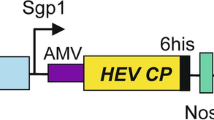
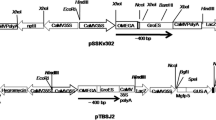
Abstract
Plants can be used as cost effective systems for the production of therapeutic proteins, including recombinant vaccines. Tobacco leaf discs were transformed with four different expression cassettes harboring hepatitis B virus ‘s’ gene encoding surface antigen. The transgenic plants accumulated varied levels of antigen. The transgenic nature of the plants and expression of the antigen was confirmed by PCR and PCR-Southern analysis and reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. The expression levels were determined by ELISA and the maximum expression levels (19.4 ng g−1 F.W. of leaves) was observed in pEFEHBS transformed plants using polyclonal antibodies whereas, monoclonal antibodies based ELISA analysis showed maximum expression (9.5 ng g−1 F.W. of leaves) in pEFEHER transformed plants. The expression levels of pEFEHBS and pEFEHER transformed plants were more in plantlets than those grown in green house. Higher proportion of the particulate form of antigen was observed when it was expressed with a C-terminal ER retention signal. Wounding of the leaves enhanced the HBsAg expression by 3.12-fold in pHBS transformed plants. The expression of HBsAg was also noted in flower buds and seeds of the transgenic plants. This is the first report on the expression of HBsAg in tobacco seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzylaminopurine
- CTAB:
-
cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide
- EFE:
-
ethylene forming enzyme
- ELISA:
-
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
- HBsAg:
-
hepatitis B surface antigen
- NAA-α:
-
naphthalene acetic acid
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
References
Biddington NL, (1992) The influence of ethylene in plant tissue culture Plant Growth Regul. 11:173–187
Bruyns AM, de Jaeger G, de Neve M, de Wilde C, van Montagu M, Depicker A, (1996) Bacterial and plant-produced scFv proteins have similar antigen-binding properties FEBS Lett. 386:5–10
Cramer CL, Boothe JG, Oishi KK, (1999) Transgenic plants for therapeutic proteins: linking upstream and down stream strategies In: Hammond J, Mc Garvey P, Yusibov V, (eds). Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, Plant Biotechnology: New Products and Applications Springer-verlag Berlin, 95–118
Fiedler U, Phillips J, Artsaenko O, Conrad U, (1997) Optimization of scFv production in transgenic plants Immunotechnology 3:205–216
Fischer R, Schillberg S, Emans N, (2000) Toward molecular farming of therapeutics in plants In: Arencibia AD, (eds). Plant Genetic Engineering: Towards the Third Millennium Elsevier Science B.V, 229–238
Gomez RL, Campbell A, Dong JG, Yang SF, Lim MAG, (1997) Ethylene biosynthesis in banana fruit: isolation of a genomic clone to ACC oxidase and expression studies Plant Sci. 123:123–131
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekama A, (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmid for gene transfer to plant cells Transgenic Res. 2:208–218
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT, (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants Science 227:1229–1231
Ituriaga G, Jefferson RA, Bevan M, (1989) Endoplasmic reticulum targeting and glycosylation of hybrid proteins in transgenic tobacco Plant Cell 1:381–390
Kapusta J, Modelska A, Figlerowicz M, Pniewski T, Letellier M, Lisowa O, Yusibov V, Koprowski H, Plucienniczak A, Legocki AB, (1999) A plant derived edible vaccine against hepatitis B virus FASEB J. 13:1796–1799
Kong Q, Richter L, Yang YF, Arntzen CJ, Mason HS, Thanavala Y, (2001) Oral immunization with hepatitis B surface antigen expressed in transgenic plants Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 98:11539–11544
Mason HS, Arntzen CJ, (1995) Transgenic plants as vaccine production systems Trends in Biotech. 13:388–392
Mason HS, Lam DMK, Arntzen CJ, (1992) Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in transgenic plants Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 89:11745–11749
Murashige T, Skoog F, (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures Physiol. Plant 15:473–497
Pelham HRB, (1990) The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum TIBS 15:483–486
Richter LJ, Thanavala Y, Arntzen CJ, Mason HS, (2000) Production of hepatitis B surface antigen in transgenic plants for oral immunization Nat. Biotechnol. 18:1167–1171
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T, (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Schouten A, Roosien J, Van Engelen FA, de Jong GAM, Borst Vrenssen AWM, Zilverentant JF, Bosch D, Stiekema WJ, Gommers FJ, Schots A, Bakker J, (1996) The C-terminal KDEL sequence increases the expression level of a single chain antibody designed to be targeted to both the cytosol and the secretory pathway in transgenic tobacco Plant Mol. Biol. 30:781–793
Smith ML, Keegan ME, Mason HS, Schuler ML, (2002) Factors important in the extraction, stability and in vitro assembly of the hepatitis B surface antigen derived from recombinant plant systems Biotechnol. Prog. 18:538–550
Smith ML, Richter L, Arntzen CJ, Schuler ML, Mason HS, (2003) Structural characterization of plant-derived hepatitis B surface antigen employed in oral immunization studies Vaccine 21:4011–4021
Stewart CN Jr., Via LE, (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique for RAPD finger print and other PCR applications Biotechniques 14:748–750
Stoger E, Ma JK, Fischer R, Christou P, (2005) Sowing the seeds of success: pharamaceutical proteins from plants Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 16:1–7
Sunil Kumar GB, Ganapathi TR, Revathi CJ, Prasad KSN, Bapat VA, (2003a) Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in tobacco cell suspension cultures Protein Expr. Purif. 32:10–17
Sunil Kumar GB, Ganapathi TR, Revathi CJ, Prasad KSN, Bapat VA, (2003b) Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in transgenic banana plants and NT-I cell line of tobacco BARC News Lett. 237:85–96
Thanavala Y, Yang YF, Lyons P, Mason HS, Arntzen CJ, (1995) Immunogenicity of transgenic plant-derived hepatitis B surface antigen Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 92:3358–3361
Thanavala Y, Mahoney M, Pal S, Scott A, Richter L, Natarajan N, Goodwin P, Arntzen CJ, Mason HS, (2005) Immunogenicity in humans of an edible vaccine for hepatitis B Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 102:3378–3382
Acknowledgement
Authors thank Shantha Biotechnics Ltd, Hyderabad for providing the pBR322 plasmid with HBV genome to clone the ‘s’ gene of the HBsAg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, G.S., Srinivas, L., Ganapathi, T. et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen expression in transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants using four different expression cassettes. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 84, 315–323 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-005-9040-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-005-9040-8