Abstract
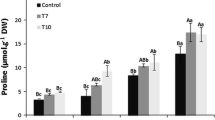
To develop salt tolerant rice, the P5CS gene of Vigna aconitifolia, encoding for proline synthesis, was introduced into the popular indica rice cultivar ADT 43. Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA 4404 harboring the binary vector pCAMBIA 1301/P5CS, carrying the proline synthesis encoding gene P5CS, was co-cultivated with embryogenic callus of rice. Adding 100 μM acetosyringone to the Linsmaier and Skoog (LS) liquid and solid co-culture medium, along with 30 mg/l hygromycin and 250 mg/l timentin, contributed to significantly higher efficiency of transformation. Southern blot analysis of T1 independent transformants revealed that the copy number of transgene varied between one and three. When transgenic plants were subjected to salt stress, these plants grew well in the presence of up to 200 mM NaCl, while control plants died within 10 days under these treatment conditions. These transgenic plants grew under salt stress for a period of 4 weeks, and were capable of flowering and set seed. T1 plants segregated into 3:1 ratio suggesting Mendelian segregation pattern of inheritance of the P5CS transgene.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P5CS:
-
Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase
- BA:
-
N6-Benzyladenine
- LS:
-
Linsmaier and Skoog medium
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- NAA:
-
Naphthalene acetic acid
- (HPT):
-
Hygromycin phosphotransferase
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4- Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Abraham E, Rigo G, Szekely G, Nagy R, Koncz C, Szabados L (2003) Light-dependent induction of proline biosynthesis by abscisic acid and salt stress is inhibited by brassinosteroid in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 51:363–372
Anoop N, Gupta AK (2003) Transgenic indica rice cv IR-50 overexpressing Vigna aconitifolia δ(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase cDNA shows tolerance to high salt. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 12:109–116
Bais HP, George J, Ravishankar GA (1999) Influence of polyamines on growth of hairy root cultures of witloof chicory (Cichorium intybus L. cv. Lucknow Local) and formation of coumarins. J Plant Growth Regul 18:33–37
Bajaj S, Targolli J, Liu LF, Ho THD, Wu R (1999) Transgenic approaches to increase dehydration-stress tolerance in plants. Mol Breed 5:493–503
Barrett C, Cassells AC (1994) An evaluation of antibiotics for the elimination of Xanthomonas campestris pv. Pelargonii (Brown) from Pelargonium x domesticum cv. ‘Grand Slam’ explant in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 36:169–175
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water studies. Plant Soil 39:205–208
Bray E (1993) Molecular responses to water deficit. Plant Physiol 103:1035–1040
Carlos Henrique SC, Usha BZ, Nilupa G, Joseph A, Halina HK, Thomas KH, John DA (2004) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of sorghum; factors that affect transformation efficiency. Genet Mol Biol 27:259–269
Chern MS, Fitzgerald HA, Yadav RC, Canlas PE, Dong X, Ronald PC (2001) Evidence for disease-resistance pathway in rice similar to the NPR1-mediated signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J 27:101–113
Data SK (2002) Recent developments in transgenics for abiotic stress tolerance in rice. JIRCAS Working Report. pp 43–53
Diah R, Takehiko H, Eiichi I, Hiroyuki A (2004) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of javanica rice cv. Rojolele. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:1193–1200
Eapen S, George L (1990) Influence of phytohormones, carbohydrates, aminoacids, growth supplements and antibiotics on somatic embryogenesis and plant differentiation in finger millet. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 22:87–93
Estopa M, Marfa V, Mele E, Messeguer J (2001) Study of different antibiotic combinations for use in the elimination of Agrobacterium with kanamycin selection in carnation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 65:211–220
Garg AK, Kim JK, Owens TG, Ranwala AP, Choi YC, Kochian LV, Wu RJ (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:15898–15903
Godwin ID, Ford-Lloyd BV, Newbury HJ (1992) In vitro approaches to extending the host-range of Agrobacterium for plant transformation. Aust J Bot 40:751–763
Hauptmann RM, Vasil V, Ozias-Akin P, Tabaeizadeh Z, Roger G, Fraley RT, Horch RB, Vasil IR (1988) Evaluation of selectable marker for obtaining stable transformation in the Gramineae. Plant Physiol 86:602–606
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Hmida-Sayari A, Gargouri-Bouzid R, Bidani A, Jaoua L, Savoure A, Jaoua S (2005) Overexpression of Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers salt tolerance in transgenic potato plants. Plant Sci 169:746–752
Ilag LL, Yadav RC, Huang N, Ronald PC, Ausubel FM (2000) Isolation and characterization of disease resistance gene homologous from rice cultivar IR64. Gene 255:245–255
