Abstract
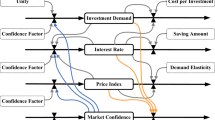
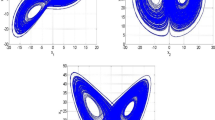
In this paper, the finite-time stabilization of nonlinear chaotic financial system (NCFS) by considering market confidence and ethics risk has been investigated. In order to address the stabilization problem of NCFS in the presence of model uncertainties and external disturbances, a robust adaptive finite-time stabilizer has been designed based on a finite-time disturbance observer (FTDO). By utilization of the proposed FTDO, the exact estimation of imposed perturbations is achieved in the sense of finite-time stability, such that a better transient performance can be attained compared with Lyapunov parameter estimation methods. Furthermore, on the basis of proposed FTDO, the continuous control input is developed, so that it avoids the possible chattering effects, and as a result, a free-chattering terminal sliding mode control is achieved in order to drive the state errors of the financial system toward zero in finite time. The investigated adaptive observer-based control strategy can keep the original structure of the system and can be implemented to stabilize other chaotic systems including dynamical economic systems. Finally, via some numerical simulations, the efficiency and reliability of the proposed approach has been illustrated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., Pi, D., Wang, B.: Enhanced global flower pollination algorithm for parameter identification of chaotic and hyper-chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(2), 1343–1358 (2019)
Asadollahi, M., Ghiasi, A.R., Badamchizadeh, M.A.: Adaptive synchronization of chaotic systems with hysteresis quantizer input. ISA Trans. 98, 137–148 (2020)
Al-khedhairi, A., Matouk, A., Khan, I.: Chaotic dynamics and chaos control for the fractional-order geomagnetic field model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 128, 390–401 (2019)
Lian, H.H., Xiao, S.P., Wang, Z., Zhang, X.H., Xiao, H.Q.: Further results on sampled-data synchronization control for chaotic neural networks with actuator saturation. Neurocomputing 346, 30–37 (2019)
Ott, E., Grebogi, C., Yorke, J.A.: Controlling chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64(11), 1196 (1990)
Mobayen, S.: Chaos synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems using composite nonlinear feedback based integral sliding mode control. ISA Trans. 77, 100–111 (2018)
Shukla, M.K., Sharma, B.: Control and synchronization of a class of uncertain fractional order chaotic systems via adaptive backstepping control. Asian J. Control 20(2), 707–720 (2018)
Durdu, A., Uyaroğlu, Y.: The shortest synchronization time with optimal fractional order value using a novel chaotic attractor based on secure communication. Chaos Solitons Fractals 104, 98–106 (2017)
Zhao, L., Yang, G.H.: Adaptive sliding mode fault tolerant control for nonlinearly chaotic systems against dos attack and network faults. J. Franklin Inst. 354(15), 6520–6535 (2017)
Li, Q., Liu, S., Chen, Y.: Combination event-triggered adaptive networked synchronization communication for nonlinear uncertain fractional-order chaotic systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 333, 521–535 (2018)
Zhou, T., Zuo, Z., Wang, Y.: Quantizer-based triggered control for chaotic synchronization with information constraints. IEEE Trans. cybern. 48(8), 2500–2508 (2017)
Harshavarthini, S., Sakthivel, R., Ma, Y.K., Muslim, M.: Finite-time resilient fault-tolerant investment policy scheme for chaotic nonlinear finance system. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 132, 109567 (2020)
Tacha, O., Munoz-Pacheco, J., Zambrano-Serrano, E., Stouboulos, I., Pham, V.T.: Determining the chaotic behavior in a fractional-order finance system with negative parameters. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(2), 1303–1317 (2018)
Soradi-Zeid, S., Jahanshahi, H., Yousefpour, A., Bekiros, S.: King algorithm: a novel optimization approach based on variable-order fractional calculus with application in chaotic financial systems. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 132, 109569 (2020)
Hajipour, A., Tavakoli, H.: Analysis and circuit simulation of a novel nonlinear fractional incommensurate order financial system. Optik 127(22), 10643–10652 (2016)
Huang, C., Cao, J.: Active control strategy for synchronization and anti-synchronization of a fractional chaotic financial system. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 473, 262–275 (2017)
Brock, W.A., Hsieh, D.A., LeBaron, B.D., Brock, W.E., et al.: Nonlinear Dynamics, Chaos, and Instability: Statistical Theory and Economic Evidence. MIT press, Cambridge (1991)
Chen, W.C.: Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in a fractional-order financial system. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 36(5), 1305–1314 (2008)
