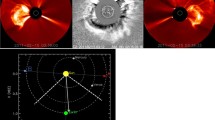
Abstract
Using in situ observations from the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), we have identified 70 Earth-affecting interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) in Solar Cycle 24. Because of the unprecedented extent of heliospheric observations in Cycle 24 that has been achieved thanks to the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) instruments onboard the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO), we observe these events throughout the heliosphere from the Sun to the Earth, and we can relate these in situ signatures to remote sensing data. This allows us to completely track the event back to the source of the eruption in the low corona. We present a summary of the Earth-affecting CMEs in Solar Cycle 24 and a statistical study of the properties of these events including the source region. We examine the characteristics of CMEs that are more likely to be strongly geoeffective and examine the effect of the flare strength on in situ properties. We find that Earth-affecting CMEs in the first half of Cycle 24 are more likely to come from the northern hemisphere, but after April 2012, this reverses, and these events are more likely to originate in the southern hemisphere, following the observed magnetic asymmetry in the two hemispheres. We also find that as in past solar cycles, CMEs from the western hemisphere are more likely to reach Earth. We find that Cycle 24 lacks in events driving extreme geomagnetic storms compared to past solar cycles.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M.V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Bedford, D.K., Eyles, C.J.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, Magnetic clouds and force-free field with constant alpha. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7217. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F., Plunkett, S.P., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2002, Successive CMEs and complex ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1266. DOI .
Cargill, P.J.: 2004, On the aerodynamic drag force acting on interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 221, 135. DOI . ADS .
Chi, Y., Shen, C., Wang, Y., Xu, M., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2016, Statistical study of the interplanetary coronal mass ejections from 1995 to 2015. Solar Phys. 291, 2419. DOI . ADS .
Delaboudinière, J.-P., Artzner, G.E., Brunaud, J., Gabriel, A.H., Hochedez, J.F., Millier, F. et al.: 1995, EIT: Extreme-Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope for the SOHO mission. Solar Phys. 162, 291. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Near-Sun and near-Earth manifestations of solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 25261. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Howard, R.A.: 2003, Coronal mass ejections and solar polarity reversal. Astrophys. J. Lett. 598, L63. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2010, A catalog of halo coronal mass ejections from SOHO. Sun Geosph. 5, 7. ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2015, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during Solar Cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 9221. DOI .
Hathaway, D.H.: 2010, The solar cycle. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 7, 1. DOI . ADS .
Hess, P., Zhang, J.: 2014, Stereoscopic study of the kinematic evolution of a coronal mass ejection and its driven shock from the Sun to the Earth and the prediction of their arrival times. Astrophys. J. 792, 49. DOI . ADS .
Hess, P., Zhang, J.: 2015, Predicting CME ejecta and sheath front arrival at L1 with a data-constrained physical model. Astrophys. J. 812(2), 144. DOI .
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., Thompson, W.T., St. Cyr, O.C., Mentzell, E., Mehalick, K., Lemen, J.R., Wuelser, J.P., Duncan, D.W., Tarbell, T.D., Wolfson, C.J., Moore, A., Harrison, R.A., Waltham, N.R., Lang, J., Davis, C.J., Eyles, C.J., Mapson-Menard, H., Simnett, G.M., Halain, J.P., Defise, J.M., Mazy, E., Rochus, P., Mercier, R., Ravet, M.F., Delmotte, F., Auchere, F., Delaboudiniere, J.P., Bothmer, V., Deutsch, W., Wang, D., Rich, N., Cooper, S., Stephens, V., Maahs, G., Baugh, R., McMullin, D., Carter, T.: 2008, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI). Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67. DOI . ADS .
Howard, T.A., Nandy, D., Koepke, A.C.: 2008, Kinematic properties of solar coronal mass ejections: Correction for projection effects in spacecraft coronagraph measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A01104. DOI . ADS .
Jackson, B.V.: 1986, HELIOS photometer measurement of in situ density enhancements. Adv. Space Res. 6, 307. DOI . ADS .
Jang, S., Moon, Y.-J., Kim, R.-S., Lee, H., Cho, K.-S.: 2016, Comparison between 2D and 3D parameters of 306 front-side halo CMEs from 2009 to 2013. Astrophys. J. 821, 95. DOI . ADS .
Karna, N., Pesnell, W.D., Zhang, J.: 2015, Appearances and statistics of coronal cavities during the ascending phase of Solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 810(2), 123. DOI .
