Abstract
We investigate the relation between characteristics of coronal mass ejections and parameterizations of the eruptive capability of solar active regions widely used in solar flare-prediction schemes. These parameters, some of which are explored for the first time, are properties related to topological features, namely, magnetic polarity-inversion lines (MPILs) that indicate large amounts of stored non-potential (i.e. free) magnetic energy. We utilize the Space Weather Database of Notifications, Knowledge, Information (DONKI) and the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronograph (LASCO) databases to find flare-associated coronal mass ejections and their kinematic characteristics, while properties of MPILs are extracted from Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic-field observations of active regions to extract the properties of source-region MPILs. The correlation between all properties and the characteristics of CMEs ranges from moderate to very strong. More significant correlations hold particularly for fast CMEs, which are most important in terms of adverse space-weather manifestations. Non-neutralized currents and the length of the main MPIL exhibit significantly stronger correlations than the rest of the properties. This finding supports a causal relationship between coronal mass ejections and non-neutralized electric currents in highly sheared, conspicuous MPILs. In addition, non-neutralized currents and MPIL length carry distinct, independent information as to the eruptive potential of active regions. The combined total amount of non-neutralized electric currents and the length of the main polarity-inversion line, therefore, reflect more efficiently than other parameters the eruptive capacity of solar active regions and the CME kinematic characteristics stemming from these regions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramenko, V.I.: 2005, Relationship between magnetic power spectrum and flare productivity in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 629, 1141. DOI . ADS .
Ahmed, O., Qahwaji, R., Colak, T., Dudok De Wit, T., Ipson, S.: 2010, A new technique for the calculation and 3D visualisation of magnetic complexities on solar satellite images. Vis. Comput. 26, 385. DOI .
Alissandrakis, C.E.: 1981, On the computation of constant alpha force-free magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 100, 197. ADS .
Anastasiadis, A., Papaioannou, A., Sandberg, I., Georgoulis, M., Tziotziou, K., Kouloumvakos, A., Jiggens, P.: 2017, Predicting flares and solar energetic particle events: The FORSPEF tool. Solar Phys. 292, 134. DOI . ADS .
Barnes, G., Longcope, D.W., Leka, K.D.: 2005, Implementing a magnetic charge topology model for solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 629, 561. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Couvidat, S.: 2015, Solar flare prediction using SDO/HMI vector magnetic field data with a machine-learning algorithm. Astrophys. J. 798, 135. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Ilonidis, S.: 2016, Predicting coronal mass ejections using machine learning methods. Astrophys. J. 821, 127. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Turmon, M., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Barnes, G., Leka, K.D.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: SHARPs – space-weather HMI active region patches. Solar Phys. 289, 3549. DOI . ADS .
Chen, A.Q., Chen, P.F., Fang, C.: 2006, On the CME velocity distribution. Astron. Astrophys. 456, 1153. DOI . ADS .
Chen, P.F.: 2011, Coronal mass ejections: models and their observational basis. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 8, 1. DOI . ADS .
Dalmasse, K., Aulanier, G., Démoulin, P., Kliem, B., Török, T., Pariat, E.: 2015, The origin of net electric currents in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 810, 17. DOI . ADS .
Dierckxsens, M., Tziotziou, K., Dalla, S., Patsou, I., Marsh, M.S., Crosby, N.B., Malandraki, O., Tsiropoula, G.: 2015, Relationship between solar energetic particles and properties of flares and CMEs: Statistical analysis of solar cycle 23 events. Solar Phys. 290, 841. DOI . ADS .
Falconer, D.A., Moore, R.L., Gary, G.A.: 2003, A measure from line-of-sight magnetograms for prediction of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1380. DOI . ADS .
Falconer, D.A., Moore, R.L., Gary, G.A.: 2008, Magnetogram measures of total nonpotentiality for prediction of solar coronal mass ejections from active regions of any degree of magnetic complexity. Astrophys. J. 689, 1433. DOI . ADS .
Fletcher, L., Dennis, B.R., Hudson, H.S., Krucker, S., Phillips, K., Veronig, A., Battaglia, M., Bone, L., Caspi, A., Chen, Q., Gallagher, P., Grigis, P.T., Ji, H., Liu, W., Milligan, R.O., Temmer, M.: 2011, An observational overview of solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 19. DOI . ADS .
