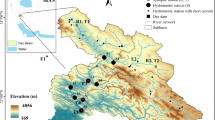
The aim of this study was to test three main hypotheses about the interannual variability of streamflow downstream from dams: (1) an almost similar long-term trend in interannual variability, (2) low variability of flow, and (3) its independence (no link) from climate variability. To test these hypotheses, the interannual variability of winter and spring streamflow downstream from three reservoirs (Gouin, Manouane, and Matawin) which induce an inversion of the natural cycle of streamflow (maximum flows in winter and minimum flows in spring) was compared to the interannual variability of streamflow in natural rivers (measured at the Matawin and Vermillon stations) over the period from 1932 to 2008 in the St-Maurice River watershed. As far as the interannual variability of flow is concerned, its long-term trend is not homogeneous downstream from the three reservoirs in both seasons. However, downstream from two reservoirs, changes in streamflow were observed to be different from those in natural rivers (no significant trend downstream from the Taureau reservoir, on the Matawin River, and significant decrease in spring flow downstream from the Manouane reservoir). Finally, coefficient of variation values for minimum flows are higher downstream from reservoirs than in natural rivers, despite the fact that watershed surface area is larger for regulated rivers than for natural ones. As for the link with climate variability, analysis of the correlation between climate variables (temperature and precipitation) and mean winter and spring daily streamflow reveals that winter streamflow downstream from the Taureau reservoir is not correlated with any climate variable, whereas spring streamflow is positively correlated with rainfall and negatively correlated with maximum temperature. Thus, downstream from reservoirs, the interannual variability of streamflow depends on climate during the spring, but not during winter.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshar A, Mariño MA, Saadatpour M, Afshar A (2011) Fuzzy TOPSIS multi-criteria decision analysis applied to Karun reservoir system. Water Resour Manage 25:545–563
Ahmadi A, Karamouz M, Moridi A (2010) Robust methods for identifying optimal reservoir operation strategies using deterministic and stochastic formulations. Water Resour Manage 24:2527–2552
Assani AA, Buffin-Bélanger T, Roy AG (2002) Analyse des impacts d’un barrage sur le régime hydrologique de la rivière Matawin (Québec, Canada). Rev Sci Eau 15:557–574
Assani AA, Gravel E, Buffin-Bélanger T, Roy AG (2005) Impacts des barrages sur les débits annuels minimums en fonction des régimes hydrologiques artificialisés au Québec (Canada). Rev Sci Eau 18:103–127
Assani AA, Stichelbout E, Roy AG, Petit F (2006) Comparison of impacts of dams on the annual maximum flow characteristics in the three regulated hydrological regimes in Québec. Hydrol Process 20:3485–3501
Assani AA, Lajoie F, Laliberté C (2007) Impacts des barrages sur les caractéristiques des débits moyens annuels en fonction du mode de gestion et de la taille des bassins versants au Québec. Rev Sci Eau 20:127–146
Assani AA, Matteau M, Mesfioui M, Campeau S (2009) Analysis of factors influencing the extent of hydrological change of annual maximum and minimum flow downstream from dams in Quebec. In: Hayes WP, Barnes MC (eds) Dams: impacts, stability and design. Nova Sciences Publishers, New-York, pp 197–214
Assani AA, Chalifour A, Légaré G, Manouane C-S, Leroux D (2011) Temporal regionalization of 7-day low flows in the St. Lawrence watershed in Quebec (Canada). Water Resour Manage. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9870-6
Boyer C, Chaumont D, Chartier I, Roy AG (2010) Impact of climate change on the hydrology of St. Lawrence tributaries. J Hydrol 384:65–83
Brandão JLB (2010) Performance of the equivalent reservoir modelling technique for multi-reservoir hydropower systems. Water Resour Manage 24:3101–3114
Celeste AB, Billib M (2010) The role of spill and evaporation in reservoir optimization models. Water Resour Manage 24:617–628
Choudhari SA, Raj PA (2010) Multiobjective multireservoir opeartion in fuzzy environment. Water Resour Manage 24:2057–2073
