Abstract
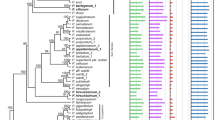
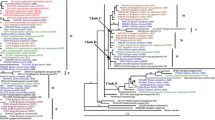
Molecular evolution of the second largest subunit of low copy nuclear RNA polymerase II (RPB2) in allotetrploid StH genomic species of Elymus is characterized here. Our study first reported a 39-bp MITE stowaway element insertion in the genic region of RPB2 gene for all tetraploid Elymus St genome and diploid Pseudoroegneria spicata and P. stipifolia St genome. The sequences on 3′-end are highly conserved, with AGTA in all sequences but H10339 (E. fibrosis), in which the AGTA was replaced with AGAA. All 12 Stowaway-containing sequences encompassed a 9 bp conserved TIRs (GAGGGAGTA). Interestingly, the 5′-end sequence of GGTA which was changed to AGTA or deleted resulted in Stowaway excision in the H genome of Elymus sepcies, in which Stowaway excision did not leave footprint. Another two large insertions in all St genome sequences are also transposable-like elements detected in the genic region of RPB2 gene. Our results indicated that these three transposable element indels have occurred prior to polyploidization, and shaped the homoeologous RPB2 loci in St and H genome of Eymus species. Nucleotide diversity analysis suggested that the RPB2 sequence may evolve faster in the polyploid species than in the diploids. Higher level of polymorphism and genome-specific amplicons generated by this gene indicated that RPB2 is an excellent tool for investigating the phylogeny and evolutionary dynamics of speciation, and the mode of polyploidy formation in Elymus species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agafonov AV (2004) Intraspecific structure and reproductive relationships between Elymus mutabilis and E. transbaicalensis (Poaceae) in southern Siberia from the viewpoint of taxonomical genetics. Russ J Genet 11:1229–1238
Barrier M, Robichaux RH, Purugganan MD (2001) Accelerated regulatory gene evolution in an adaptive radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10208–10213
Brumfield RT, Beeri P, Nickerson DA, Edwards SV (2003) The utility of single nucleotide polymorphisms in inferences of population history. Trends Ecol 18:249–256
Bureau TE, Wessler SR (1992) Tourist: a large family of small inverted repeat elements frequently associated with maize genes. Plant Cell 4:1283–1294
Bureau TE, Wessler SR (1994) Stowaway: a new family of inverted repeat elements associated with the genes of both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. Plant Cell 6:907–916
Caldwell KS, Dvorak J, Lagudah ES, Akhunov E, Luo MC, Wolters P, Powell W (2004) Sequence polymorphism in polyploid wheat and their D-genome diploid ancestor. Genetics 167:941–947
Charrier B, Foucher F, Kondorosi E, D’Aubenton-Carafa Y, Thermes C, Kondorosi A, Ratet P (1999) Bigfoot: a new family of MITE elements characterized from the Medicago genus. Plant J 18:431–441
Comai L, Tyagi AP, Winter K, Holmes-Davis R, Reynolds SH, Stevens Y, Byers B (2000) Phenotypic instability and rapid gene silencing in newly formed Arabidopsis allotetraploids. Plant Cell 12:1551–1567
Denton AL (1997) Evolution of RNA polymerase II introns: ancient polymorphism and paraphyly in the genus Rhododendron. Ph.D. dissertation. University of Washington, Seattle
Denton AL, McConaughy BL, Hall BD (1998) Usefulness of RNA polymerase II coding sequences for estimation of green plant phylogeny. Mol Biol Evol 15:1082–1085
Dewey DR (1971) Synthetic hybrids of Hordeum bogdanii with Elymus canadensis and Sitanion hystrix. Am J Bot 58:902–908
Dewey DR (1982) Genomic and phylogenetic relationships among North American perennial Triticeae. In: Estes JR, Tyrl RJ, Brunken JN (eds) Grasses and grasslands: systematics and ecology. University of Oklahoma Press, pp 51–88
Dewey DR (1984) The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization within the perennial Triticeae. In: Gustafson JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement. Plenum Press, New York, pp 209–279
Engels WR, Johnson-Schlitz DM, Eggleston WB, Sved J (1990) High-frequency P element loss in Drosophila is homolog dependent. Cell 62:515–525
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Feschotte C, Jiang N, Wessler SR (2002) Plant transposable elements: where genetics meets genomics. Nat Rev Genet 3:329–341
Fu Y-X, Li W-H (1993) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics 133:693–709
Gibson TJ, Spring J (1998) Genetic redundancy in vertebrates: polypoidy and persistence of genes encoding multidomain proteins. Trends Genet 14:46–49