Florios, K., Kontogiannis, I., Park, S.-H., Guerra, J.A., Benvenuto, F., Bloomfield, D.S., Georgoulis, M.K.: 2018, Forecasting solar flares using magnetogram-based predictors and machine learning. Solar Phys. 293(2), 28. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K.: 2008, Magnetic complexity in eruptive solar active regions and associated eruption parameters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L06S02. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K.: 2013, Toward an efficient prediction of solar flares: Which parameters, and how? Entropy 15, 5022. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K.: 2018, The ambivalent role of field-aligned electric currents in the solar atmosphere. In: Keiling, A., Marghitu, O., Wheatland, M. (eds.) Electric Currents in Geospace and Beyond, Geophys. Mono. Ser. 235, 371. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K., Rust, D.M.: 2007, Quantitative forecasting of major solar flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 661, L109. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K., Nindos, A., Zhang, H.: 2019, The source and engine of coronal mass ejections. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 377(2148), 20180094. DOI . ADS .
Georgoulis, M.K., Titov, V.S., Mikić, Z.: 2012, Non-neutralized electric current patterns in solar active regions: origin of the shear-generating Lorentz force. Astrophys. J. 761, 61. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2016, History and development of coronal mass ejections as a key player in solar terrestrial relationship. Geosci. Lett. 3, 8. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295. DOI . ADS .
Guennou, C., Pariat, E., Leake, J.E., Vilmer, N.: 2017, Testing predictors of eruptivity using parametric flux emergence simulations. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 7, A17. DOI . ADS .
Guerra, J.A., Park, S.-H., Gallagher, P.T., Kontogiannis, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Bloomfield, D.S.: 2018, Active region photospheric magnetic properties derived from line-of-sight and radial fields. Solar Phys. 293, 9. DOI . ADS .
Kontogiannis, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Park, S.-H., Guerra, J.A.: 2017, Non-neutralized electric currents in solar active regions and flare productivity. Solar Phys. 292, 159. DOI . ADS .
Kontogiannis, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Park, S.-H., Guerra, J.A.: 2018, Testing and improving a set of morphological predictors of flaring activity. Solar Phys. 293, 96. DOI . ADS .
Leka, K.D., Barnes, G.: 2007, Photospheric magnetic field properties of flaring versus flare-quiet active regions. IV. A statistically significant sample. Astrophys. J. 656, 1173. DOI . ADS .
Leka, K.D., Canfield, R.C., McClymont, A.N., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 1996, Evidence for current-carrying emerging flux. Astrophys. J. 462, 547. DOI . ADS .
Mason, J.P., Hoeksema, J.T.: 2010, Testing automated solar flare forecasting with 13 years of Michelson Doppler imager magnetograms. Astrophys. J. 723, 634. DOI . ADS .
Mays, M.L., Taktakishvili, A., Pulkkinen, A., MacNeice, P.J., Rastätter, L., Odstrcil, D., Jian, L.K., Richardson, I.G., LaSota, J.A., Zheng, Y., Kuznetsova, M.M.: 2015, Ensemble modeling of CMEs using the WSA-ENLIL+cone model. Solar Phys. 290(6), 1775. DOI . ADS .
Möstl, C., Amla, K., Hall, J.R., Liewer, P.C., De Jong, E.M., Colaninno, R.C., Veronig, A.M., Rollett, T., Temmer, M., Peinhart, V., Davies, J.A., Lugaz, N., Liu, Y.D., Farrugia, C.J., Luhmann, J.G., Vršnak, B., Harrison, R.A., Galvin, A.B.: 2014, Connecting speeds, directions and arrival times of 22 coronal mass ejections from the sun to 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 787, 119. DOI . ADS .
Murray, S.A., Guerra, J.A., Zucca, P., Park, S.-H., Carley, E.P., Gallagher, P.T., Vilmer, N., Bothmer, V.: 2018, Connecting coronal mass ejections to their solar active region sources: Combining results from the HELCATS and FLARECAST projects. Solar Phys. 293, 60. DOI . ADS .
Pal, S., Nandy, D., Srivastava, N., Gopalswamy, N., Panda, S.: 2018, Dependence of coronal mass ejection properties on their solar source active region characteristics and associated flare reconnection flux. Astrophys. J. 865(1), 4. DOI . ADS .
