Abstract
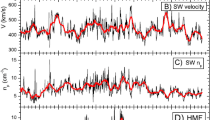
Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are energetic, charged particles coming from outside the solar system. These particles encounter an outward-moving turbulent solar wind with cyclic magnetic-field fluctuations when entering the heliosphere. This causes convection and diffusion in the heliosphere. The GCR counts detected by the ground-based neutron-monitor stations show intensity changes with a fluctuation of ∼ 11 years and are anti-correlated with the sunspot numbers with some time lags. GCRs experience various types of modulation from different solar activity features and are important components of space weather. The previous solar cycle, Cycle 23, has shown anomalous behavior with a prolonged deep minimum, which was characterized by a record-setting high Galactic cosmic-ray flux observed at Earth. Solar Cycle 24 started much later than expected and progressed sluggishly toward its maxima. In this paper, we study the heliospheric modulation and intermediate-term periodicities of GCRs during the ascending phase of Cycle 24. We utilize simultaneous solar, interplanetary plasma, magnetic field, and geomagnetic activity data including the tilt angle of the heliospheric current sheet, and we study their relation with GCRs. The wavelet power spectrum of GCRs exhibits the presence of a variety of prominent short- and mid-term periodicities including the well-known Rieger and quasi-biennial periodicities. Possible explanations of the observed results are discussed in the light of numerical models.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia, H.S., Lopate, C., Ygbuhay, R.C., Duldig, M.L.: 2010, Adv. Space Res. 46(7), 934. DOI .
Alania, M.V., Modzelewska, R., Wawrzynczak, A.: 2014, J. Geophys. Res. 119(6), 4164. DOI .
Antalová, A., Kudela, K., Rybák, J.: 2001, Space Sci. Rev. 97(1/4), 355. DOI .
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin: 2012, Solar Phys. 279(1), 269. DOI .
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin: 2015, Solar Phys. DOI .
Badruddin, Singh, M., Singh, Y.P.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 466(2), 697.
Balogh, A., Erdős, G.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176(1–4), 177.
Bazilevskaya, G.A., Krainev, M.B., Svirzhevskaya, A.K., Svirzhevsky, N.S.: 2013, Cosm. Res. 51(1), 29.
Bazilevskaya, B., Broomhall, A.-M., Elsworth, Y., Nakariakov, V.M.: 2014a, Space Sci. Rev. 186, 359.
Bazilevskaya, G.A., Cliver, E.W., Kovaltsov, G.A., Ling, A.G., Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F., Usoskin, I.G.: 2014b, Space Sci. Rev. 186(1–4), 409.
Belov, A.V.: 2000, Space Sci. Rev. 93, 79.
Burlaga, L.F., McDonald, F.B., Ness, N.F.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98(A1), 1. DOI .
Caballero, R., Valdés-Galicia, J.F.: 2001, Adv. Space Res. 27(3), 583.
Cane, H.V., Wibberenz, G., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1999, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26(5), 565.
Chowdhury, P., Dwivedi, B.N., Ray, P.C.: 2011, New Astron. 16(7), 430.
Chowdhury, P., Jain, R., Awasthi, A.K.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 778(1), 28.
Chowdhury, P., Khan, M., Ray, P.C.: 2010a, Astrophys. Space Sci. 326(2), 191.
Chowdhury, P., Khan, M., Ray, P.C.: 2010b, Planet. Space Sci. 58(7–8), 1045.
Chowdhury, P., Kudela, K., Dwivedi, B.N.: 2013, Solar Phys. 286(2), 577. DOI .
Chowdhury, P., Choudhary, D.P., Gosain, S., Moon, Y.-J.: 2015, Astrophys. Space Sci. 356(1), 7.
Cliver, E.W., Ling, A.G.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 556(1), 432.
Cliver, E.W., Richardson, I.G., Ling, A.G.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176(1–4), 3.
De Moortel, I., Munday, S.A., Hood, A.W.: 2004, Solar Phys. 222(2), 203.
