Abstract
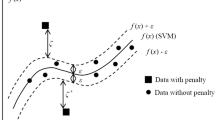
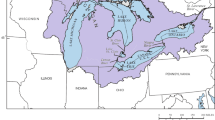
This research presents a model that simultaneously forecasts required water releases 1 and 2 days ahead from two reservoirs that are in series. In practice, multiple reservoir system operation is a difficult process that involves many decisions for real-time water resources management. The operator of the reservoirs has to release water from more than one reservoir taking into consideration different water requirements (irrigation, environmental issues, hydropower, recreation, etc.) in a timely manner. A model that forecasts the required real-time releases in advance from a multiple reservoir system could be an important tool to allow the operator of the reservoir system to make better-informed decisions for releases needed downstream. The model is developed in the form of a multivariate relevance vector machine (MVRVM) that is based on a sparse Bayesian regression model approach. With this Bayesian approach, a predictive confidence interval is obtained from the model that captures the uncertainty of both the model and the data. The model is applied to the multiple reservoir system located in the Lower Sevier River Basin near Delta, Utah. The results show that the model learns the input–output patterns with high accuracy. Computing multiple-time-ahead predictions in real-time would require a model which guarantees not only good prediction accuracy but also robustness with respect to future changes in the nature of the inputs data. A bootstrap analysis is used to guarantee good generalization ability and robustness of the MVRVM. Test results demonstrate good performance of predictions and statistics that indicate robust model generalization abilities. The MVRVM is compared in terms of performance and robustness with another multiple output model such as Artificial Neural Network (ANN).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeloye AJ (2009) Multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks models for generalized reservoir storage-yield-reliability function for reservoir planning. J Hydrol Eng 14(6):731–738
ASCE Task Committee on the Application of ANNs in Hydrology (2000a) Artificial neural networks in hydrology, I: preliminary concepts. J Hydrol Eng 5(2):115–123
ASCE Task Committee on the Application of ANNs in Hydrology (2000b) Artificial neural networks in hydrology, II: hydrologic application. J Hydrol Eng 5(2):124–137
Berger B, Hansen R, Hilton A (2002) Using the world-wide-web as a support system to enhance water management. Paper presented at the 18th ICID Congress and 53rd IEC Meeting, Int Comm on Irrig and Drain, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Berger B, Hansen R, Jensen R (2003) Sevier river basin system description. Sevier River Water Users Association, Delta
Demuth H, Beale M, Hagan M (2009) Neural network toolbox user’s guide. The MathWorks Inc, MA
Duda RO, Hart P, Stork D (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Edited by Wiley Interscience, NY
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1998) An introduction of the bootstrap, monographs on statistics and applied probability 57. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
El-Shafie A, Reda Taha M, Noureldin A (2007) A neuro-fuzzy model for inflow forecasting of the Nile river at Aswan high dam. Water Resour Manage 21:533–556
El-Shafie A, Abdin AE, Noureldin A, Taha MR (2009) Enhancing inflow forecasting model at Aswan high dam utilizing radial basis neural network and upstream monitoring stations measurements. Water Resour Manage 23:2289–2315
Ghosh S, Mujumdar PP (2007) Statistical downscaling of GCM simulations to streamflow using relevance vector machine. Adv Water Resour 31:132–146
Guldal V, Tongal H (2010) Comparison of recurrent neural network, adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and stochastic models in Egirdir lake level forecasting. Water Resour Manage 24:105–128
Hong WC, Pai PF (2007) Potential assessment of the support vector regression technique in rainfall forecasting. Water Resour Manage 21:495–513
Khalil A, McKee M, Kemblowski MW, Asefa T (2005a) Sparse Bayesian learning machine for real-time management of reservoir releases. Water Resour Res 41:W11401
Khalil A, McKee M, Kemblowski MW, Asefa T, Bastidas L (2005b) Multiobjective analysis of chaotic dynamic systems with sparse learning machines. Adv Water Resour 29:72–88
Khalil A, Almasari M, McKee M, Kemblowski MW, Kaluarachchi J (2005c) Applicability of statistical learning algorithms in groundwater quality modeling. Water Resour Res 41:W05010
Khalil A, McKee M, Kemblowski M, Asefa T (2005d) Basin-scale water management and forecasting using neural networks. J Am Water Resour Res 41(1):195–208
Labadie JW (2004) Optimal operation of multireservoir systems: state-of-the-art review. J Water Resour Plan Manage 130(2):93–111
Legates DR, McCabe GJ (1999) Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour Res 35(1):233–241
Lobbrecht AH, Solomatine DP (2002) Machine learning in real-time control of water systems. Urban Water 4:283–289
Nourani V, Mehdi K, Akira M (2009) A multivariate ANN-wavelet approach for rainfall–runoff modeling. Water Resour Manage 23:2877–2894
Pal M, Goel A (2007) Estimation of discharge and end depth in trapezoidal channel by support vector machines. Water Resour Manage 21:1763–1780
Rezaeian Zadeh M, Amin S, Khalili D, Singh VP (2010) Daily outflow prediction by multi layer perceptron with logistic sigmoid and tangent sigmoid activation functions. Water Resour Manage 24:2673–2688
Shirsath PB, Singh AK (2010) A comparative study of daily pan evaporation estimation using ANN, regression and climate based models. Water Resour Manage 24:1571–1581
Sivapragasam C, Muttil N (2005) Discharge rating curve extension—a new approach. Water Resour Manage 19:505–550
Thayananthan A (2005) Template-based pose estimation and tracking of 3D hand motion. PhD thesis, Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Thayananthan A, Navaratnam R, Stenger B, Torr PHS, Cipolla R (2008) Pose estimation and tracking using multivariate regression. Pattern Recogn Lett 29(8):1302–1310
Tipping ME (2001) Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J Mach Learn 1:211–244
Tipping M, Faul A (2003) Fast marginal likelihood maximization for sparse Bayesian models. Paper presented at Ninth International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Soc for Artif Intel Stat, Key West, FL
Trichakis IC, Nikolos IK, Karatzas GP (2010) Artificial neural network (ANN) based modeling for karstic groundwater level simulation. Water Resour Manage
Tripathi S, Govindaraju R (2006) On selection of kernel parameters in relevance vector machines for hydrologic applications. Stoch Eviron Res Risk Assess 21:747–764
World Commission on Dams (2000) Dams and development: a new framework for decision-making. Earthscan Publications Ltd, London and Sterling
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ticlavilca, A.M., McKee, M. Multivariate Bayesian Regression Approach to Forecast Releases from a System of Multiple Reservoirs. Water Resour Manage 25, 523–543 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9712-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9712-y