Palmerio, E., Kilpua, E.K.J., James, A.W., Green, L.M., Pomoell, J., Isavnin, A., Valori, G.: 2017, Determining the intrinsic CME flux rope type using remote-sensing solar disk observations. Solar Phys. 292, 39. DOI . ADS .
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2017, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections resulting from earth-directed CMEs using SOHO and ACE Combined data during solar cycle 23. Solar Phys. 292, 30. DOI . ADS .
Papaioannou, A., Anastasiadis, A., Sandberg, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Tsiropoula, G., Tziotziou, K., Jiggens, P., Hilgers, A.: 2015, A novel forecasting system for solar particle events and flares (FORSPEF). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 632, 012075. DOI . ADS .
Papaioannou, A., Sandberg, I., Anastasiadis, A., Kouloumvakos, A., Georgoulis, M.K., Tziotziou, K., Tsiropoula, G., Jiggens, P., Hilgers, A.: 2016, Solar flares, coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particle event characteristics. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 6(27), A42. DOI . ADS .
Park, S.-H., Cho, K.-S., Bong, S.-C., Kumar, P., Chae, J., Liu, R., Wang, H.: 2012, The occurrence and speed of CMEs related to two characteristic evolution patterns of helicity injection in their solar source regions. Astrophys. J. 750, 48. DOI . ADS .
Park, S.-H., Guerra, J.A., Gallagher, P.T., Georgoulis, M.K., Bloomfield, D.S.: 2018, Photospheric shear flows in solar active regions and their relation to flare occurrence. Solar Phys. 293(8), 114. DOI . ADS .
Patsourakos, S., Georgoulis, M.K., Vourlidas, A., Nindos, A., Sarris, T., Anagnostopoulos, G., Anastasiadis, A., Chintzoglou, G., Daglis, I.A., Gontikakis, C., Hatzigeorgiu, N., Iliopoulos, A.C., Katsavrias, C., Kouloumvakos, A., Moraitis, K., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Pavlos, G., Sarafopoulos, D., Syntelis, P., Tsironis, C., Tziotziou, K., Vogiatzis, I.I., Balasis, G., Georgiou, M., Karakatsanis, L.P., Malandraki, O.E., Papadimitriou, C., Odstrčil, D., Pavlos, E.G., Podlachikova, O., Sandberg, I., Turner, D.L., Xenakis, M.N., Sarris, E., Tsinganos, K., Vlahos, L.: 2016, The major geoeffective solar eruptions of 2012 March 7: Comprehensive sun-to-earth analysis. Astrophys. J. 817, 14. DOI . ADS .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI . ADS .
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P.: 2007, Numerical Recipes 3rd Edition: The Art of Scientific Computing, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Qiu, J., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2005, Magnetic reconnection flux and coronal mass ejection velocity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 634, L121. DOI . ADS .
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) investigation for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 207. DOI . ADS .
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., Wachter, R., Couvidat, S., Rabello-Soares, M.C., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Akin, D.J., Allard, B.A., Miles, J.W., Rairden, R., Shine, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J., Elmore, D.F., Norton, A.A., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 229. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2007, A Characteristic Magnetic Field Pattern Associated with All Major Solar Flares and Its Use in Flare Forecasting. Astrophys. J. Lett. 655, L117. DOI . ADS .
Schrijver, C.J.: 2016, The nonpotentiality of coronae of solar active regions, the dynamics of the surface magnetic field, and the potential for large flares. Astrophys. J. 820, 103. DOI . ADS .
Sheeley, N.R., Walters, J.H., Wang, Y.-M., Howard, R.A.: 1999, Continuous tracking of coronal outflows: Two kinds of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 24739. DOI . ADS .
Shibata, K., Magara, T.: 2011, Solar flares: Magnetohydrodynamic processes. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 8, 6. DOI . ADS .
Syntelis, P., Archontis, V., Tsinganos, K.: 2017, Recurrent CME-like eruptions in emerging flux regions. I. On the mechanism of eruptions. Astrophys. J. 850, 95. DOI . ADS .
Syntelis, P., Gontikakis, C., Patsourakos, S., Tsinganos, K.: 2016, The spectroscopic imprint of the pre-eruptive configuration resulting into two major coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 588, A16. DOI . ADS .