Dikpati, M., de Toma, G., Gilman, P.A., Arge, C.N., White Oran, R.: 2004, Astrophys. J. 601(2), 1136.
Dorman, I.V., Dorman, L.I.: 1967, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 29(4), 429.
Gil, A., Alania, M.V.: 2010, Adv. Space Res. 45(3), 429.
Gil, A., Alania, M.V.: 2012, Solar Phys. 278(2), 447.
Gil, A., Alania, M.V.: 2013, Adv. Space Res. 52(5), 951.
Gleeson, L.J., Axford, W.I.: 1968, Astrophys. J. 154, 1011.
Heber, B.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176(1–4), 265.
Heber, B., Kopp, A., Gieseler, J., Müller-Mellin, R., Fichtner, H., Scherer, K., Potgieter, M.S., Ferreira, S.E.S.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 699(2), 1956.
Howe, R., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Hill, F., Komm, R.W., Larsen, R.M., Schou, J., Thompson, M.J., Toomre, J.: 2000, Science 287(5462), 2456.
Jokipii, J.R.: 1971, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 9, 27. DOI .
Jokipii, J.R., Thomas, B.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 243, 1115.
Kane, R.P.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. DOI .
Kane, R.P.: 2011, Solar Phys. 269(2), 451.
Kane, R.P.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289(7), 2727.
Kato, C., Munakata, K., Yasue, S., Inoue, K., McDonald, F.B.: 2003, J. Geophys. Res. 108(A10), 1367. SSH 4-1. DOI .
Kóta, J.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176(1–4), 391.
Krainev, M.B., Storini, M., Bazilevskaya, G.A., Fluckiger, E.O., Makhmutov, V.S., Sladkova, A.I., Starodubtsev, S.A.: 1999, In: Proc. 26th ICRC, Salt Lake City, US, 7, 155.
Kudela, K., Ananth, A.G., Venkatesan, D.: 1991, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 15871. DOI .
Kudela, K., Slivka, M., Stehlik, M., Geranios, A.: 1993, Astrophys. Space Sci. 199(1), 125. DOI .
Kudela, K., Mavromichalaki, H., Papaioannou, A., Gerontidou, M.: 2010, Solar Phys. 266(1), 173.
Laurenza, M., Vecchio, A., Storini, M., Carbone, V.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 749(2), 167.
Leske, R.A., Cummings, A.C., Mewaldt, R.A., Stone, E.C.: 2013, Space Sci. Rev. 176(1–4), 253.
Lockwood, M.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106(A8), 16021.
Mavromichalaki, H., Belehaki, A., Rafios, X.: 1998, Astron. Astrophys. 330, 764.
Mavromichalaki, H., Paouris, E., Karalidi, T.: 2007, Solar Phys. 245(2), 369.
Mavromichalaki, H., Preka-Papadema, P., Liritzis, I., Petropoulos, B., Kurt, V.: 2003, New Astron. 8(8), 777.
McComas, D.J., Ebert, R.W., Elliott, H.A., Goldstein, B.E., Gosling, J.T., Schwadron, N.A., Skoug, R.M.: 2008, Geophys. Res. Lett. 35(18), L18103.
McDonald, F.B., Webber, W.R., Reames, D.V.: 2010, Geophys. Res. Lett. 37(18), L1810.
Mewaldt, R.A., Davis, A.J., Lave, K.A., Leske, R.A., Stone, E.C., et al.: 2010, Astrophys. J. Lett. 723(1), L1.
Minarovjech, M., Kudela, K.: 2004, Solar Phys. 224(1–2), 285.
Modzelewska, R., Alania, M.V.: 2013, Solar Phys. 286(2), 593.
Moraal, H., Stoker, P.H.: 2010, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115(A12), A12109.
Nagashima, K., Morishita, I.: 1980, Planet. Space Sci. 28, 177.
Obridko, V.N., Shelting, B.D.: 2007, Adv. Space Res. 40(7), 1006.
