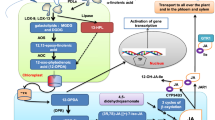
Abstract
WRKY transcription factors play essential roles in diverse signaling pathways related to plant defense responses. However, research focusing on the WRKY family in tomato is fairly limited. In this work, a pathogen-induced SpWRKY1 gene from the wild tomato Solanum pimpinellifolium L3708 showing that its overexpression in cultivated tomato Solanum lycopersicum cv. Zaofen No. 2 results in markedly increased resistance to Phytophthora infestans than untransformed wild-type plant, mainly demonstrated by less severe cell death, lower reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, malonaldehyde (MDA) content, relative electrolyte leakage (REL) and stomatal conductance; and higher peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, chlorophyll content and photosynthetic rate. This resistance was also coupled with enhanced the expression of ROS scavenging-related genes, SA/JA-responsive genes and SA/JA biosynthesis-related genes. This overexpression was accompanied by regulating the expression of an ABA biosynthetic gene, reveals a potentially positive role of SpWRKY1 in ABA-mediated stomatal closure. Furthermore, transgenic tomato also displayed an enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stress by decreasing ROS generation, reducing MDA content and REL, improving POD, SOD and proline content, keeping leaf relative water content, preventing chlorophyll loss, and protecting photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance, accompanied by not only enhanced expression of some ROS scavenging-related and stress-related genes, but also directly up-regulated the expressions of PR genes in response to salt and drought stress. These findings broaden our knowledge about the functions of SpWRKY1 in diverse signalling pathways and may be useful in improving tomato plants tolerance to biotic and abiotic stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Abdallat AM, Ali-Sheikh-Omar MA, Alnemer LM (2015) Overexpression of two ATNAC3-related genes improves drought and salt tolerance in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:989–1001
Atamian HS, Eulgem T, Kaloshian I (2012) SlWRKY70 is required for Mi-1-mediated resistance to aphids and nematodes in tomato. Planta 235:299–309
Bergougnoux V (2014) The history of tomato: from domestication to biopharming. Biotechnol Adv 32:170–189
Bhattarai KK, Atamian HS, Kaloshian I, Eulgem T (2010) WRKY72-type transcription factors contribute to basal immunity in tomato and Arabidopsis as well as gene-for-gene resistance mediated by the tomato R gene Mi-1. Plant J 63:229–240
Birkenbihl RP, Diezel C, Somssich IE (2012) Arabidopsis WRKY33 is a key transcriptional regulator of hormonal and metabolic responses toward Botrytis cinerea infection. Plant Physiol 159:266–285
Cai RH, Zhao Y, Wang YF, Lin YX, Peng XJ, Li Q, Chang YW, Jiang HY, Xiang Y, Cheng BJ (2014) Overexpression of a maize WRKY58 gene enhances drought and salt tolerance in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 119:565–577
Cao WH, Liu J, He XJ, Mu RL, Zhou HL, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2007) Modulation of ethylene responses affects plant salt-stress responses. Plant Physiol 143:707–719
Chen Z, Cuin TA, Zhou M, Twomey A, Naidu BP, Shabala S (2007) Compatible solute accumulation and stress-mitigating effects in barley genotypes contrasting in their salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 58:4245–4255
Chen LG, Zhang LP, Yu DQ (2010) Wounding-induced WRKY8 is involved in basal defense in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:558–565
Chen XT, Liu J, Lin GF, Wang AR, Wang ZH, Lu GD (2013) Overexpression of AtWRKY28 and AtWRKY75 in Arabidopsis enhances resistance to oxalic acid and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Cell Rep 32:1589–1599
Coll NS, Epple P, Dangl JL (2011) Programmed cell death in the plant immune system. Cell Death Differ 18:1247–1256
Dang FF, Wang YN, Yu L, Eulgem T, Lai Y, Liu ZQ, Wang X, Qiu AL, Zhang TX, Lin J, Chen YS, Guan DY, Cai HY, Mou SL, He SL (2013) CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ 36:757–774
Du MM, Zhai QZ, Deng L, Li SY, Li HS, Yan LH, Huang Z, Wang B, Jiang HL, Huang TT, Li CB, Wei JN, Kang L, Li JF, Li CY (2014) Closely related NAC transcription factors of tomato differentially regulate stomatal closure and reopening during pathogen attack. Plant Cell 26:3167–3184
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Gamboa-Melendez H, Judelson HS (2015) Development of a bipartite ecdysone-responsive gene switch for the oomycete Phytophthora infestans and its use to manipulate transcription during axenic culture and plant infection. Mol Plant Pathol 16:83–91
