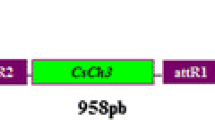
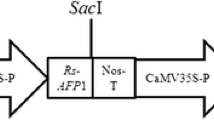
Abstract
An Agrobacterium-mediated transformation protocol for grapevine cv. Crimson Seedless using sonication and anti-necrotic agents has been optimized, and transgenic lines carrying wheat chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase genes have exhibited enhanced tolerance to downy mildew incited by Plasmopara viticola. cDNA clones encoding chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase have been isolated from a cDNA library, constructed from scab-infected Sumai-3 wheat, and introduced into a plant cloning vector to generate the plasmids pCAMBAR.chi.11 and pCAMBAR.638. Embryogenic cultures, established from in vitro-derived leaves, of Crimson Seedless were used as explants for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation studies. Sonication of somatic embryos in a bacterial suspension of A. tumefaciens and incorporation of anti-necrotic agents in the co-cultivation medium significantly enhanced transformation efficiency. Transformation efficiency of embryos with either chitinase or β-1,3-glucanase gene was highest when embryos were suspended in a bacterial cell suspension at 0.5 OD600 and sonicated for 2 or 3 s at 60 kHz. Transformation efficiency with chitinase was highest on incorporation of 2 or 3 mg l−1 phenylalanine, 1 or 2 mg l−1 silver nitrate or 400 mg l−1 l-cysteine in co-cultivation medium while incorporation of 20 mg l−1 sodium thiosulphate produced highest transformation efficiency with β-1,3-glucanase. Confirmed transgenic grapevine lines harboring anti-fungal genes exhibited higher levels of chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase transcripts as well as enzymatic activities. Moreover, transgenic lines showed enhanced tolerance to P. viticola infection following detached leaf assays.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama T, Kaku H, Shibuya N (1998) Purification, characterization and NH2-terminal sequencing of an endo-(1-3,1-4)-β-glucanase from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 134:3–10
Armstrong CL, Rout JR (2001) A novel Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation method. Int Patent Publ WOO1/09302 A2
Baribault TJ, Skene KGM, Cain PA, Scott NS (1990) Transgenic grapevines: regeneration of shoots expressing beta-glucuronidase. J Exp Bot 41:1045–1049
Beyer EM (1976) A potent inhibitor of ethylene action in plants. Plant Physiol 58:268–271
Bornhoff BA, Harst M, Zyprian E, Topfer R (2005) Transgenic plants of Vitis vinifera cv. Seyval blanc. Plant Cell Rep 24:433–438
Brown MV, Moore JN, Fenn P, McNew RW (1999) Evaluation of grape germplasm for downy mildew resistance. Fruit Var J 53:22–29
Chhikara S, Chaudhury D, Dhankher OP, Jaiwal PK (2012) Combined expression of a barley class II chitinase and type I ribosome inactivating protein in transgenic Brassica juncea provides protection against Alternaria brassicae. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:83–89
Christou P (1996) Electric discharge particle acceleration (Accell®) technology for the creation of transgenic plants with altered characteristics. Field Crops Res 45:143–151
Coutos-Thevenot P, Poinssot B, Bonomelli A, Yean H, Breda C, Buffard D, Esnault R, Hain R, Boulay M (2001) In vitro tolerance to Botrytis cinerea of grapevine 41B rootstock in transgenic plants expressing the stilbene synthase Vst1 gene under the control of a pathogen-inducible PR 10 promoter. J Exp Bot 52:901–910
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1–42
Dutt M, Vasconcellos M, Grosser JW (2011) Effects of antioxidants on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and accelerated production of transgenic plants of Mexican lime (Citrus aurantifolia Swingle). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107:79–89
Enriquez-Obregon GA, Prieto-Sansonov DL, de la Riva GA, Perez M, Selman-Housein G, Vazquez-Padron RI (1999) Agrobacterium-mediated Japonica rice transformation: procedure assisted by an anti-necrotic treatment. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 59:159–168
