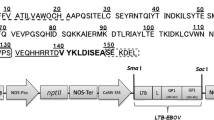
Abstract
Improving foreign protein accumulation is crucial for enhancing the commercial success of plant-based production systems since product yields have a major influence on process economics. Cereal grain evolved to store large amounts of proteins in tightly organized aggregates. In maize, γ-Zein is the major storage protein synthesized by the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and stored in specialized organelles called protein bodies (PB). Zera® (γ-Zein ER-accumulating domain) is the N-terminal proline-rich domain of γ-zein that is sufficient to induce the assembly of PB formation. Fusion of the Zera® domain to proteins of interest results in assembly of dense PB-like, ER-derived organelles, containing high concentration of recombinant protein. Our main goal was to increase recombinant protein accumulation in plants in order to enhance the efficiency of orally-delivered plant-made vaccines. It is well known that oral vaccination requires substantially higher doses than parental formulations. As a part of a project to develop a plant-made plague vaccine, we expressed our model antigen, the Yersinia pestis F1-V antigen fusion protein, with and without a fused Zera® domain. We demonstrated that Zera®-F1-V protein accumulation was at least 3× higher than F1-V alone when expressed in three different host plant systems: Ncotiana benthamiana, Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and Nicotiana tabacum NT1 cells. We confirmed the feasibility of using Zera® technology to induce protein body formation in non-seed tissues. Zera® expression and accumulation did not affect plant development and growth. These results confirmed the potential exploitation of Zera® technology to substantially increase the accumulation of value-added proteins in plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aa:
-
Amino acid
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FD:
-
Freeze-dried (powdered)
- NT1:
-
Nicotiana tabacum NT1 cells
- PB:
-
Protein body
- SP:
-
Signal peptide
- TSP:
-
Total soluble protein
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- W.T:
-
Wild type
- Zera® :
-
γ-Zein ER-accumulating domain
References
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Molecular biology of the cell, 4th edn. Garland Science, New York
Alvarez ML, Guelman S, Halford NG, Lustig S, Reggiardo MI, Riabushkina N, Shewry P, Stein J, Vallejos RH (2000) Silencing of HMW glutenins in transgenic wheat expressing extra HMW subunits. Theor Appl Genet 100:319–327
Alvarez ML, Pinyerd HL, Crisantes JD, Rigano MM, Pinkhasov J, Walmsley AM, Mason HS, Cardineau GA (2006) Plant-made subunit vaccine against pneumonic and bubonic plague is orally immunogenic in mice. Vaccine 24:2477–2490
Alvarez ML, Pinyerd HL, Topal E, Cardineau GA (2008) P19-dependent and P19-independent reversion of F1-V gene silencing in tomato. Plant Mol Biol 68:61–79
Baschong W, Hasler H, Häner M, Kistler J, Aebi U (2003) Repetitive versus monomeric antigen presentation: direct visualization of antibody affinity and specificity. J Struct Biol 153:258–262
Becker D, Kemper E, Schell J, Materson R (1992) New plant binary vectors with selectable markers located proximal to the left T-DNA border. Plant Mol Biol 20:1195–1197
Coleman CE, Herman EM, Takasaki K, Larkins BA (1996) The maize γ-zein sequesters α-zeins and stabilizes its accumulation in protein bodies of transgenic tobacco endosperm. Plant Cell 8:2335–2345
Conrad U, Fiedler U (1998) Compartment-specific accumulation of recombinant immunoglobulins in plant cells: an essential tool for antibody production and immunomodulation of physiological functions and pathogen activity. Plant Mol Biol 38:101–109
D’Aoust M, Lerouge P, Busse U, Bilodeau P, Trépanier S, Gomord V, Faye L, Vézina L (2005) Efficient and reliable production of pharmaceuticals in alfalfa. In: Fisher R, Schillberg S (eds) Molecular farming. Wiley, Berlin, pp 1–12
Dang W, Wei ZM (2007) An optimized agrobacterium-mediated transformation for soybean for expression of binary insect resistance genes. Plant Sci 173:381–389
Doran P (2000) Foreign protein production in plant tissue cultures. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:199–204
Doran P (2006) Foreign protein degradation and instability in plants and plant tissue cultures. Trends Biotechnol 24:426–432
Du Y, Rosqvist R, Forsberg A (2002) Role of fraction 1 antigen of Yersinia pestis in inhibition of phagocytosis. Infect Immun 70:1453–1460
Fields KA, Nilles ML, Cowan C, Straley SC (1999) Virulence role of V antigen of Yersinia pestis at the bacterial surface. Infect Immun 67:5395–5408
Fisher R, Stoger E, Schillberg S, Christou P, Twyman R (2004) Plant-based production of biopharmaceuticals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:152–158