Eum H-I, Simonovic SP (2010) Integrated reservoir management system for adaptation to climate change: the Nakdong River Basin in Korea. Water Resour Manage 24:3397–3417
Fortier C, Assani AA, Mesfioui M, Roy AG (2010) Comparison of the interannual and interdecadal variability of heavy flood characteristics upstream and downstream from dams in invrsed hydrologic regime: case study of Matawin River (Quebec, Canada). River Res Applic doi:10.1002/rra.1423
Göncü S, Albek E (2010) Modeling climate change effects on streams and reservoirs with HSPF. Water Resour Manage 24:707–726
Hobson P, Fabris R, Develter E, Linden LG, Burch MD, Brookes JD (2010) Reservoir inflow monitoring for improved management of treated water quality- A south Australian experience. Water Resour Manage 24:4161–4174
Hunçal O, Altan-Sakarya AB, Ger AM (2011) Optimization of multireservoir systems by genetic algorithm. Water Resour Manage 25:1465–1487
Kumar DN, Baliarsingh F, Raju KS (2010) Optimal reservoir operation for flood control using folded dynamic programming. Water Resour Manage 24:1045–1064
Lajoie F, Assani AA, Roy AG, Mesfioui M (2007) Impacts of dams on monthly flow characteristics. The influence of watershed size and seasons. J Hydrol 334:423–439
Li L, Xu H, Chen X, Simonovic SP (2010) Streamflow forecast and reservoir operation performance assessment under climate change. Water Resour Manage 24:83–104
Lombard F (1987) Rank tests for changepoint problems. Biometrika 74:615–624
López-Moreno JI, Vicente-Serrano SM, Begueria S, Garcia-Ruiz JM, Portela MM, Almeida AB (2009) Dam effects on droughts magnitude and duration in a transboundary basin: the Lower River Tagus, Spain and Portugal. Water Resour Res 45:W02405. doi:10.1029/2008WR007198
Lu XX, Siew RY (2006) Water discharge and sediment flux changes over the past decades in the Lower Mekong River: possible impacts of the Chinese dams. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 10:181–195
Matteau M, Assani AA, Mesfioui M (2009) Application of multivariate statistical analysis methods to the dams hydrologic impact studies. J Hydrol 371:120–128
Meddi M, Assani AA, Meddi H (2010) Temporal of annual rainfall in the Macta and Tafna catchments, Northwestern Algeria. Water Resour Manage 24:3817–3833
Moyle PB, Mount JF (2007) Homogenous rivers, homogenous faunas. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:5711–5712
Olsson O, Ikramova M, Bauer M, Froebrich J (2010) Applicability of adapted reservoir operation for water stress mitigation under dry year conditions. Water Resour Manage 24:277–297
Poff NL, Olden JD, Merritt DM, Pepin DM (2007) Homogenization of regional river dynamics by dams and global biodiversity implications. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:5732–5737
Pradhan D, Ancev T, Drynan R, Harris M (2011) Management of water reservoir (Embungs) in west Timor, Indonesia. Water Resour Manage 25:339–356
Quessy J-F, Favre A-C, Saïd M, Champagne M (2011) Statistical inference in Lombard’s smooth-change model. Environmetrics. doi:10.1002/env.1108 (in press)
Rani D, Moreira MM (2010) Simulation-optimization modeling: a survey and potential application in reservoir system operation. Water Resour Manage 24:1107–1138
Ticlavilca AM, McKee M (2011) Multivariate Bayesian regression approach to forecast releases from a system of multiple reservoirs. Water Resour Manage 25:523–543
Wang Y-M, Chang J-X, Huang Q (2010) Simulation with RBF neural network model for reservoir operation rules. Water Resour Manage 24:2597–2610
Yang D, Ye B, Kane DL (2004) Streamflow changes over Siberian Yenissei River basin. J Hydrol 296:59–80
Ye B, Yang D, Kane DL (2003) Changes in Lena River streamflow hydrology: human impacts versus natural variations. Water Resour Res 39. doi:10.1029/2003WR001991
Yun R, Singh VP, Dong Z (2010) Long-term stochastic reservoir operation using a noisy genetic algorithm. Water Resour Manage 24:3159–3172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assani, A.A., Landry, R., Daigle, J. et al. Reservoirs Effects on the Interannual Variability of Winter and Spring Streamflow in the St-Maurice River Watershed (Quebec, Canada). Water Resour Manage 25, 3661–3675 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9875-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9875-1