Gomez-Cadenas A, Verhey SD, Holappa LD, Shen Q, Ho TH, Walker-Simmons MK (1999) An abscisic acid-induced protein kinase, PKABA1, mediates abscisic acid-suppressed gene expression in barley aleurone layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:1767–1772
Gupta S, Rashotte AM (2014) Expression patterns and regulation of SlCRF3 and SlCRF5 in response to cytokinin and abiotic stresses in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). J Plant Physiol 171:349–358
Hoegen E, Stromberg A, Pihlgren U, Kombrink E (2002) Primary structure and tissue-specific expression of the pathogenesis-related protein PR-1b in potatodagger. Mol Plant Pathol 3:329–345
Huang XS, Luo T, Fu XZ, Fan QJ, Liu JH (2011) Cloning and molecular characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene from Poncirus trifoliata whose ectopic expression confers dehydration/drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot 62:5191–5206
Huang SX, Gao YF, Liu JK, Peng XL, Niu XL, Fei ZJ, Cao SQ, Liu YS (2012) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Solanum lycopersicum. Mol Genet Genomics 287:495–513
Huang YJ, Yin XR, Zhu CQ, Wang WW, Grierson D, Xu CJ, Chen KS (2013) Standard addition quantitative real-time PCR (SAQPCR): a novel approach for determination of transgene copy number avoiding PCR efficiency estimation. PLoS One 8:e53489
Hundertmark M, Hincha DK (2008) LEA (late embryogenesis abundant) proteins and their encoding genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 9:118
Irzhansky I, Cohen Y (2006) Inheritance of resistance against Phytophthora infestans in Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium L3707. Euphytica 149:309–316
Jia CG, Zhang LP, Liu LH, Wang JS, Li CY, Wang QM (2013) Multiple phytohormone signalling pathways modulate susceptibility of tomato plants to Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. J Exp Bot 64:637–650
Jiang YQ, Deyholos MK (2009) Functional characterization of Arabidopsis NaCl-inducible WRKY25 and WRKY33 transcription factors in abiotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 69:91–105
Jiang YZ, Duan YJ, Yin J, Ye SL, Zhu JR, Zhang FQ, Lu WX, Fan D, Luo KM (2014) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the Populus WRKY transcription factor family and analysis of their expression in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. J Exp Bot 65:6629–6644
Juszczuk IM, Szal B, Rychter AM (2012) Oxidation-reduction and reactive oxygen species homeostasis in mutant plants with respiratory chain complex I dysfunction. Plant Cell Environ 35:296–307
Khare N, Goyary D, Singh NK, Shah P, Rathore M, Anandhan S, Sharma D, Arif M, Ahmed Z (2010) Transgenic tomato cv. Pusa Uphar expressing a bacterial mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase gene confers abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103:267–277
Kumar AS, Lakshmanan V, Caplan JL, Powell D, Czymmek KJ, Levia DF, Bais HP (2012) Rhizobacteria Bacillus subtilis restricts foliar pathogen entry through stomata. Plant J 72:694–706
Lee HA, Kim SY, Oh SK, Yeom SI, Kim SB, Kim MS, Kamoun S, Choi D (2014) Multiple recognition of RXLR effectors is associated with nonhost resistance of pepper against Phytophthora infestans. New Phytol 203:926–938
Li JB, Luan YS (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of a pathogen-induced WRKY transcription factor gene from late blight resistant tomato varieties Solanum pimpinellifolium L3708. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 87:25–31
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331
Li J, Brader G, Kariola T, Palva ET (2006) WRKY70 modulates the selection of signaling pathways in plant defense. Plant J 46:477–491
Li JB, Luan YS, Jin H (2012) The tomato SlWRKY gene plays an important role in the regulation of defense responses in tobacco. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:671–676
Li JB, Luan YS, Yin YL (2014) SpMYB overexpression in tobacco plants leads to altered abiotic and biotic stress responses. Gene 547:145–151
Li JB, Luan YS, Liu Z (2015) Overexpression of SpWRKY1 promotes resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae and tolerance to salt and drought stress in transgenic tobacco. Physiol Plant. doi:10.1111/ppl.12315
Liu KM, Wang L, Xu YY, Chen N, Ma QB, Li F, Chong K (2007) Overexpression of OsCOIN, a putative cold inducible zinc finger protein, increased tolerance to chilling, salt and drought, and enhanced proline level in rice. Planta 226:1007–1016
