Abstract
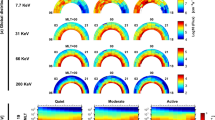
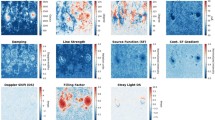
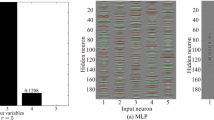
The global distribution of magnetic field and other plasma parameters on the source surface, which we set at 2.5 solar radii, is important for coronal and heliospheric modeling. In this article, we introduce a new data-driven self-consistent method to obtain the global distribution of different parameters. The magnetic and polarized brightness (\(pB\)) observations are used to derive the magnetic field and electron density on the source surface, respectively. Then, an artificial neural network (ANN) machine learning technique is applied to establish an empirical relation among the solar wind velocity, the magnetic field properties, and the electron density. The ANN is trained with global observational data, and is validated to be more reliable than the Wang–Sheeley–Arge (WSA) model for reconstructing the solar wind velocity, especially at high latitudes. The plasma temperature distribution is derived by solving a simplified one-dimensional (1D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) equation system on the source surface. Using the method in this study we can obtain the global distribution for all the parameters self-consistently based on magnetic and polarized brightness observations. The modeling results of four Carrington rotations from different solar cycle phases are presented to validate the method.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G.: 1969, Solar Phys. 9, 131. DOI .
Arden, W.M., Norton, A.A., Sun, X.: 2014, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 1476. DOI .
Arge, C.N., Pizzo, V.J.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 105, 10465. DOI .
Arge, C.N., Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Mayer, L.R.: 2003, AIP Conf. Proc. 679, 190. DOI .
Billings, D.E.: 1966, A Guide to the Solar Corona, Academic Press, New York.
Bussy-Virat, C.D., Ridley, A.J.: 2014, Space Weather 12, 337. DOI .
Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Fry, C., Sun, W., Deehr, C., Akasofu, S.I.: 2004, Space Weather 2. S09001. DOI .
Everson, R.W., Dikpati, M.: 2017, Astrophys. J. 850, 152. DOI .
Feng, X., Ma, X., Xiang, C.: 2015, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 10. DOI .
Feng, X., Yang, L., Xiang, C., Wu, S.T., Zhou, Y., Zhong, D.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 723, 300. DOI .
Feng, X., Jiang, C., Xiang, C., Zhao, X., Wu, S.T.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 758, 62. DOI .
Frazin, R.A., Janzen, P.: 2002, Astrophys. J. 570, 408. DOI .
Freeland, S.L., Handy, B.: 1998, Solar Phys. 182, 497. DOI .
Fry, C., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Sun, W., Deehr, C., Akasofu, S.I.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1070. DOI .
Gary, G.A.: 2001, Solar Phys. 203, 71. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 106, 29207. DOI .
Guhathakurta, M., Holzer, T.E., Macqueen, R.M.: 1996, Astrophys. J. 458, 817. DOI .
Hayashi, K.: 2005, Astrophys. J. Suppl., 161, 480. DOI .
Hayashi, K., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2016, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 7367. DOI .
Hayashi, K., Yang, S., Deng, Y.: 2016, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 121, 1046. DOI .
Hayashi, K., Benevolenskaya, E., Hoeksema, T., Liu, Y., Zhao, X.P.: 2006, Astrophys. J. Lett. 636, L165. DOI .
Hayashi, K., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.I.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1102. DOI .
Hayes, A.P., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 548, 1081. DOI .
Hoeksema, J.T., Wilcox, J.M., Scherrer, P.H.: 1983, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 88, 9910. DOI .
Hofmeister, S.J., Veronig, A., Temmer, M., Vennerstrom, S., Heber, B., Vrsnak, B.: 2018, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 1738. DOI .
Jackson, B.V., Odstrcil, D., Yu, H.S., Hick, P.P., Buffington, A., Mejia-Ambriz, J.C., Kim, J., Hong, S., Kim, Y., Han, J.: 2015, Space Weather 13, 104. DOI .
Jiang, C., Feng, X.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 769, 144. DOI .
Jones, S.I., Davila, J.M., Uritsky, V.: 2016, Astrophys. J. 820, 113. DOI .
Kim, T.K., Pogorelov, N.V., Borovikov, S.N., Jackson, B.V., Yu, H.S., Tokumaru, M.: 2014, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 7981. DOI .
Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K., Hayashi, K., Jackson, B.V.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 26, 467. DOI .
Koutchmy, S., Lamy, P.L.: 1985, The f-Corona and the Circum-Solar Dust Evidences and Properties 85, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 63. DOI .
Kramar, M., Airapetian, V., Mikić, Z., Davila, J.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 2927. DOI .
Lee, C., Luhmann, J., Hoeksema, J., Sun, X., Arge, C., de Pater, I.: 2011, Solar Phys. 269, 367. DOI .
Levine, R.H., Schulz, M., Frazier, E.N.: 1982, Solar Phys. 77, 363. DOI .
Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Biesecker, D.A., Forsyth, R.J., Gibson, S.E., Lazarus, A.J., Lecinski, A., Riley, P., Szabo, A., Thompson, B.J.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 104, 9809. DOI .
Liu, Y., Hoeksema, J., Scherrer, P., Schou, J., Couvidat, S., Bush, R., Duvall, T., Hayashi, K., Sun, X., Zhao, X.: 2012, Solar Phys. 279, 295. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, Astrophys. J. 634, 651. DOI .
MacNeice, P.: 2009, Space Weather 7, 1. DOI .
McComas, D.J., Elliott, H.A., Gosling, J.T., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L09102. DOI .
Mikic, Z., Linker, J.A., Schnack, D.D., Lionello, R., Tarditi, A.: 1999, Phys. Plasmas 6, 2217. DOI .