Helfgott DM, Mason-Gamer RJ (2004) The evolution of North American Elymus (Triticeae, Poaceae) allotetraploids: evidence from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene sequences. Syst Bot 29:850–861
Ishiguro A, Kimura M, Yasui K, Iwata A, Ueda S, Ishihama A (1998) Two large subunits of the fission yeast RNA polymerase II provide platforms for the assembly of small subunits. J Mol Biol 279:703–712
Jensen KB (1990) Cytology, fertility, and morphology of Elymus kengii (Keng) Tzvelev and E. grandiglumis (Keng) A. Löve (Triticeae: Poaceae). Genome 33:563–570
Jensen KB (1993) Cytology of Elymus magellanicus and its interspecific hybrids with P. spicata, H. violaceum, E. subsecundus, E. lanceolatus, and E. glaucus (Poaceae: Triticeae). Genome 36:72–76
Jensen KB, Salomon B (1995) Cytogenetics and morphology of Elymus panormitanus var. heterophyllus (Keng) À. Löve and its relationship to Elymus panormitanus (Poaceae: Triticeae). Int J Plant Sci 156:731–739
Jensen KB, Liu ZW, Lu BR, Salomon B (1994) Biosystematic study of hexaploids Elymus tschimganicus and E. glaucissimus. I. Morphology and genomic constitution. Chromosome Res 2:209–215
Junghans H, Metzlaff M (1990) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of total plant DNA. Biotechniques 8:176–177
Kashkush K, Feldman M, Levy AA (2002) Gene loss, silencing and activation in a newly synthesized wheat allotetraploid. Genetics 160:1651–1659
Kolodziej PA, Woychik N, Liao S, Young RA (1990) RNA polymerase II subunit composition, stoichiometry, and phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 10:1915–1920
Larkin R, Guilfoyle T (1993) The second largest subunit of RNA polymerase II from Arabibopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1038
Lawton-Rauh A, Robichaux RH, Purugganan MD (2003) Patterns of nucleotide variation in homoeologous regulatory genes in the allotetraploid Hawaiian silversword alliance (Asteraceae). Mol Ecol 12:1301–1313
Liu B, Wendel JF (2003) Epigenetic phenomena and the evolution of plant allopolyploids genome evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:365–379
Liu Q, Ge S, Tang H, Zhang X, Zhu G, Lu BR (2006) Phylogenetic relationships in Elymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) based on the nuclear ribosomal transcribed spacer and chloroplast trnL-F sequences. New Phytologist 170:411–420
Löve Á (1984) Conspectus of the Triticeae. Feddes Repert 95:425–521
Manninen I, Schukman AH (1993) BARE-1, a copia-like retroelement in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Mol Biol 22:829–846
Mason-Gamer RJ (2001) Origin of North America Elymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) allotetraploids based of granule-bound starch synthase gene sequences. Syst Bot 26:757–758
Mason-Gamer RJ, Orme NL, Anderson CM (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of North American Elymus and the monogenomic Triticeae (Poaceae) using three chloroplast DNA data sets. Genome 45:991–1002
McMillan E, Sun GL (2004) Genetic relationships of tetraploid Elymus species and their genomic donor species inferred from polymerase chain reaction-restriction length polymorphism analysis of chloroplast gene regions. Theor Appl Genet 108:535–542
Oxelman B, Yoshikawa N, McConaughy BL, Luo J, Denton AL, Hall BD (2004) RPB2 gene phylogeny in flowering plants, with particular emphasis on asterids. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:462–479
Panaud O, Vitte C, Hivert J, Muzlak S, Talag J, Brar D, Sarr A (2002) Characterization of transposable elements in the genome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using representational difference analysis (RDA). Mol Genet Genom 268:113–121
Petersen G, Seberg O (2000) Phylogenetic evidence for excision of Stowaway miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements in Triticeae (Poaceae). Mol Biol Evol 17:1589–1596
Redinbaugh MG, Jones TA, Zhang Y (2000) Ubiquity of the St chloroplast genome in St-containing Triticeae polyploids. Genome 43:846–852
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2005) DNA sequence polymorphism, version 4.10.4.; DNAsp4 computer software. Barcelona University, Barcelona, Spain
Sabot F, Guyot R, Wicker T, Chantret N, Laubin B, Chalhoub B, Leroy P, Sourdille P, Bernard M (2005) Updating of transposable element annotations from large wheat genomic sequences reveals diverse activities and gene associations. Mol Gen Genom 274:119–130
Schulman AH, Kalendar R (2005) A movable feast: diverse retrotransposons and their contribution to barley genome dynamics. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:598–605
Sidow A, Thomas K (1993) A molecular evolutionary framework for eukaryotic model organisms. Curr Biol 4:596–603