Frame BR, Shou H, Chikwamba R, Zhang Z, Xiang C, Fonger T, Pegg SE, Li B, Nettleton D, Pei D, Wang K (2002) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of maize embryos using a standard binary vector system. Plant Physiol 129:13–22
Ganesan M, Bhanumathi P, Ganesh Kumari K, Lakshmi Prabha A, Song P-S, Jayabalan N (2009) Transgenic Indian cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) harboring rice chitinase gene (Chi II) confers resistance to two fungal pathogens. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 5:63–74
Giannakis C, Bucheli CS, Skene KGM, Robinson SP, Steele SN (1998) Chitinase and B-l,3-glucanase in grapevine leaves: a possible defense against powdery mildew infection. Aust J Grape Wine Res 4:14–22
Gustavo AR, Gonzalez-Cabrera J, Vazquez-Padron R, Ayra-Pardo C (1998) Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a natural tool for plant transformation. Electron J Biotechnol 1:1–15
Harborne JB (1988) The flavonoids: advances in research. Chapman & Hall, London
Heath MC (2000) Non-host resistance and nonspecific plant defenses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:315–319
Imota T, Yagishita L (1971) A simple activity measurement of lysozyme. Agric Biol Chem 35:1154–1156
Iocco P, Franks T, Thomas MR (2001) Genetic transformation of major wine grape cultivars of Vitis vinifera L. Transgenic Res 10:105–112
Kikkert JK, Ali GS, Wallace PG, Reustle GM, Reisch B (2000) Expression of fungal chitinase in Vitis vinifera L. ‘Merlot’ and ‘Chardonnay’ plants produced by biolistic transformation. Acta Hortic 528:297–303
Kumar V, Sharma A, Prasad BCN, Gururaj HB, Ravishankar GA (2006) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated genetic transformation resulting in hairy root formation is enhanced by ultrasonication and acetosyringone treatment. Electron J Biotechnol 9:349–357
Kwapata K, Sabzikar R, Sticklen MB, Kelly JD (2010) In vitro regeneration and morphogenesis studies in common bean. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100:97–105
Li WL, Faris JD, Muthukrishnan S, Liu DJ, Chen PD, Gill BS (2001) Isolation and characterization of novel cDNA clones of acidic chitinases and β‐1,3‐glucanases from wheat spikes infected with Fusarium graminearium. Theor Appl Genet 102:353–362
Li JT, Dhenkey SA, Dutt M, van Aman M, Tattersaki J, Kelley KT (2006) Optimizing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of grapevine. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:220–227
Li JT, Dhekney SA, Dutt M, Gray DJ (2008) An improved protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of grapevine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 93:311–321
Llyod G, McCown B (1981) Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot tip culture. Int Plant Prop Soc Proc 30:421–427
Lodhi MA, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars and Vitis species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:6–13
Lopez-Perez AJ, Velasco L, Pazos-Navarro M, Dabauza M (2008) Development of highly efficient genetic transformation protocols for table grape Sugraone and Crimson Seedless at low Agrobacterium density. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 94:189–199
Lorence A, Chevone BI, Mendes P, Nessler CL (2004) myo-inositol oxygenase offers a possible entry point into plant ascorbate biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 134:1200–1205
Mayer AM, Harel E (1979) Polyphenol oxidases in plants. Phytochem 18:193–215
Mehdy MC (1994) Active oxygen species in plant defense against pathogens. Plant Physiol 105:467–472
Mondal KK, Bhattacharya RC, Koundal KR, Chatterjee SC (2007) Transgenic Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) expressing tomato glucanase leads to arrested growth of Alternaria brassicae. Plant Cell Rep 26:247–252
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Negishi O, Ozawa T (2000) Inhibition of enzymatic browning and protection of sulfhydryl enzymes by thiol compounds. Phytochem 54:481–487