Liu HX, Zhou XY, Dong N, Liu X, Zhang HY, Zhang ZY (2011) Expression of a wheat MYB gene in transgenic tobacco enhances resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum, and to drought and salt stresses. Funct Integr Genomics 11:431–443
Liu WX, Zhang FC, Zhang WZ, Song LF, Wu WH, Chen YF (2013) Arabidopsis Di19 functions as a transcription factor and modulates PR1, PR2, and PR5 expression in response to drought stress. Mol Plant 6:1487–1502
Liu B, Hong YB, Zhang YF, Li XH, Huang L, Zhang HJ, Li DY, Song FM (2014) Tomato WRKY transcriptional factor SlDRW1 is required for disease resistance against Botrytis cinerea and tolerance to oxidative stress. Plant Sci 227:145–156
Liu H, Yu CY, Li HX, Ouyang B, Wang TT, Zhang JH, Wang X, Ye ZB (2015) Overexpression of ShDHN, a dehydrin gene from Solanum habrochaites enhances tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in tomato. Plant Sci 231:198–211
McGrann GR, Steed A, Burt C, Goddard R, Lachaux C, Bansal A, Corbitt M, Gorniak K, Nicholson P, Brown JK (2015) Contribution of the drought tolerance-related stress-responsive NAC1 transcription factor to resistance of barley to Ramularia leaf spot. Mol Plant Pathol 16:201–209
Miljkovic D, Stare T, Mozetic I, Podpecan V, Petek M, Witek K, Dermastia M, Lavrac N, Gruden K (2012) Signalling network construction for modelling plant defence response. PLoS One 7:e51822
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467
Mobin M, Wu CH, Tewari RK, Paek KY (2015) Studies on the glyphosate-induced amino acid starvation and addition of precursors on caffeic acid accumulation and profiles in adventitious roots of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:291–301
Mur LA, Kenton P, Atzorn R, Miersch O, Wasternack C (2006) The outcomes of concentration-specific interactions between salicylate and jasmonate signaling include synergy, antagonism, and oxidative stress leading to cell death. Plant Physiol 140:249–262
Nowakowska M, Nowicki M, Kłosinska U, Maciorowski R, Kozik EU (2014) Appraisal of artificial screening techniques of tomato to accurately reflect field performance of the late blight resistance. PLoS One 9:e109328
Nowicki M, Fooled MR, Nowakowska M, Kozik EU (2012) Potato and tomato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans: an overview of pathology and resistance breeding. Plant Dis 96:4–17
Peng XX, Hu YJ, Tang XK, Zhou PL, Deng XB, Wang HH, Guo ZJ (2012) Constitutive expression of rice WRKY30 gene increases the endogenous jasmonic acid accumulation, PR gene expression and resistance to fungal pathogens in rice. Planta 236:1485–1498
Qiu YP, Yu DQ (2009) Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Environ Exp Bot 65:35–47
Qiu DY, Xiao J, Ding XH, Xiong M, Cai M, Cao YL, Li XH, Xu CG, Wang SP (2007) OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:492–499
Qiu DY, Xiao J, Xie WB, Liu HB, Li XH, Xiong LZ, Wang SP (2008) Rice gene network inferred from expression profiling of plants overexpressing OsWRKY13, a positive regulator of disease resistance. Mol Plant 1:538–551
Ramamoorthy R, Jiang SY, Kumar N, Venkatesh PN, Ramachandran S (2008) A comprehensive transcriptional profiling of the WRKY gene family in rice under various abiotic and phytohormone treatments. Plant Cell Physiol 49:865–879
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–258
Rushton DL, Tripathi P, Rabara RC, Lin J, Ringler P, Boken AK, Langum TJ, Smidt L, Boomsma DD, Emme NJ, Chen X, Finer JJ, Shen QJ, Rushton PJ (2012) WRKY transcription factors: key components in abscisic acid signalling. Plant Biotechnol J 10:2–11
Sathiyaraj G, Lee OR, Parvin S, Khorolragchaa A, Kim YJ, Yang DC (2011) Transcript profiling of antioxidant genes during biotic and abiotic stresses in Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Mol Biol Rep 38:2761–2769
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Segarra G, Santpere G, Elena G, Trillas I (2013) Enhanced Botrytis cinerea resistance of Arabidopsis plants grown in compost may be explained by increased expression of defense-related genes, as revealed by microarray analysis. PLoS One 8:e56075
Seo PJ, Lee AK, Xiang F, Park CM (2008) Molecular and functional profiling of Arabidopsis pathogenesis-related genes: insights into their roles in salt response of seed germination. Plant Cell Physiol 49:334–344
Shan DP, Huang JG, Yang YT, Guo YH, Wu CA, Yang GD, Gao Z, Zheng CC (2007) Cotton GhDREB1 increases plant tolerance to low temperature and is negatively regulated by gibberellic acid. New Phytol 176:70–81
Shen HS, Liu CT, Zhang Y, Meng XP, Zhou X, Chu CC, Wang XP (2012) OsWRKY30 is activated by MAP kinases to confer drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 80:241–253