Small RL, Wendel JF (2000) Phylogeny, duplication, and intraspecific variation of Adh sequences in New World diploid cottons (Gossypium L., Malvaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 16:73–84
Small RL, Wendel JF (2002) Differential evolutionary dynamics of duplicated paralogous Adh loci in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium). Mol Biol Evol 19:597–607
Small RL, Ryburn JA, Cronn RC, Seelanan T, Wendel JF (1998) The tortoise and the hare. Choosing between noncoding plastome and unclear Adh sequences for phylogeny reconstruction in a recently diverged plant group. Am J Bot 85:1301–1315
Small RL, Ryburn JA, Wendel JF (1999) Low levels of nucleotide diversity at homoeologous Adh loci in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium L.). Mol Biol Evol 16:491–501
Small RL, Cronn RC, Wendel JF (2004) Use of nuclear genes for phylogeny reconstruction in plants. Aust Syst Bot 17:145–170
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Tate JA (2003) Advances in the study of polyploidy since plant speciation. New Phytol 161:173–191
Song WY, Pi LY, Bureau TE, Ronald PC (1998). Identification and characterization of 14 transposon-like elements in the noncoding regions of members of the Xa21 family of disease resistance genes in rice. Mol Gen Genet 258:449–456
Sweetser D, Nonet M, Young RA (1987) Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1192–1196
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP beta version 4.0b2. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony – Macintosh version. Sinaeur Associates, Sunderland, MA
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation of hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmouguin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Thuriaux P, Sentenac A (1992) Yeast nuclear RNA polymerases. In: Jones E, Pringle J, Broach J (eds) The molecular and cellular biology of the yeast Saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 1–48
Torabinejad J, Mueller RJ (1993) Genome Constitution of the Australian hexaploid grass Elymus scabrus (Poaceae: Triticeae). Genome 36:147–151
Wang RR-C, von Bothmer R, Dvorak J, Fedak G, Linde-Laursen I, Muramatsu M (1994) Genome symbols in the Triticeae. In: Wang RR-C, Jensen KB, Jaussi C (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd international Triticeae symposium, June 20–24, 1994, Logan, Utah. Utah State University Publication Design and Production, Logan, pp 29–34
Warrilow D, Symons RH (1996) Sequence analysis of the second-largest subunit of tomato RNA polymerase II. Plant Mol Biol 30:337–342
Watterson GA (1975) On the number of segregation sites in genetical models without recombination. Theor Popul Biol 7:256–276
Wessler SR, Bureau TE, White SE (1995). LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: important players in the evolution of plant genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:814–821
Wicker T, Guyot R, Yahiaoui N, Keller B (2003a) CACTA transposons in Triticeae. A diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Physiol 132:52–63
Wicker T, Yahiaoui N, Guyot R, Schlagenhauf E, Liu ZD, Dubcovsky J, Keller B (2003b) Rapid genome divergence at orthologous low molecular weight glutenin loci of the A and Am genome of wheat. Plant Cell 15:1186–1197
Xu DH, Ban T (2004) Phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships between Elymus humidus and other Elymus species based on sequencing of non-coding regions of cpDNA and AFLP of unclear DNA. Theor Appl Genet 108:1443–1448
Xu ZN, Yan XH, Maurais S, Fu HH, O’Brien DG, Mottinger J, Dooner HK (2004) Jittery, a mutator distant relative with a paradoxical mobile behavior: excision without reinsertion. Plant Cell 16:1105–1114
Zhang Q, Arbuckle J, Wesssler SR (2000) Recent, extensive, and preferential insertion of members of the miniature inverted-repeat transposable element family Heartbreaker into genic region of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1160–1165
Acknowledgements
This research was supported with grants from NSERC, a Senate Research Grant at Saint Mary’s University. Thanks go to Dr. Björn Salomon at Swedish University of Agricultural Science and Regional Plant Introduction Station, USDA for kindly supplying the seeds used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G., Daley, T. & Ni, Y. Molecular evolution and genome divergence at RPB2 gene of the St and H genome in Elymus species. Plant Mol Biol 64, 645–655 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9183-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9183-6