Nirala NK, Das DK, Srivatsava PS, Sopory SK, Upadhyaya KC (2010) Expression of a rice chitinase gene enhances antifungal potential in transgenic grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Vitis 49(4):181–187
Nishizawa Y, Saruta M, Nakazono K, Nishio Z, Soma M, Yoshida T, Nakajima E, Hibi T (2003) Characterization of transgenic rice plants over-expressing the stress-inducible β-glucanase gene Gns1. Plant Mol Biol 51:143–152
Nookaraju A, Barreto MS, Agrawal DC (2008) Rapid in vitro propagation of grapevine cv. Crimson Seedless—influence of basal media and plant growth regulators. J Appl Hort 10:44–49
Olhoft PM, Somers DA (2001) l-Cysteine increases Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA delivery into soybean cotyledonary-node cells. Plant Cell Rep 20:706–711
Olhoft PM, Lin K, Galbraith J, Nielsen NC, Somers DA (2001) The role of thiol compounds in increasing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean cotyledonary-node cells. Plant Cell Rep 20:731–737
Olhoft PM, Flagel LE, Donovon CM, Somers DA (2003) Efficient soybean transformation using hygromycin B selection in the cotyledonary-node method. Planta 216:723–735
Parimalan R, Giridhar P, Ravishankar GA (2011) Enhanced shoot organogenesis in Bixa orellana L. in the presence of putrescine and silver nitrate. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:285–290
Paz MM, Shou H, Guo Z, Zhang Z, Banerjee AK, Wang K (2004) Assessment of conditions affecting Agrobacterium-mediated soybean transformation using the cotyledonary node explant. Euphytica 136:167–179
Perl O, Lotan O, Abu-Abied M, Holland D (1996) Establishment of an Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system for grape (Vitis vinifera L.): the role of antioxidants during grape-Agrobacterium interactions. Nat Biotechnol 14:624–628
Richard-Forget FC, Goupy PM, Nicolas JJ (1992) Cysteine as an inhibitor of enzymatic browning. 2. Kinetic studies. J Agric Food Chem 40:2108–2113
Sakihama Y, Mano J, Sano S, Asada K, Yamasaki H (2000) Reduction of phenoxyl radicals mediated by monodehydroascorbate reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279:949–954
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Santarem ER, Trick HN, Essig JS, Finer JJ (1998) Sonication assisted Agrobacterium mediated transformation of soybean immature cotyledons: optimization of transient expression. Plant Cell Rep 17:752–759
Vamos-Vigyazo L (1981) Polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase in fruits and vegetables. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 15:49–127
Vishnevetsky J, White TL Jr, Palmateer AJ, Flaishman M, Cohen Y, Elad Y, Velcheva M, Hanania U, Sahar N, Dgani O, Perl A (2011) Improved tolerance toward fungal diseases in transgenic Cavendish banana (Musa spp. AAA group) cv. Grand Nain. Transgenic Res 20:61–72
Yamamoto T, Iketani H, Ieki H, Nishizawa Y, Notsuka K, Hibi T, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2000) Transgenic grapevine plants expressing a rice chitinase with enhanced resistance to fungal pathogens. Plant Cell Rep 19:639–646
Zhao Z-Y, Gu W, Cai T, Tagliani L, Hondred D, Bond D, Schroeder S, Rudert M, Pierce D (2001) High throughput genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in maize. Mol Breed 8:323–333
Zhu Q, Maher EA, Masoud S, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ (1994) Enhanced protection against fungal attack by constitutive co-expression of chitinase and glucanase genes in transgenic tobacco. Bio/Technol 12:807–812
Acknowledgments
Financial support in the form of Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Govt. of India to Nookaraju and supply of chitinase and glucanase vectors by Dr. Muthukrishnan Subbarat, Professor in Biochemistry, Kansas State University are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nookaraju, A., Agrawal, D.C. Enhanced tolerance of transgenic grapevines expressing chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase genes to downy mildew. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 111, 15–28 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0166-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0166-1