Shi WN, Hao LL, Li J, Liu DD, Guo XQ, Li H (2014a) The Gossypium hirsutum WRKY gene GhWRKY39-1 promotes pathogen infection defense responses and mediates salt stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell Rep 33:483–498
Shi WN, Liu DD, Hao LL, Wu CA, Guo XQ, Li H (2014b) GhWRKY39, a member of the WRKY transcription factor family in cotton, has a positive role in disease resistance and salt stress tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 118:17–32
Shu S, Guo SR, Sun J, Yuan LY (2012) Effects of salt stress on the structure and function of the photosynthetic apparatus in Cucumis sativus and its protection by exogenous putrescine. Physiol Plant 146:285–296
Su XH, Zhou P, Wang R, Luo ZP, Xia ZL (2015) Overexpression of the maize psbA gene enhances sulfur dioxide tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:303–311
Sun H, Hu X, Ma J, Hettenhausen C, Wang L, Sun G, Wu J, Wu J (2014) Requirement of ABA signalling-mediated stomatal closure for resistance of wild tobacco to Alternaria alternata. Plant Pathol 63:1070–1077
Sun XC, Gao YF, Li HR, Yang SZ, Liu YS (2015) Over-expression of SlWRKY39 leads to enhanced resistance to multiple stress factors in tomato. J Plant Biol 58:52–60
Wang C, Deng PY, Chen LL, Wang XT, Ma H, Hu W, Yao NC, Feng Y, Chai RH, Yang GX, He GY (2013) A wheat WRKY transcription factor TaWRKY10 confers tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in transgenic tobacco. PLoS One 8:e65120
Wang Z, Fang HD, Chen Y, Chen KP, Li GY, Gu SL, Tan XL (2014a) Overexpression of BnWRKY33 in oilseed rape enhances resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol Plant Pathol 15:677–689
Wang L, Liu Y, Cai GH, Jiang SS, Pan JW, Li DQ (2014b) Ectopic expression of ZmSIMK1 leads to improved drought tolerance and activation of systematic acquired resistance in transgenic tobacco. J Biotechnol 172:18–29
Wei KF, Chen J, Chen YF, Wu LJ, Xie DX (2012) Molecular phylogenetic and expression analysis of the complete WRKY transcription factor family in maize. DNA Res 19:153–164
Wi SJ, Ji NR, Park KY (2012) Synergistic biosynthesis of biphasic ethylene and reactive oxygen species in response to hemibiotrophic Phytophthora parasitica in tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 159:251–265
Xia XJ, Wang YJ, Zhou YH, Tao Y, Mao WH, Shi K, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2009) Reactive oxygen species are involved in brassinosteroid-induced stress tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol 150:801–814
Yan HR, Jia HH, Chen XB, Hao LL, An HL, Guo XQ (2014) The cotton WRKY transcription factor GhWRKY17 functions in drought and salt stress in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana through ABA signaling and the modulation of reactive oxygen species production. Plant Cell Physiol 55:2060–2076
Yang B, Jiang Y, Rahman MH, Deyholos MK, Kav NN (2009) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in canola (Brassica napus L.) in response to fungal pathogens and hormone treatments. BMC Plant Bio 9:68
Yu FF, Huaxia YF, Lu WJ, Wu CA, Cao XC, Guo XQ (2012) GhWRKY15, a member of the WRKY transcription factor family identified from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), is involved in disease resistance and plant development. BMC Plant Biol 12:144
Yue YS, Zhang MC, Zhang JC, Tian XL, Duan LS, Li ZH (2012) Overexpression of the AtLOS5 gene increased abscisic acid level and drought tolerance in transgenic cotton. J Exp Bot 63:3741–3748
Zeng LZ, Zhou J, Li B, Xing D (2015) A high-sensitivity optical device for the early monitoring of plant pathogen attack via the in vivo detection of ROS bursts. Front Plant Sci 6:96
Zhang CZ, Liu L, Zheng Z, Sun YY, Zhou LX, Yang YH, Cheng F, Zhang ZH, Wang XW, Huang SW, Xie BY, Du YC, Bai YL, Li JM (2013) Fine mapping of the Ph-3 gene conferring resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 126:2643–2653
Zhu ZG, Shi JL, Cao JL, He MY, Wang YJ (2012) VpWRKY3, a biotic and abiotic stress-related transcription factor from the Chinese wild Vitis pseudoreticulata. Plant Cell Rep 31:2109–2120
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31272167, 31471880 and 61472061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Jb., Luan, Ys. & Liu, Z. SpWRKY1 mediates resistance to Phytophthora infestans and tolerance to salt and drought stress by modulating reactive oxygen species homeostasis and expression of defense-related genes in tomato. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 123, 67–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0815-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0815-2