Owens, M.J., Forsyth, R.J.: 2013, Living Rev. Solar Phys. 10, 5.
Owens, M.J., Usoskin, I., Lockwood, M.: 2012, Geophys. Res. Lett. 39(19), L19102.
Pacini, A.A., Usoskin, I.G.: 2015, Solar Phys. 290(3), 943.
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Belov, A., Gushchina, R., Yanke, V.: 2012, Solar Phys. 280(1), 255.
Parker, E.N.: 1965, Planet. Space Sci. 13(1), 9.
Pogorelov, N.V., Suess, S.T., Borovikov, S.N., Ebert, R.W., McComas, D.J., Zank, G.P.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 772(1), 17, 2.
Potgieter, M.: 2013, Living Rev. Solar Phys. 10, 3.
Potgieter, M.S., Burger, R.A., Ferreira, S.E.S.: 2001, Space Sci. Rev. 97(1/4), 295.
Potgieter, M.S., Vos, E.E., Boezio, M., De Simone, N., Di Felice, V., Formato, V.: 2014, Solar Phys. 289(1), 391.
Richardson, I.G.: 2013, J. Space Weather Space Clim. 3, A08.
Rybanský, M.: 1975, Bull. Astron. Inst. Czechoslov. 28, 367.
Sabbah, I., Kudela, K.: 2011, J. Geophys. Res. 116(A4), A04103.
Sabbah, I., Rybanský, M.: 2006, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 111(A1), A01105.
Singh, M., Badruddin, Ananth, A.G.: 2005, Proc. 29th ICRC Pune. In: India, E., Sripathi Acharya, B., Gupta, S., Jagadeesan, P., Jain, A., Karthikeyan, S., Morris, S., Suresh, T. (eds.): 2, Tata Inst. Fund. Res., Mumbai, 139.
Singh, Y.P., Gautam, S., Badruddin: 2012, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 89, 48.
Smith, E.J., Balogh, A.: 2008, Geophys. Res. Lett. 35(22), L22103.
Stone, E.C., Cummings, A.C., McDonald, F.B., Heikkila, B.C., Lal, N., Ebber, W.R.: 2013, Science 341(6142), 150.
Storini, M., Laurenza, M., Fujii, Z.: 2003, In: Proc. 28th ICRC, Tsukuba, Japan, 4049.
Torrence, C., Compo, G.P.: 1998, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79(1), 61.
Usoskin, I.G., Kananen, H., Mursula, K., Tanskanen, P., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103(A5), 9567.
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Kananen, H., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2001, Adv. Space Res. 27(3), 571.
Vecchio, A., Laurenza, M., Carbone, V., Storini, M.: 2010, Astrophys. J. Lett. 709(1), L1.
Vecchio, A., Laurenza, M., Meduri, D., Carbone, V., Storini, M.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 749(1), 27.
Zhao, L.-L., Qin, G., Zhang, M., Heber, B.: 2014, J. Geophys. Res. 119(3), 1493.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the referee for constructive and valuable comments that improved the manuscript considerably. This work was supported by the BK21 plus program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea. We thank Dr. Ilya Usoskin and the Sodankyla Geophysical Observatory for the online availability of the Oulu neutron-monitor data. We also thank the Royal Observatory of Belgium for the sunspot number data, the SOHO LASCO team members for the CME data base and the Slovak Central Observatory in Hurbanovo for the online availability of the MCI data. The availability of geomagnetic, interplanetary plasma and magnetic field data through the NASA/GSFC OMNI Web interface and the HCS inclination data (courtesy J.T. Hoeksema) is also acknowledged. KK wishes to acknowledge VEGA agency 2/0040/13 and 2/0026/16 for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, P., Kudela, K. & Moon, YJ. A Study of Heliospheric Modulation and Periodicities of Galactic Cosmic Rays During Cycle 24. Sol Phys 291, 581–602 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0832-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0832-7