Jogeswar G, Pallela R, Jakka NM, Reddy PS, Rao JV, Sreeniwasulu N, Kavi Kishor PB (2006) Antioxidative response in different sorghum species under short term salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 28:465–475
Karthikeyan A, Karutha Pandian S, Ramesh M (2009) High frequency plant regeneration from embryogenic callus of a popular indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 15:371–375
Katiyar SK, Chandel G, Singh P, Pratibha R (1999) Genetic variation and effect of 2, 4- D in in vitro plant regeneration in indica rice cultivars. Oryza 36:254–256
Kerven GL, Asher AJ, Edward DG, Ostatek BZ (1991) Sterile solution culture technique for aluminium toxicity studies involving organic acids. J Plant Nutrit 14:975–986
Kumar SG, Reddy AM, Sudhakar C (2003) NaCl effects on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) with contrasting salt tolerance. Plant Sci 165:1245–1251
Kumar KK, Maruthasalam S, Loganathan M, Sudhakar D, Balasubramanian P (2005) An improved Agrobacterium-mediated transformation protocol for recalcitrant elite indica rice cultivars. Plant Mol Biol Rep 23:67–73
Kumar V, Shriram V, Kavi Kishor PB, Jawali N, Shitole MG (2009) Enhanced proline accumulation and salt stress tolerance of transgenic indica rice by over-expressing P5CSF129A gene. Plant Biotechnol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11816-009-0118-3
Lin YJ, Zhang QF (2005) Optimizing the tissue culture conditions for high efficiency transformation of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 23:540–547
Ling HQ, Kirseleit D, Ganal MW (1998) Effect of ticarcillin/potassium clavulanate on callus growth and shoot regeneration in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill). Plant Cell Rep 17:843–847
Linsmaier EM, Skoog F (1965) Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 18:100–127
Matysik J, Bhalu AB, Mohanty P (2002) Molecular mechanisms of quenching of reactive oxygen species by proline under stress in plants. Curr Sci 82:525–532
Misra N, Gupta A (2005) Effect of salt stress on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of green gram. Plant Sci 169:331–339
Mohammad HK, Hamid R, Zahoor Swati A, Zubeda C (2007) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation to build resistance against bacterial blight in rice. Pak J Bot 39:1285–1292
Mohanty A, Kathuria H, Ferjani A, Sakamoto A, Mohanty P, Murata N, Tyagi AK (2002) Transgenic plants of an elite indica rice variety Pusa Basmati 1 harbouring the codA gene are highly tolerant to salt stress. Theor Appl Genet 106:51–57
Molinari HBC, Marur CJ, Filho JCB, Kobayashi AK, Pileggi M, Junior RPL, Pereira LFP, Vieira LGE (2004) Osmotic adjustment in transgenic citrus rootstock Carrizo citrange (Citrus sinensis Osb. X Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf.) overproducing proline. Plant Sci 167:1375–1381
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of higher molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nauerby B, Billing K, Wyndaele R (1997) Influence of the antibiotic timentin on plant regeneration compared to carbenicillin and cefotaxime in concentration suitable for elimination of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Sci 123:169–177
Okkels FT, Pedersen MG (1988) The toxicity to plant tissue and to Agrobacterium tumefaciens of some antibiotics. Acta Hortic 225:199–207
Ozawa K (2009) Eatablishment of a high efficiency Agrobacterium–mediated transformation system of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 176:522–527
Park SH, Pinson SMR, Smith RH (1996) T-DNA integration into genomic DNA of rice following Agrobacterium tumefaciens inoculation of isolated shoot apices. Plant Mol Biol 32:1135–1148
Pileggi M (2002) Genetic transformation of the lettuce cultivar Grand Rapids (Lectuca sativa L.) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens to improve osmotic stress tolerance. Gen Mol Res 1:176
Pius J, George G, Eapen S, Rao PS (1993) Enhanced plant regeneration in pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum) by ethylene inhibitor and cefotaxime. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 32:91–96
Predieri S, Fabbri F, Malavasi F (1989) High frequency shoot regeneration from leaves of the apple rootstock M26 (Malus pumila Mill.). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 17:133–142
Qiao G, Zhou J, Jiang J, Sun Y, Pan L, Song H, Jiang J, Zhuo R, Wang X, Sun Z (2010) Transformation of Liquidambar formosana L. via Agrobacterium tumefaciens using a mannose selection system and recovery of salt tolerant lines. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 102:163–170
Rashid H, Shuuji Y, Kinya T, Kokichi H (1996) Transgenic plant production mediated by Agrobacterium in indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 15:727–730
Saharan V, Yadav RC, Yadav NR, Chapagain BP (2004) High frequency plant regeneration from desiccated calli of indica rice. Afr J Biotechnol 3:256–575
Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Agarwal S, Meena RC (2005) Differences in response to salinity stress in tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes. Biol Plant 49:85–91
Sawahel WA, Hassan AH (2002) Generation of transgenic wheat plants producing high levels of the osmoprotectant proline. Biotech Lett 24:721–725
Selvaraj KN, Ramasamy C (2006) Drought, agricultural risk and rural income case of water limiting rice production environment. Econ Politic Week 2739
Shehata AM, Wannarat W, Skirvin RM, Norton MA (2010) The dual role of carbenicillin in shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis of horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 102:397–402
Somboonwatthanaku I, Dorling S, Leung S, McManus MT (2010) Proline biosynthetic gene expression in tissue cultures of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to saline treatment. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103:369–376
Sridevi G, Dhandapani M, Veluthambi K (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of white ponni, a non-basmati variety of indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr Sci 88:128–132
Strizhov N, Abraham E, Okresz L, Blickling S, Zilberstein A, Schell J, Koncz C, Szabados L (1997) Differential expression of two P5CS genes controlling proline accumulation during salt-stress requires ABA and is regulated by ABA1, ABI1 and AXR2 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 12:557–569
Su J, Wu R (2004) Stress-inducible synthesis of proline in transgenic rice confers faster growth under stress conditions than that with constitutive synthesis. Plant Sci 166:941–948
Tang W, Luo H, Ronald Newton J (2004) Effects of antibiotics on the elimination of Agrobacterium tumefaciens from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) zygotic embryo explants and on transgenic plant regeneration. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 70:71–81
Terada R, Asao H, Iida A (2004) A large–scale Agrobacterium–mediated transformation procedure with a strong positive–negative selection for gene targeting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 22:653–659
Tyagi H, Rajasubramaniam S, Dasgupta I (2007) Regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of a popular indica rice variety ADT 39. Curr Sci 93:678–683
Vendruscolo ECG, Schuster I, Pileggi M, Scapim CA, Molinari HBC, Marur CJ, Vieira LGE (2007) Stress-induced synthesis of proline confers tolerance to water deficit in transgenic wheat. J Plant Physiol 164:1367–1376
Yamchi A, Rastgar Jazii F, Mousavi A, Karkhane AA, Renu S (2007) Proline accumulation in transgenic tobacco as a result of expression of the Arabidopsis Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) during osmotic stress. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 16:9–15
Yoshiba Y, Kiyosue T, Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1997) Regulation of levels of proline as an osmolyte in plants under water stress. Plant Cell Physiol 38:1095–1102
Zaidi MA, Narayanan M, Sardana R, Taga I, Postel S, Johns R, McNulty M, Mottiar Y, Mao J, Loit E, Altosaar I (2006) Optimizing tissue culture media for efficient transformation of different indica rice genotypes. Agron Res 4:563–575
Zhu BC, Su J, Chan MC, Verma DPS, Fan YL, Wu R (1998) Overexpression of a Delta (1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene and analysis of tolerance to water- and salt-stress in transgenic rice. Plant Sci 139:41–48
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research grant from University Grants Commission, Govt. of India, New Delhi [F.No.34-251/2008(SR)]. A. Karthikeyan is grateful to University Grants Commission for the award of UGC Research Fellowship in Sciences for Meritorious Students (RFSMS) (F.4-3/2007(BSR)/11-61/2008). The authors gratefully acknowledge the use of the Bioinformatics Infrastructure facility, Alagappa University funded by the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and technology, Government of India (No. BT/BI/25/001/2006). The strains DH5α and Agrobacterium strain EHA 105 harbouring the binary plasmid pCAMBIA 1301and plasmid pUbP5CS were kindly provided by Dr. K. Veluthambi and Dr. A. K. Gupta (Department of Plant Biotechnology, School of Biotechnology, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India), respectively. The strain LBA 4404 was kindly provided by Dr. P. Balasubramanian, Centre for Plant Molecular Biology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. We also thank Prof. A. Ganapathi for allowing us to perform non-radioactive Southern blot analysis and K. Subramanyam for technical support at Department of Biotechnology, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karthikeyan, A., Pandian, S.K. & Ramesh, M. Transgenic indica rice cv. ADT 43 expressing a Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) gene from Vigna aconitifolia demonstrates salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 107, 383–395 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9989-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9989-4