Abstract
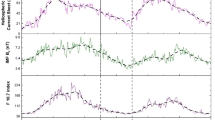
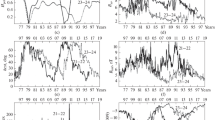
In this work the galactic cosmic ray modulation in relation to solar activity indices and heliospheric parameters during the years 1996 – 2010 covering solar cycle 23 and the solar minimum between cycles 23 and 24 is studied. A new perspective of this contribution is that cosmic ray data with a rigidity of 10 GV at the top of the atmosphere obtained from many ground-based neutron monitors were used. The proposed empirical relation gave much better results than those in previous works concerning the hysteresis effect. The proposed models obtained from a combination of solar activity indices and heliospheric parameters give a standard deviation < 10 % for all the cases. The correlation coefficient between the cosmic ray variations of 10 GV and the sunspot number reached a value of r=−0.89 with a time lag of 13.6±0.4 months. The best reproduction of the cosmic ray intensity is obtained by taking into account solar and interplanetary indices such as sunspot number, interplanetary magnetic field, CME index, and heliospheric current sheet tilt. The standard deviation between the observed and calculated values is about 7.15 % for all of solar cycle 23; it also works very well during the different phases of the cycle. Moreover, the use of the cosmic ray intensity of 10 GV during the long minimum period between cycles 23 and 24 is of special interest and is discussed in terms of cosmic ray intensity modulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia, H.S., Ygbuhay, R.C.: 2011, Adv. Space Res. 48, 61.
Baisultanova, L.M., Belov, A.V., Yanke, V.G.: 1995, In: Proc. 24th ICRC 4, 1090.
Belov, A.V.: 2000, Space Sci. Rev. 93, 79.
Belov, A., Baisultanova, L., Eroshenko, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Yanke, V., Pchelkin, V., Plainaki, C., Mariatos, G.: 2005, J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S20.
Belov, A.V., Gushchina, R.T., Sirotina, I.V.: 1995, In: Proc. 24th ICRC 4, 542.
Belov, A.V., Gushchina, R.T., Yanke, V.G.: 1999, In: Proc. 26th ICRC 7, 175.
Belov, A., Shelding, B.D., Gushchina, R.T., Obridko, V.N., Kharshiladze, A.F., Yanke, V.G.: 2001, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 63, 1923.
Caballero, R., Valdés-Galicia, J.F.: 2004, Solar Phys. 212, 209.
Cane, H.V., Wibberenz, G., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1999, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 565.
Chirkov, N.P., Kuzmin, A.I.: 1979, In: Proc. 16th ICRC 4, 360.
de Toma, G.: 2011, Solar Phys. 274, 195.
Dorman, L.I.: 1963, In: Wilson, J.G., Wouthuysen, S.A. (eds.) Progress in Elementary Particle and Cosmic Ray Physics, Elsevier, New York.
Dvornikov, V.M., Sdobnov, V.E.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 24209.
Ferreira, S.E.S., Potgieter, M.S.: 2004, Astron. J. 603, 744.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2010, In: Hasan, S.S., Rutten, R.J. (eds.) Magnetic Coupling Between the Interior and Atmosphere of the Sun, Springer, Berlin, 289.
Hatton, G.J.: 1980, Solar Phys. 66, 159.
Jokipii, J.R., Thomas, B.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 243, 1115.
Kane, R.P.: 2006, Solar Phys. 233, 107.
Kane, R.P.: 2011, Solar Phys. 269, 451.
Kota, J., Jokipii, J.R.: 1991, Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 1979.
Krymsky, G.F., Kuzmin, A.I., Chirkov, N.P., Krivoshapkin, P.A., Skripin, G.V., Altukhov, A.M.: 1966, Geomagn. Aeron. 6, 991.
Lantos, P.: 2005, Solar Phys. 229, 373.
Lockwood, J.A.: 1971, Space Sci. Rev. 12, 658.
Lockwood, M.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 16021.
Lockwood, J.A., Webber, W.R., Hoeksema, J.T.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7521.
Lockwood, J.A., Webber, W.R.: 1996, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 21573.
Mavromichalaki, H., Belehaki, A., Rafios, X.: 1998, Astron. Astrophys. 330, 764.
Mavromichalaki, H., Marmatsouri, E., Vassilaki, A.: 1990, Solar Phys. 125, 409.
Mavromichalaki, H., Paouris, E., Karalidi, T.: 2006, In: Solomos, N.H. (ed.) Recent Advances in Astronomy and Astrophysics, AIP Conf. Proc. 848, 184.
Mavromichalaki, H., Paouris, E., Karalidi, T.: 2007, Solar Phys. 245, 369 (Paper I).
Mavromichalaki, H., Petropoulos, B.: 1987, Earth Moon Planets 37, 79.
Moraal, H.: 1976, Space Sci. Rev. 19, 845.
Nagashima, K., Morishita, I.: 1980, Planet. Space Sci. 28, 117.
Paouris, E.: 2007, In: Mavromichalaki, H., Papaioannou, A. (eds.) Proc. Solar Extreme Events 2007, National & Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, 284.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Interscience, New York.
Potgieter, M.S.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 83, 147.
Otaola, J., Perez-Enriquez, R., Valdes-Galicia, J.F.: 1985, In: Proc. 19th ICRC 4, 93.
Usoskin, I., Kananen, H., Mursula, K., Tanskanen, P., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 9567.
Usoskin, I.G., Alanko, K., Mursula, K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2002, Solar Phys. 207, 389.
Webber, W.R., Lockwood, J.A.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8735.
Webber, W.R., Lockwood, J.A.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A09103.
Wibberenz, G., Cane, H.V.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18315.
Xanthakis, J., Mavromichalaki, H., Petropoulos, B.: 1981, Astrophys. Space Sci. 74, 303.
Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Gopalswamy, N.: 2008, Ann. Geophys. 26, 3103.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the providers of the solar, interplanetary, neutron monitor, and geomagnetic data used in this work. The coronal mass ejection index (P i) data are taken from the SOHO/LASCO CME catalog ( http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/ ). This CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. Thanks are due to our colleagues at the neutron monitor stations of the worldwide network for providing cosmic ray data. A list of these stations may be accessed at the website http://cr0.izmiran.rssi.ru/ThankYou/ and http://www.nmdb.eu . Finally, many thanks are due to the anonymous referees for their useful comments, which have significantly improved this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Belov, A. et al. Galactic Cosmic Ray Modulation and the Last Solar Minimum. Sol Phys 280, 255–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0051-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-0051-4