Morgan, H.: 2015, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 219, 23. DOI .
Newkirk, G., Fisk, L.A.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 90, 3391. DOI .
Odstrcil, D.: 2003, Adv. Space Res. 32, 497. DOI .
Owens, M.J., Challen, R., Methven, J., Henley, E., Jackson, D.R.: 2013, Space Weather 11, 225. DOI .
Owens, M.J., Spence, H.E., McGregor, S., Hughes, W.J., Quinn, J.M., Arge, C.N., Riley, P., Linker, J., Odstrcil, D.: 2008, Space Weather 6, S08001. DOI .
Patoul, J.d., Foullon, C., Riley, P.: 2015, Astrophys. J. 814, 68. DOI .
Quémerais, E., Lamy, P.: 2002, Astron. Astrophys. 393, 295. DOI .
Reiss, M.A., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Nikolic, L., Vennerstrom, S., Schöngassner, F., Hofmeister, S.J.: 2016, Space Weather 14, 495. DOI .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Arge, C.N.: 2015, Space Weather 13, 154. DOI .
Riley, P., Lionello, R.: 2011, Solar Phys. 270, 575. DOI .
Riley, P., Linker, J., Mikic, Z., Lionello, R., Ledvina, S.A., Luhmann, J.G.: 2006, Astrophys. J. 653, 1510. DOI .
Riley, P., Lionello, R., Linker, J., Mikic, Z., Luhmann, J., Wijaya, J.: 2011, Solar Phys. 274, 361. DOI .
Riley, P., Ben-Nun, M., Linker, J., Mikic, Z., Svalgaard, L., Harvey, J., Bertello, L., Hoeksema, T., Liu, Y., Ulrich, R.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 769. DOI .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, Solar Phys. 6, 442. DOI .
Schulz, M., Frazier, E.N., Boucher, D.J.: 1978, Solar Phys. 60, 83. DOI .
Shen, F., Feng, X., Xiang, C.: 2012, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 77, 125. DOI .
Shen, F., Feng, X., Wu, S., Xiang, C.: 2007, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112, A06109. DOI .
Shen, F., Feng, X., Xiang, C., Song, W.: 2010, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 72, 1008. DOI .
Shen, F., Shen, C., Wang, Y., Feng, X., Xiang, C.: 2013, Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 1457. DOI .
Shen, F., Shen, C., Zhang, J., Hess, P., Wang, Y., Feng, X., Cheng, H., Yang, Y.: 2014, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 7128. DOI .
Shen, F., Yang, Z., Zhang, J., Wei, W., Feng, X.: 2018, Astrophys. J. 866, 18. DOI .
Strachan, L., Panasyuk, A.V., Kohl, J.L., Lamy, P.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 745, 51. DOI .
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K.: 2010, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, A04102. DOI .
Tokumaru, M., Satonaka, D., Fujiki, K.i., Hayashi, K., Hakamada, K.: 2017, Solar Phys. 292, 41. DOI .
Tóth, G., van der Holst, B., Huang, Z.: 2011, Astrophys. J. 732, 102. DOI .
Van de Hulst, H.: 1950, Bull. Astron. Inst. Neth. 11, 135.
Wang, T., Davila, J.M.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289, 3723. DOI .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 355, 726. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Young, P.R., Muglach, K.: 2014, Astrophys. J. 780, 103. DOI .
Wei, F.S., Feng, X.S., Cai, H.C., Zhou, Q.J.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108, 1238. DOI .
Wiegelmann, T., Petrie, G.J.D., Riley, P.: 2017, Space Sci. Rev. 210, 249. DOI .
Wiengarten, T., Kleimann, J., Fichtner, H., Cameron, R., Jiang, J., Kissmann, R., Scherer, K.: 2013, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 29. DOI .
Wintoft, P., Lundstedt, H.: 1997, Phys. Chem. Earth 22, 617. DOI .
Wintoft, P., Lundstedt, H.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 104, 6729. DOI .
Yang, Y., Shen, F., Yang, Z., Feng, X.: 2018, Space Weather 16, 1227. DOI .
Zhao, X., Dryer, M.: 2014, Space Weather 12, 448. DOI .
Zhao, X., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 100, 19. DOI .
Acknowledgements
The data for this work are available at the official websites of NSO/GONG, SOHO/LASCO, and IPS group at Nagoya University. We acknowledge the use of them. The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) magnetograms are downloaded from the website of the National Solar Observatory (NSO, http://gong.nso.edu/ ). SOHO is a joint mission of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The SOHO/LASCO data used here are produced by a consortium of the Naval Research Laboratory (USA), Max-Planck-Institut fuer Aeronomie (Germany), Laboratoire d’Astronomie (France), and the University of Birmingham (UK). The polarized brightness (\(pB\)) data can be downloaded from the LASCO instrument website at NRL ( http://lasco-www.nrl.navy.mil/content/retrieve/polarize/ ). The IPS data is provided by the solar wind group at the Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research (ISEE), Nagoya University, and can be downloaded from the official website ( http://stsw1.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/ips_data-e.html ). We acknowledge the use of the OMNIWeb service provided by the NASA/GSFC Space Physics Data Facility. The Ulysses and near-Earth in situ data in this work are both obtained from the web interface at http://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov . This work is jointly supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41774184, 41474152, 41731067, and 41531073) and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories. FS is also supported by the National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals. The calculations were performed on TianHe-1 (A) at the National Supercomputer Center in Tianjin, China. We thank the editor and the anonymous reviewer for the suggestions that greatly improved this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Shen, F. Modeling the Global Distribution of Solar Wind Parameters on the Source Surface Using Multiple Observations and the Artificial Neural Network Technique. Sol Phys 294, 111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1496-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1496-5