Wang, Z., Huang, X., Shen, H.: Control of an uncertain fractional order economic system via adaptive sliding mode. Neurocomputing 83, 83–88 (2012)
Xin, B., Chen, T., Ma, J.: Neimark-sacker bifurcation in a discrete-time financial system. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 2010,(2010)
Mircea, G., Neamţu, M., Bundău, O., OPRIS, D.: Uncertain and stochastic financial models with multiple delays. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 22(06), 1250131 (2012)
Yu, H., Cai, G., Li, Y.: Dynamic analysis and control of a new hyperchaotic finance system. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(3), 2171–2182 (2012)
Xin, B., Li, Y.: 0-1 test for chaos in a fractional order financial system with investment incentive. In: Abstract and Applied Analysis, vol. 2013. Hindawi (2013)
Xin, B., Peng, W., Kwon, Y., Liu, Y.: Modeling, discretization, and hyperchaos detection of conformable derivative approach to a financial system with market confidence and ethics risk. Adv. Diff. Equ. 2019(1), 138 (2019)
Earle, T.C.: Trust, confidence, and the 2008 global financial crisis. Risk Anal. Int. J. 29(6), 785–792 (2009)
Hiltzik, M.: The New Deal: A Modern History. Simon and Schuster, New York (2011)
Derwall, J., Koedijk, K., Ter Horst, J.: A tale of values-driven and profit-seeking social investors. J. Bank. Finance 35(8), 2137–2147 (2011)
Rasmussen, D.C.: Adam smith on what is wrong with economic inequality. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 110(2), 342 (2016)
Xin, B., Zhang, J.: Finite-time stabilizing a fractional-order chaotic financial system with market confidence. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 1399–1409 (2015)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 38(3), 751–766 (2000)
Ma, J., Park, J.H., Xu, S.: Global adaptive finite-time control for uncertain nonlinear systems with actuator faults and unknown control directions. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2533–2545 (2019)
Zhang, C., Li, Y., Qi, G., Sheng, A.: Distributed finite-time control for coordinated circumnavigation with multiple non-holonomic robots. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(1), 573–588 (2019)
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Zhao, W.: Finite-time prescribed performance control of mems gyroscopes. Nonlinear Dyn. 101, 1–12 (2020)
Rabiee, H., Ataei, M., Ekramian, M.: Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control based on adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer for uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 109, 108515 (2019)
Yu, X., Yang, J., Li, S.: Disturbance observer-based autonomous landing control of unmanned helicopters on moving shipboard. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(1), 131–150 (2020)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Continuous finite-time stabilization of the translational and rotational double integrators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 43(5), 678–682 (1998)
Zuo, Z., Tie, L.: Distributed robust finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 47(6), 1366–1375 (2016)
Zou, A.M., de Ruiter, A.H., Kumar, K.D.: Distributed finite-time velocity-free attitude coordination control for spacecraft formations. Automatica 67, 46–53 (2016)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Geometric homogeneity with applications to finite-time stability. Math. Control Signals Syst. 17(2), 101–127 (2005)
Feng, Y., Han, F., Yu, X.: Chattering free full-order sliding-mode control. Automatica 50(4), 1310–1314 (2014)
Mobayen, S., Ma, J., Pujol-Vazquez, G., Acho, L., Zhu, Q.: Adaptive finite-time stabilization of chaotic flow with a single unstable node using a nonlinear function-based global sliding mode. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Elect. Eng. 43(1), 339–347 (2019)
Xi, X., Mobayen, S., Ren, H., Jafari, S.: Robust finite-time synchronization of a class of chaotic systems via adaptive global sliding mode control. J. Vib. Control 24(17), 3842–3854 (2018)
Wang, Z.W., She, J.H., Wang, G.J.: Adaptive equivalent-input-disturbance approach to improving disturbance-rejection performance. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 17, 1–12 (2020)
Mobki, H., Sabegh, A.M., Azizi, A., Ouakad, H.M.: On the implementation of adaptive sliding mode robust controller in the stabilization of electrically actuated micro-tunable capacitor. Microsyst. Technol. 26, 1–14 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaei, M.J., Mirzaei, M., Aslmostafa, E. et al. Robust observer-based stabilizer for perturbed nonlinear complex financial systems with market confidence and ethics risks by finite-time integral sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn 105, 2283–2297 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06695-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06695-7