Frigerio L, Pastres A, Prada A, Vitale A (2001) Influence of KDEL on the fate of trimeric or assembly-defective phaseolin: selective use of an alternative route to vacuoles. Plant Cell 13:1109–1126
Geli MI, Torrent M, Ludevid D (1994) Two structural domains mediate two sequential events in γ-zein targeting: protein endoplasmic reticulum retention and protein body formation. Plant cell 6:1911–1922
Haq T, Mason H, Clements J, Arntzen C (1995) Oral immunization with a recombinant bacterial antigen produced in transgenic plants. Science 268:714–716
Heath D, Anderson G, Mauro M, Welkos S, Andrews G, Adamovicz J, Friedlander AM (1998) Protection against experimental bubonic and pneumonic plague by recombinant capsular F1-V antigen fusion protein vaccine. Vaccine 16:1131–1137
Hellens R, Mullineaux P (2000) A guide to Agrobacterium binary Ti vectors. Trends Plant Sci 5:446–451
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykas PJJ, Schilpperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir-and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefasiens Ti plasmid. Nature 303:179–180
Holsters M, Silva B, Van Vliet F, Genetello C, De Block M, Dhaese P, Depicker A, Inze D, Engler G, Villarroel R, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1980) The functional organization of the nopaline A. tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid 3:212–230
Hood E, Gelvin S, Melchers S, Hoekema A (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Huang Z, Mason H (2004) Conformational analysis of hepatitis B surface antigen fusions in an Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system. Plant Biotechnol J 2:241–249
Jorgensen RA, Cluster PD, English J, Que Q, Napoli CA (1996) Chalcone synthase cosuppression phenotypes in petunia flowers: comparison of sense vs. antisense constructs and single-copy vs. complex T-DNA sequences. Plant Mol Biol 31:957–973
Judge NA, Mason HS, O’Brien AD (2004) Plant cell-based intimin vaccine given orally to mice primed with intimin reduces time of Escherichia coli O157:H7 shedding in feces. Infect Immun 72:168–175
Kogan MJ, Dacol I, Gorostiza P, Lopez-Iglesias C, Pons M, Sanz F, Ludevid D, Giralt E (2001) Self-assembly of the amphipathic helix (VHLPPP) 8. A mechanism for zein protein body formation. J Mol Biol 312:907–913
Kogan MJ, Dacol I, Gorostiza P, Lopez-Iglesias C, Pons R, Pons M, Sanz F, Giralt E (2002) Supramolecular properties of the proline-rich gamma-zein N-terminal domain. Biophys J 83:1194–1204
Koncz C, Schell J (1986) The promoter of the TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol Gen Genet 204:383–396
Langridge WH (2000) Edible vaccines. Sci Am 283:66–71
Larkins B, Hurkman W (1978) Synthesis and deposition of zein in protein bodies of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 62:258–263
Lending CR, Larkins B (1989) Changes in the zein composition of protein bodies during endosperm development. Plant Cell 1:1011–1023
Li X, Wu Y, Zhang DZ, Gillikin JW, Boston RS, Franceschi VR, Okita TW (1993) Rice prolamine protein body biogenesis: a BiP-mediated process. Science 262:1054–1056
Loertscher J, Larson L, Matson CK, Parrish ML, Felthauser A, Sturm A, Tachibana C, Bard M, Wright R (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation is required for cold adaptation and regulation of sterol biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryot Cell 5:712–722
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ludevid MD, Torrent M, Martinez-Izquierdo JA, Puigdomenech P, Palau J (1984) Subcellular localization of glutelin-2 in maize (Zea mays L.) endosperm. Plant Mol Biol 3:227–234
Ludevid MD, Torrent M, Lasserre-Ramassamy S (2004) Production of peptides and proteins by accumulation in plant endoplasmic reticulum derived protein bodies. International Patent number WO2004003207
Mainieri D, Rossi M, Archinti M, Bellucci M, De Marchis F, Vavassori S, Pompa A, Arcioni S, Vitale A (2004) Zeolin: a new recombinant storage protein constructed using maize γ-zein and bean phaseolin. Plant Physiol 136:3447–3456
Mayo KJ, Gonzales BJ, Mason HS (2006) Genetic transformation of tobacco NT1 cells with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nat Protoc 1:1105–1111
Munro S, Pelham HR (1987) A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell 48:899–907
Narvàez-Vàsquez J, Orozco-Càrdenas ML, Ryan CA (1992) Differential expression of a chimeric CaMV-tomato proteinase inhibitor I gene in transformed nighshade, tobacco and alfalfa plants. Plant Mol Biol 20:1149–1157
O’Hagan DT (1992) Oral delivery of vaccines. Formulation and clinical pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 22:1–10