Kwon, R.-Y., Zhang, J., Vourlidas, A.: 2015, Are halo-like solar coronal mass ejections merely a matter of geometric projection effects? Astrophys. J. Lett. 799, L29. DOI . ADS .
Lee, J.-O., Moon, Y.-J., Lee, K.-S., Kim, R.-S.: 2014, dependence of geomagnetic storms on their associated halo CME parameters. Solar Phys. 289, 2233. DOI . ADS .
Lemen, J., Title, A., Akin, D., Boerner, P., Chou, C., Drake, J., Duncan, D., Edwards, C., Friedlaender, F., Heyman, G., Hurlburt, N., Katz, N., Kushner, G., Levay, M., Lindgren, R., Mathur, D., McFeaters, E., Mitchell, S., Rehse, R., Schrijver, C., Springer, L., Stern, R., Tarbell, T., Wuelser, J.-P., Wolfson, C.J., Yanari, C., Bookbinder, J., Cheimets, P., Caldwell, D., Deluca, E., Gates, R., Golub, L., Park, S., Podgorski, W., Bush, R., Scherrer, P., Gummin, M., Smith, P., Auker, G., Jerram, P., Pool, P., Soufli, R., Windt, D., Beardsley, S., Clapp, M., Lang, J., Waltham, N.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Huang, C.-L., Spence, H.E.: 2015, Extreme geomagnetic disturbances due to shocks within CMEs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 4694. DOI . ADS .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Kilpua, E.K.J., Jian, L.K., Liu, Y., Eastwood, J.P., Harrison, R.A., Webb, D.F., Temmer, M., Odstrcil, D., Davies, J.A., Rollett, T., Luhmann, J.G., Nitta, N., Mulligan, T., Jensen, E.A., Forsyth, R., Lavraud, B., de Koning, C.A., Veronig, A.M., Galvin, A.B., Zhang, T.L., Anderson, B.J.: 2012, Multi-point shock and flux rope analysis of multiple interplanetary coronal mass ejections around 2010 August 1 in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 758, 10. DOI . ADS .
Olmedo, O., Zhang, J., Wechsler, H., Poland, A., Borne, K.: 2008, Automatic detection and tracking of coronal mass ejections in coronagraph time series. Solar Phys. 248, 485. DOI . ADS .
Poomvises, W., Zhang, J., Olmedo, O.: 2010, Coronal mass ejection propagation and expansion in three-dimensional space in the heliosphere based on Stereo/SECCHI observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 717, L159. DOI . ADS .
Pulkkinen, T.: 2007, Space weather: Terrestrial perspective. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 4, 1. DOI . ADS .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 1995, Regions of abnormally low proton temperature in the solar wind (1965 – 1991) and their association with ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 23397. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2004, Identification of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 1 AU using multiple solar wind plasma composition anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 9104. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during Solar Cycle 23 (1996 – 2009): Catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys. 264, 189. DOI . ADS .
Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Zhang, J., Berdichevsky, D.B., Biesecker, D.A., Kasper, J.C., Kataoka, R., Steinberg, J.T., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.-C., Zhukov, A.N.: 2006, Major geomagnetic storms (\(\mathit{Dst} \leq-100~\mbox{nT}\)) generated by corotating interaction regions. J. Geophys. Res. 111(A10), 7. DOI .
Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, Relating white light and in situ observations of coronal mass ejections: A review. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1201. DOI . ADS .
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Pan, Z., Zhang, M., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2013, Full halo coronal mass ejections: Do we need to correct the projection effect in terms of velocity? J. Geophys. Res. (Space Physics) 118, 6858. DOI . ADS .
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Pan, Z., Miao, B., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2014, Full-halo coronal mass ejections: Arrival at the Earth. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 5107. DOI .
Stone, R.G., Frandsen, A.M., Mewaldt, R.A., Christian, E.R., Margolies, D., Ormes, J.F., Snow, F.: 1998, The advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1. DOI .
Subramanian, P., Lara, A., Borgazzi, A.: 2012, Can solar wind viscous drag account for coronal mass ejection deceleration? Geophys. Res. Lett. 39, 19107. DOI . ADS .
Temmer, M., Nitta, N.V.: 2015, Interplanetary propagation behavior of the fast coronal mass ejection on 23 July 2012. Solar Phys. 290, 919. DOI . ADS .
