Abstract
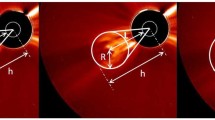
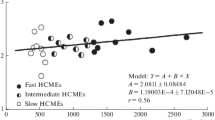
A proper characterization of the kinematics of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) is important not only for practical purposes, i.e. space weather forecasting, but also to improve our current understanding of the physics behind their evolution in the middle corona and into the heliosphere. The first and core step toward this goal is the estimation of the three main components of the CME speeds, namely the expansion speed relative to the center of motion in both, the radial and lateral directions, and the propagation speed (i.e. \(V_{\mathrm{front}}\), \(V_{\mathrm{lat}}\), \(V_{\mathrm{bulk}}\), respectively). To this aim, we exploit the observations obtained with COR2 onboard the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) from 2007 to 2014 to investigate the relationships among the different components as a function of the heliocentric distance of the CME events. Here, we analyze a sample of 475 CMEs. The selected events exhibit clear flux rope signatures as seen either edge on (i.e. F-CMEs: three-part structure, presence of a cavity) or face on (i.e. L- or loop CMEs) in white light images. Our main findings are: i) L-CMEs show almost twice as large expansion speeds compared to F-CMEs (\(V_{\mathrm {front},\mathrm{L}}=367~\mbox{km}\,\mbox{s}^{-1}\), \(V_{\mathrm{lat},\mathrm{L}}=365~\mbox{km}\,\mbox{s}^{-1}\) vs. \(V_{\mathrm{front},\mathrm{F}}=215~\mbox{km}\,\mbox{s}^{-1}\), \(V_{\mathrm{lat},\mathrm{F}}= 182~\mbox{km}\,\mbox{s}^{-1}\)); ii) the relationship between the two components of the expansion speeds is linear and does not change with height; iii) the ratio of the propagation speed to the lateral expansion speed is a function of the angular width that describes the self-similarity evolution of a CME; and iv) 65% of the CMEs exhibit a self-similar evolution at 10 solar radii, reaching 70% at 15 solar radii.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balmaceda, L.A., Vourlidas, A., Stenborg, G., Dal Lago, A.: 2018, How reliable are the properties of coronal mass ejections measured from a single viewpoint? Astrophys. J. 863(1), 57. DOI. ADS.
Braga, C.R., Dal Lago, A., Stenborg, G.: 2013, Pseudo-automatic characterization of the morphological and kinematical properties of coronal mass ejections using a texture-based technique. Adv. Space Res. 51, 1949. DOI. ADS.
Braga, C.R., Dal Lago, A., Echer, E., Stenborg, G., Rodrigues Souza de Mendonça, R.: 2017, Pseudo-automatic determination of coronal mass ejections’ kinematics in 3D. Astrophys. J. 842, 134. DOI. ADS.
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M.V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Bedford, D.K., Eyles, C.J.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357. DOI. ADS.
Colaninno, R.C., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Analysis of the velocity field of CMEs using optical flow methods. Astrophys. J. 652(2), 1747. DOI. ADS.
Cremades, H., Iglesias, F.A., Merenda, L.A.: 2020, Asymmetric expansion of coronal mass ejections in the low corona. Astron. Astrophys. 635, A100. DOI. ADS.
Dal Lago, A., Vieira, L.E.A., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., de Gonzalez, A.L.C., Guarnieri, F.L., Schuch, N.J., Schwenn, R.: 2004, Comparison between halo CME expansion speeds observed on the sun, the related shock transit speeds to Earth and corresponding ejecta speeds at 1 au. Solar Phys. 222, 323. DOI. ADS.
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2009, Causes and consequences of magnetic cloud expansion. Astron. Astrophys. 498(2), 551. DOI. ADS.
Démoulin, P., Vourlidas, A., Pick, M., Bouteille, A.: 2012, Initiation and development of the white-light and radio coronal mass ejection on 2001 April 15. Astrophys. J. 750(2), 147. DOI. ADS.
Domingo, V., Fleck, B., Poland, A.I.: 1995, The SOHO mission: an overview. Solar Phys. 162, 1. DOI. ADS.
Fox, N.J., Velli, M.C., Bale, S.D., Decker, R., Driesman, A., Howard, R.A., Kasper, J.C., Kinnison, J., Kusterer, M., Lario, D., Lockwood, M.K., McComas, D.J., Raouafi, N.E., Szabo, A.: 2016, The Solar Probe Plus mission: humanity’s first visit to our star. Space Sci. Rev. 204(1-4), 7. DOI.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.L.: 2008, Coronal mass ejections, type II radio bursts, and solar energetic particle events in the SOHO era. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3033. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Dal Lago, A., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2009, The expansion and radial speeds of coronal mass ejections. Cent. Eur. Astrophys. Bull. 33, 115. ADS.