Pickering FS, Reis PJ (1993) Effects of abnormal supplements of methionine in wool growth of grazing sheep. Aust J Exp Agric 33:7
Samac DA, Temple SJ (2004) Development and utilization of transformation in Medicago species. In: Liang GH, Skinner DZ (eds) Genetically modified crops: their development, uses and risks. Haworth Press, New York, pp 165–202
Sambrook J, Fitsch EF, Maniatis T (1981) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Schenk BU, Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can J Bot 50:199–204
Semenza JC, Hardwick KG, Dean N, Pelham HR (1990) ERD2, a yeast gene required for the receptor-mediated retrieval of luminal ER proteins from the secretory pathway. Cell 61:1349–1357
Sitia R, Backaaman I (2003) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum protein factory. Nature 426:891–894
Sojikul P, Buehner N, Mason HS (2003) A plant signal peptide-hepatitis B surface antigen fusion protein with enhanced stability and immunogenicity expressed in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2209–2214
Sparrow P, Irwin J, Dale P, Twyman R, Ma J (2007) Pharma-planta: road testing the developing regulatory guidelines for plant-made pharmaceuticals. Transgenic Res 16:147–161
Streatfield S (2006) Mucosal immunization using recombinant plant-made vaccines. Methods 38:150–157
Streatfield S (2007) Approaches to achieve high-level heterologous protein production in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 5:2–15
Tabe LM, Higgins CM, McNabb WC, Higgins TJ (1993) Genetic engineering of grain and pasture legumes for improved nutritive value. Genetica 90:181–200
Tabe LM, Wardley-Richardson T, Ceriotti A, Aryan A, Mc Nabb W, Moore A, Higgins TJ (1995) A biotechnological approach to improving the nutritive value of alfalfa. J Anim Sci 73:2752–2759
Thanavala Y, Huang Z, Mason H (2006) Plant-derived vaccines: a look back at the highlights and a view to the challenges on the road ahead. Expert Rev Vaccin 5:249–260
Thompson C, Movva N, Tizard R, Crameri R, Davies J, Lauwereys M, Botterman J (1987) Characterization of the herbicide resistance gene bar from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. EMBO J 6:2519–2523
Torrent M, Llompart B, Lasserre-Ramassamy S, Llop-Tous I, Bastida M, Marzabal P, Westerholm-Pavinen A, Saloheimo M, Heifetz P, Ludevid D (2009) Eukaryotic protein production in designed storage organelles. BMC Biol 7:1–14
Verdaguer B, Kochko A, Ch Fux, Beachy R, Fauquet C (1998) Functional organization of the cassava vein mosaic virus promoter. Plant Mol Biol 37:1055–1067
Virgilio M, Marchis F, Bellucci M, Mainieri D, Rossi M, Benvenuto E, Arcioni S, Vitale A (2008) The human immunodeficiency virus antigen Nef forms protein bodies in leaves of transgenic tobacco when fused to zeolin. J Exp Bot 59:2815–2829
Vitale A, Pedrazzini E (2005) Recombinant pharmaceuticals from plants: the plant endomembrane system as bioreactor. Mol Interv 5:216–225
Walker KA, Sato SJ (1981) Morphogenesis in callus tissue of Medicago sativa: the role of ammonium ion in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 1:109–121
Wandelt CI, Khan MR, Craig S, Schroeder HE, Spencer D, Higgins TJ (1992) Vicilin with carboxy-terminal KDEL is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum and accumulates at high levels in the leaves of transgenic plants. Plant J 2:181–192
Zhang Y, Darlington HD, Jones HD, Halford NG, Napier JA, Davey MR, Lazzeri PA, Shewry PR (2003) Expression of the gamma-zein protein of maize in seeds of transgenic barley: effects on grain composition and properties. Theor Appl Genet 106:1139–1146
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge Joyce Van Eke (Boyce Thompson Institute, Ithaca, NY) for providing the tobacco NT1 calli; Stephen Temple and Forage Genetics International (Nampa, ID) for alfalfa clone R2236 and alfalfa transformation protocol; and the research team at ERA biotech (Barcelona, Spain) for plasmid pUC18:Zera® and Zera® antibody. The authors are particularly grateful to Dow Agrosciences (Indianapolis, IN), ERA Biotech (Barcelona, Spain), and the ASU/ITESM Collaborative on Biotechnology Research for the partial support of this project. The authors are also very grateful with Paul Arnold for his help with the editing of the paper, and with the undergraduate students Amber Gustin, Deborah Pauley and Julliane Miller for their collaboration with plant transformation experiments and plant tissue culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, M.L., Topal, E., Martin, F. et al. Higher accumulation of F1-V fusion recombinant protein in plants after induction of protein body formation. Plant Mol Biol 72, 75–89 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9552-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9552-4