Thernisien, A.F.R., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Modeling of flux rope coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 652, 763. DOI . ADS .
Vršnak, B., Sudar, D., Ruždjak, D., Žic, T.: 2007, Projection effects in coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 469, 339. DOI . ADS .
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Vrbanec, D., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A., Čalogović, J., Dumbović, M., Lulić, S., Moon, Y.-J., Shanmugaraju, A.: 2013, Propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: The drag-based model. Solar Phys. 285, 295. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S.: 2003, Multiple magnetic clouds: Several examples during March–April, 2001. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1370. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S., Zhou, G.P., Wang, J.X.: 2002, A statistical study on the geoeffectiveness of earth-directed coronal mass ejections from March 1997 to December 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1340. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S., Xue, X.H.: 2003a, An interplanetary cause of large geomagnetic storms: Fast forward shock overtaking preceding magnetic cloud. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(13), 1700. DOI .
Wang, Y.M., Ye, P.Z., Wang, S., Xiong, M.: 2003b, Theoretical analysis on the geoeffectiveness of shock overtaking preceding magnetic cloud. Solar Phys. 216, 295. DOI .
Wang, Y., Shen, C., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2004, Deflection of coronal mass ejection in the interplanetary medium. Solar Phys. 222, 329. DOI .
Wang, Y., Zhou, G., Ye, P., Wang, S., Wang, J.: 2006, A study of the orientation of interplanetary magnetic clouds and solar filaments. Astrophys. J. 651, 1245. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y., Chen, C., Gui, B., Shen, C., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2011, Statistical study of coronal mass ejection source locations: Understanding CMEs viewed in coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res. 116, A04104. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y., Wang, B., Shen, C., Shen, F., Lugaz, N.: 2014, Deflected propagation of a coronal mass ejection from the corona to interplanetary space. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 5117. DOI . ADS .
Webb, D.F., Cliver, E.W., Crooker, N.U., St. Cyr, O.C., Thompson, B.J.: 2000, Relationship of halo coronal mass ejections, magnetic clouds, and magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 7491. DOI .
Wu, C.-C., Lepping, R.P.: 2016, Relationships among geomagnetic storms, interplanetary shocks, magnetic clouds, and sunspot number during 1995 – 2012. Solar Phys. 291, 265. DOI . ADS .
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 7105. DOI .
Zhang, J., Hess, P., Poomvises, W.: 2013, A comparative study of coronal mass ejections with and without magnetic cloud structure near the Earth: Are all interplanetary CMEs flux ropes? Solar Phys. 284, 89. DOI . ADS .
Zhang, J., Poomvises, W., Richardson, I.G.: 2008, Sizes and relative geoeffectiveness of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and the preceding shock sheaths during intense storms in 1996 – 2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, 2109. DOI . ADS .
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Bothmer, V.: 2003, Identification of solar sources of major geomagnetic storms between 1996 and 2000. Astrophys. J. 582, 520. DOI .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., Nitta, N.V., Poomvises, W., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.-C., Yashiro, S., Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (\(\mathit{Dst} \leq-100~\mbox{nT}\)) during 1996 – 2005. J. Geophys. Res. 112, 10102. DOI .
Zhao, X.P., Webb, D.F.: 2003, Source regions and storm effectiveness of frontside full halo coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1234. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous referee for useful suggestions that improved the quality of this manuscript. This research was performed while Phillip Hess held an NRC Research Associateship award at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. JZ is supported by NSF AGS-1249270 and AGS-1460188. The SECCHI data are produced by an international consortium of NRL, LMSAL, and NASA GSFC (USA), RAL and U. Bham (UK), MPS (Germany), CSL (Belgium), IOTA and IAS (France). The SOHO/LASCO data used here are produced by a consortium of the Naval Research Laboratory (USA), Max-Planck-Institut fuer Sonnensystemforschung (Germany), Laboratoire d’Astronomie (France), and the University of Birmingham (UK). SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The AIA data are courtesy of SDO (NASA) and the AIA consortium. The SSN used was obtained from the WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Brussels. Active region and flare information was obtained from NOAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Earth-affecting Solar Transients
Guest Editors: Jie Zhang, Xochitl Blanco-Cano, Nariaki Nitta, and Nandita Srivastava
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hess, P., Zhang, J. A Study of the Earth-Affecting CMEs of Solar Cycle 24. Sol Phys 292, 80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1099-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1099-y