Goussies, N., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.: 2010, Tracking of coronal white-light events by texture. Solar Phys. 262, 481. DOI. ADS.
Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, The large-scale structure of the heliospheric current sheet during the ULYSSES epoch. Space Sci. Rev. 72(1-2), 137. DOI. ADS.
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., Thompson, W.T., St Cyr, O.C., Mentzell, E., Mehalick, K., Lemen, J.R., Wuelser, J.P., Duncan, D.W., Tarbell, T.D., Wolfson, C.J., Moore, A., Harrison, R.A., Waltham, N.R., Lang, J., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Mapson-Menard, H., Simnett, G.M., Halain, J.P., Defise, J.M., Mazy, E., Rochus, P., Mercier, R., Ravet, M.F., Delmotte, F., Auchere, F., Delaboudiniere, J.P., Bothmer, V., Deutsch, W., Wang, D., Rich, N., Cooper, S., Stephens, V., Maahs, G., Baugh, R., McMullin, D., Carter, T.: 2008, Sun Earth connection coronal and heliospheric investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67. DOI. ADS.
Isavnin, A., Vourlidas, A., Kilpua, E.K.J.: 2014, Three-dimensional evolution of flux-rope CMEs and its relation to the local orientation of the heliospheric current sheet. Solar Phys. 289(6), 2141. DOI. ADS.
Kahler, S.W., Vourlidas, A.: 2005, Fast coronal mass ejection environments and the production of solar energetic particle events. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S01. DOI
Korreck, K.E., Szabo, A., Chinchilla, T.N., Lavraud, B., Luhmann, J., Niembro, T., Higginson, A., Alzate, N., Wallace, S., Paulson, K., Rouillard, A., Kouloumvakos, A., Poirier, N., Kasper, J.C., Case, A.W., Stevens, M.L., Bale, S.D., Pulupa, M., Whittlesey, P., Livi, R., Goetz, K., Larson, D., Malaspina, D.M., Morgan, H., Narock, A.A., Schwadron, N.A., Bonnell, J., Harvey, P., Wygant, J.: 2020, Source and propagation of a streamer blowout coronal mass ejection observed by the Parker Solar Probe. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 246(2), 69. DOI. ADS.
Kouloumvakos, A., Patsourakos, S., Hillaris, A., Vourlidas, A., Preka-Papadema, P., Moussas, X., Caroubalos, C., Tsitsipis, P., Kontogeorgos, A.: 2013, CME expansion as the driver of metric type II shock emission as revealed by self-consistent analysis of high-cadence EUV images and radio spectrograms. Solar Phys. 289(6), 2123. DOI.
Low, B.C.: 1984, Self-similar magnetohydrodynamics - part four - the physics of coronal transients. Astrophys. J. 281, 392. DOI. ADS.
Low, B.C., Hundhausen, A.J.: 1987, The velocity field of a coronal mass ejection: the event of September 1, 1980. J. Geophys. Res. 92(A3), 2221. DOI. ADS.
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2016, The radial speed-expansion speed relation for Earth-directed CMEs. Space Weather 14, 368. DOI. ADS.
Michalek, G., Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2009, Expansion speed of coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 260, 401. DOI. ADS.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Vourlidas, A., Raymond, J.C., Linton, M.G., Al-haddad, N., Savani, N.P., Szabo, A., Hidalgo, M.A.: 2018, Understanding the internal magnetic field configurations of ICMEs using more than 20 years of wind observations. Solar Phys. 293(2), 25. DOI. ADS.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Szabo, A., Korreck, K.E., Alzate, N., Balmaceda, L.A., Lavraud, B., Paulson, K., Narock, A.A., Wallace, S., Jian, L.K., Luhmann, J.G., Morgan, H., Higginson, A., Arge, C.N., Bale, S.D., Case, A.W., de Wit, T.D., Giacalone, J., Goetz, K., Harvey, P.R., Jones-Melosky, S.I., Kasper, J.C., Larson, D.E., Livi, R., McComas, D.J., MacDowall, R.J., Malaspina, D.M., Pulupa, M., Raouafi, N.E., Schwadron, N., Stevens, M.L., Whittlesey, P.L.: 2020, Analysis of the internal structure of the streamer blowout observed by the parker solar probe during the first solar encounter. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 246(2), 63. DOI.
Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A., Kliem, B.: 2010, Toward understanding the early stages of an impulsively accelerated coronal mass ejection. SECCHI observations. Astron. Astrophys. 522, A100. DOI. ADS.
Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2018, EUHFORIA: European heliospheric forecasting information asset. J. Space Weather Space 8, A35. DOI. ADS.
Poomvises, W., Zhang, J., Olmedo, O.: 2010, Coronal mass ejection propagation and expansion in three-dimensional space in the heliosphere based on stereo/SECCHI observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 717(2), L159. DOI. ADS.
R Core Team: 2019, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/.
Sachdeva, N., Subramanian, P., Vourlidas, A., Bothmer, V.: 2017, CME dynamics using STEREO and LASCO observations: the relative importance of Lorentz forces and solar wind drag. Solar Phys. 292(9), 118. DOI. ADS.
Schwenn, R., dal Lago, A., Huttunen, E., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2005, The association of coronal mass ejections with their effects near the Earth. Ann. Geophys. 23, 1033. DOI. ADS.
Scolini, C., Rodriguez, L., Mierla, M., Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2019, Observation-based modelling of magnetised coronal mass ejections with EUHFORIA. Astron. Astrophys. 626, A122. DOI. ADS.
Subramanian, P., Vourlidas, A.: 2007, Energetics of solar coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 467(2), 685. DOI. ADS.
Subramanian, P., Arunbabu, K.P., Vourlidas, A., Mauriya, A.: 2014, Self-similar expansion of solar coronal mass ejections: implications for Lorentz self-force driving. Astrophys. J. 790(2), 125. DOI. ADS.
Thernisien, A.: 2011, Implementation of the graduated cylindrical shell model for the three-dimensional reconstruction of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 194, 33. DOI. ADS.
Venables, W.N., Ripley, B.D.: 2002, Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York. ISBN 0-387-95457-0. http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/pub/MASS4.
Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2006, The proper treatment of coronal mass ejection brightness: a new methodology and implications for observations. Astrophys. J. 642(2), 1216. DOI.
Vourlidas, A., Webb, D.F.: 2018, Streamer-blowout coronal mass ejections: their properties and relation to the coronal magnetic field structure. Astrophys. J. 861(2), 103. DOI. ADS.
Vourlidas, A., Subramanian, P., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A.: 2000, Large-angle spectrometric coronagraph measurements of the energetics of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 534(1), 456.
Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A., Esfandiari, E., Patsourakos, S., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G.: 2010, Comprehensive analysis of coronal mass ejection mass and energy properties over a full solar cycle. Astrophys. J. 722, 1522. DOI. ADS.
Vourlidas, A., Lynch, B.J., Howard, R.A., Li, Y.: 2013, How many CMEs have flux ropes? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Solar Phys. 284, 179. DOI. ADS.
Vourlidas, A., Balmaceda, L.A., Stenborg, G., Dal Lago, A.: 2017, Multi-viewpoint coronal mass ejection catalog based on STEREO COR2 observations. Astrophys. J. 838, 141. DOI. ADS.
Wickham, H.: 2007, Reshaping data with the reshape package. J. Stat. Softw. 21(12), 1. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v21/I12/.
Wickham, H.: 2016, ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, Springer, New York. ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org.
Xie, H., Ofman, L., Lawrence, G.: 2004, Cone model for halo CMEs: application to space weather forecasting. J. Geophys. Res., Space Phys. 109, A03109. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the valuable referee’s suggestions that helped improve the manuscript. L.B. and A.V. acknowledge grants NNX16AH70G and NNX17AC47G. G.S. acknowledges the support from the NASA STEREO/SECCHI (NNG17PP27I) program. The SECCHI data are produced by an international consortium of the NRL, LMSAL, and NASA GSFC (USA), RAL and University of Birmingham (UK), MPS (Germany), CSL (Belgium), IOTA and IAS (France). The MVCC CME list and APL solar site are supported by NASA NNX16AH70G and APL internal funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection:
Towards Future Research on Space Weather Drivers
Guest Editors: Hebe Cremades and Teresa Nieves-Chinchilla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balmaceda, L.A., Vourlidas, A., Stenborg, G. et al. On the Expansion Speed of Coronal Mass Ejections: Implications for Self-Similar Evolution. Sol Phys 295, 107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01672-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01672-6