Abstract
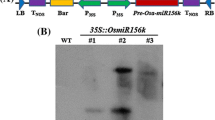
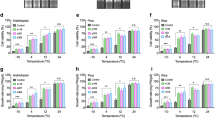
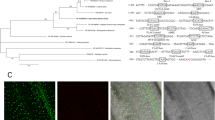
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant is sensitive to chilling, particularly at early stages of seedling development. Here a novel cold-inducible gene, designated OsCOIN (O ryza s ativa cold-inducible), was isolated and characterized. Results showed that OsCOIN protein, a RING finger protein, was localized in both nuclear and cytoplasm membrane. OsCOIN is expressed in all rice organs and strongly induced by low temperature, ABA, salt and drought. Over-expression of OsCOIN in transgenic rice lines significantly enhanced their tolerance to cold, salt and drought, accompanied by an up-regulation of OsP5CS expression and an increase of cellular proline level.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguan K, Sugawara K, Suzuki N, Kusano T (1993) Low-temperature-dependent expression of a rice gene encoding a protein with a leucine-zipper motif. Mol Gen Genet 240:1–8
Andaya VC, Mackill DJ (2003) Mapping of QTLs associated with cold tolerance during the vegetative stage in rice. J Exp Bot 54:2579–2585
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Chen JQ, Dong Y, Wang YJ, Liu Q, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2003) An AP2/EREBP-type transcription-factor gene from rice is cold-inducible and encodes a nuclear-localized protein. Theor Appl Genet 107:972–979
Dai XY, Xu YY, Ma QB, Xu WY, Wang T, Xue YB, Chong K (2007) Overexpression of an R1R2R3 MYB gene, OsMYB3R-2, increases tolerance to freezing, drought, and salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1739–1751
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SS, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S15–S45
Fukutaku Y, Yamada Y (1984) Source of proline nitrogen in water-stressed soybean (Glycine max). Part II. Fate of 15N-labeled protein. Plant Physiol 61:622–628
Ge L, Chen H, Jiang JF, Zhao Y, Xu ML, Xu YY, Tan KH, Xu ZH, Chong K (2004) Overexpression of OsRAA1 causes pleiotropic phenotypes in transgenic rice plants, including altered leaf, flower, and root development and root response to gravity. Plant Physiol 135:1502–1513
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Huang J, Wang JF, Wang QH, Zhang HS (2005) Identification of a rice zinc finger protein whose expression is transiently induced by drought, cold but not by salinity and abscisic acid. DNA Seq 16:130–136
Hur J, Jung KH, Lee CH, An GH (2004) Stress-inducible OsP5CS2 gene is essential for salt and cold tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 167:417–426
Igarashi Y, Yoshiba Y, Sanada Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Wada K, Shinozaki K (1997) Characterization of the gene for delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase and correlation between the expression of the gene and salt tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Plant Mol Biol 33:857–865
Kadpel R, Rao N (1985) Alterations in the biosynthesis of proteins and nucleic acids in finger millet (Eleucine coracana) seedlings during water stress and the effect of proline on protein biosynthesis. Plant Sci 40:73–79
Kim JC, Lee SH, Cheong YH, Yoo CM, Lee SI, Chun HJ, Yun DJ, Hong JC, Lee SY, Lim CO, Cho MJ (2001) A novel cold-inducible zinc finger protein from soybean, SCOF-1, enhances cold tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant J 25:247–259
Koorneef M, Reuling G, Karssen C (1984) The isolation and characterization of abscisic acid-insensitive mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 61:377–383
Lang V, Mantyla E, Welin B, Sundberg B, Palva ET (1994) Alterations in Water status, endogenous abscisic acid content, and expression of rab18 gene during the development of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 104:1341–1349
Leon-Kloosterziel KM, Gil MA, Ruijs GJ, Jacobsen SE, Olszewski NE, Schwartz SH, Zeevaart JA, Koornneef M (1996) Isolation and characterization of abscisic acid-deficient Arabidopsis mutants at two new loci. Plant J 10:655–661
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158
Mantyla E, Lang V, Palva ET (1995) Role of abscisic acid in drought-induced freezing tolerance, cold acclimation, and accumulation of LT178 and RAB18 proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 107:141–148
Morsy MR, Almutairi AM, Gibbons J, Yun SJ, de Los Reyes BG (2005) The OsLti6 genes encoding low-molecular-weight membrane proteins are differentially expressed in rice cultivars with contrasting sensitivity to low temperature. Gene 344:171–180
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6309–6314
Nakagahra M, Okuno K, Vaughan D (1997) Rice genetic resources: history, conservation, investigative characterization and use in Japan. Plant Mol Biol 35:69–77
Nikolopoulos D, Manetas Y (1991) Compatible solutes and in vitro stability of Salsola soda enzymes: proline incompatibility. Phytochem 30:411–413
Ohnishi T, Sugahara S, Yamada T, Kikuchi K, Yoshiba Y, Hirano HY, Tsutsumi N (2005) OsNAC6, a member of the NAC gene family, is induced by various stresses in rice. Genes Genet Syst 80:135–139
Pramanik MH, Imai R (2005) Functional identification of a trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase gene that is involved in transient induction of trehalose biosynthesis during chilling stress in rice. Plant Mol Biol 58:751–62
Rabbani MA, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan MA, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133:1755–1767
Ramanjulu S, Bartels D (2002) Drought- and desiccation-induced modulation of gene expression in plants. Plant Cell Environ 25:141–151
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Mariatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. In: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schobert B, Tschesche H (1978) Unusual solution properties of proline and its interaction with proteins. Bioch Biophys Acta 541:270–277
Shimizu H, Sato K, Berberich T, Miyazaki A, Ozaki R, Imai R, Kusano T (2005) LIP19, a basic region leucine zipper protein, is a Fos-like molecular switch in the cold signaling of rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1623–1634
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Thomashow MF (1999) Plant cold acclimation: freezing tolerance genes and regulatory mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:571–599
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11632–11637
Varagona MJ, Schmidt RJ, Raikhel NV (1992) Nuclear localization signal(s) required for nuclear targeting of the maize regulatory protein Opaque-2. Plant Cell 4:1213–1227
Venekamp JH, Lamp JE, Koot JTM (1989) Organic acids as sources of drought-induced proline synthesis in field bean plants. J Plant Physiol 133:654–659
Xiong L, Lee H, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of osmotic stress-responsive gene expression by the LOS6/ABA1 locus in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:8588–8596
Xu ML, Jiang JF, Ge L, Xu YY, Chen H, Zhao Y, Bi YR, Wen JQ, Chong K (2005) FPF1 transgene leads to altered flowering time and root development in rice. Plant Cell Rep 24:79–85
Yamada M, Morishita H, Urano K, Shiozaki N, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Yoshiba Y (2005) Effects of free proline accumulation in petunias under drought stress. J Exp Bot 56:1975–1981
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Dewang Zhou (University of Alabama at Birmingham) for critical reading and useful comments of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Program of the P.R. China (2005CB120806), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30470866) and the State High-tech Project (2006AA10Z169), as well as innovation grants of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Wang, L., Xu, Y. et al. Overexpression of OsCOIN, a putative cold inducible zinc finger protein, increased tolerance to chilling, salt and drought, and enhanced proline level in rice. Planta 226, 1007–1016 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0548-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0548-5