Tiwari, S.K., Falconer, D.A., Moore, R.L., Venkatakrishnan, P., Winebarger, A.R., Khazanov, I.G.: 2015, Near-Sun speed of CMEs and the magnetic nonpotentiality of their source active regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 5702. DOI . ADS .
Török, T., Leake, J.E., Titov, V.S., Archontis, V., Mikić, Z., Linton, M.G., Dalmasse, K., Aulanier, G., Kliem, B.: 2014, Distribution of electric currents in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 782, L10. DOI . ADS .
van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Culhane, J.L.: 2009, Magnetic flux emergence, activity, eruptions and magnetic clouds: Following magnetic field from the sun to the heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 351. DOI . ADS .
Vasantharaju, N., Vemareddy, P., Ravindra, B., Doddamani, V.H.: 2018, Statistical study of magnetic nonpotential measures in confined and eruptive flares. Astrophys. J. 860, 58. DOI . ADS .
Venkatakrishnan, P., Ravindra, B.: 2003, Relationship between CME velocity and active region magnetic energy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 2181. DOI . ADS .
Vourlidas, A., Buzasi, D., Howard, R.A., Esfand iari, E.: 2002, Mass and energy properties of LASCO CMEs. In: Wilson, A. (ed.) Solar Variability: From Core to Outer Frontiers, SP-506, ESA, Noordwijk, 91. ADS .
Vourlidas, A., Lynch, B.J., Howard, R.A., Li, Y.: 2013, How many CMEs have flux ropes? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Solar Phys. 284, 179. DOI . ADS .
Vršnak, B., Sudar, D., Ruždjak, D.: 2005, The CME-flare relationship: Are there really two types of CMEs? Astron. Astrophys. 435, 1149. DOI . ADS .
Webb, D.F., Howard, T.A.: 2012, Coronal mass ejections: Observations. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 9, 3. DOI . ADS .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N.: 2009, Statistical relationship between solar flares and coronal mass ejections. In: Gopalswamy, N., Webb, D.F. (eds.) Universal Heliophysical Processes, IAU Symp 257, 233. DOI . ADS .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105. DOI . ADS .
Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Gopalswamy, N., Howard, R.A.: 2006, Different power-law indices in the frequency distributions of flares with and without coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 650, L143. DOI . ADS .
Zhao, X., Dryer, M.: 2014, Current status of CME/shock arrival time prediction. Space Weather 12, 448. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewer for providing constructive comments, which improved the content of this manuscript. Also, Kostas Florios for useful advice regarding the statistical methods used. This research has been funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme through the Flare Likelihood And Region Eruption foreCASTing” (FLARECAST) project, under grant agreement No. 640216 and supported by grant DE 787/5-1 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). The data used are courtesy of NASA/SDO, the HMI science team and the Geostationary Satellite System (GOES) team. This CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: CME Linear Speed Threshold Selection
Appendix: CME Linear Speed Threshold Selection
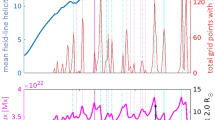
In this analysis we examined the different correlations exhibited between eruptive-flare characteristics and MPIL properties for fast and slow events. The speed threshold chosen to distinguish between these two classes was 750 km s−1, based on the conclusions of the statistical study of Sheeley et al. (1999). As such, 750 km s−1 is a threshold in a statistical sense, meaning that there is a degree of confluence between the two groups around this value. In order to cross-check the validity of this threshold, we examine here the correlation between the 24-hour averaged MPIL property values with the CME linear speed, for various threshold values ranging from 500 to 900 km s−1. The results for all parameters are shown in Figure 14. All parameters (with the exception of \(E_{\mathrm{Ising}}\)) exhibit a systematic increase in the correlation coefficient between 700 and 800 km s−1 after which the correlation coefficient drops and the size of the sample decreases. For most parameters, the maximum correlation is found within this range. Therefore, we deem that 750 km s−1 is a reasonable threshold choice that also ensures that the two populations have comparable sizes (14 vs. 18). Additionally, Figure 14 demonstrates that any threshold selection above 700 km s−1 would not alter significantly the conclusions of the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontogiannis, I., Georgoulis, M.K., Guerra, J.A. et al. Which Photospheric Characteristics Are Most Relevant to Active-Region Coronal Mass Ejections?. Sol Phys 294, 130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1523-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1523-6