Abstract
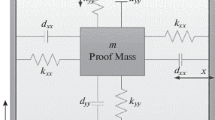
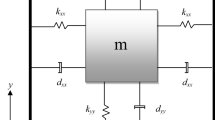
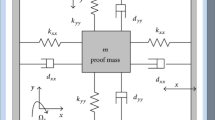
This paper addresses the finite-time prescribed performance control of MEMS gyroscopes. From the perspective of practical engineering, this paper arranges the desirable transient and steady-state performances according to the engineering requirements in the controller design procedure. For the tracking performance, prescribed performance control is studied to limited the steady-state error and the maximum overshoot. For the prescribed settling time, super-twisting sliding mode control and nonsingular terminal sliding mode control are employed to achieve finite-time convergence, respectively. The system stability is verified via Lyapunov approach. Through simulation tests, it is demonstrated that prescribed performance and finite-time convergence can be obtained under the proposed control scheme.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park, S., Horowitz, R.: Adaptive control for the conventional mode of operation of MEMS gyroscopes. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 12(1), 101–108 (2003)
Park, S., Horowitz, R., Hong, S.K., Nam, Y.: Trajectory-switching algorithm for a MEMS gyroscope. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56(6), 2561–2569 (2007)
Fei, J., Batur, C.: A novel adaptive sliding mode control with application to mems gyroscope. ISA Trans. 48(1), 73–78 (2009)
Yue, F., Li, X.: Adaptive sliding mode control based on friction compensation for opto-electronic tracking system using neural network approximations. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(4), 2601–2612 (2019)
Zou, W., Ahn, C.K., Xiang, Z.: Fuzzy-approximation-based distributed fault-tolerant consensus for heterogeneous switched nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3009730
Xu, B., Shou, Y., Luo, J., Pu, H., Shi, Z.: Neural learning control of strict-feedback systems using disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(5), 1296–1307 (2019)
Li, S., Ahn, C.K., Guo, J., Xiang, Z.: Neural network-based sampled-data control for switched uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2954231
Gao, F., Chen, W., Li, Z., Li, J., Xu, B.: Neural network-based distributed cooperative learning control for multiagent systems via event-triggered communication. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(2), 407–419 (2020)
He, W., Dong, Y.: Adaptive fuzzy neural network control for a constrained robot using impedance learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(4), 1174–1186 (2018)
He, W., Gao, H., Zhou, C., Yang, C., Li, Z.: Reinforcement learning control of a flexible two-link manipulator: an experimental investigation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.2975232
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Wei, Q., Yang, T., Zhang, P.: Serial-parallel estimation model-based sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.2981807
Xu, B., Wang, X., Chen, W., Shi, P.: Robust intelligent control of SISO nonlinear systems using switching mechanism. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2954231
Deng, Y., Zhang, X., Im, N., Zhang, G., Zhang, Q.: Model-based event-triggered tracking control of underactuated surface vessels with minimum learning parameters. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2951709
Li, T.S., Wang, D., Feng, G., Tong, S.C.: A DSC approach to robust adaptive NN tracking control for strict-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Cybern. 40(3), 915–927 (2010)
Fei, J., Yan, W.: Adaptive control of mems gyroscope using global fast terminal sliding mode control and fuzzy-neural-network. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(1), 103–116 (2014)
Guo, Y., Xu, B., Zhang, R.: Terminal sliding mode control of mems gyroscopes with finite-time learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3018107
Fei, J., Feng, Z.: Adaptive fuzzy super-twisting sliding mode control for microgyroscope. Complexity Article no.6942642 (2019)
Van, M., Ge, S.S., Ren, H.: Finite time fault tolerant control for robot manipulators using time delay estimation and continuous nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(7), 1681–1693 (2017)
Xu, B.: Composite learning finite-time control with application to quadrotors. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 48(10), 1806–1815 (2018)
Li, J., Du, H., Cheng, Y., Wen, G., Chen, X., Jiang, C.: Position tracking control for permanent magnet linear motor via fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2595–2605 (2019)
Fei, J., Liang, X.: Adaptive backstepping fuzzy neural network fractional-order control of microgyroscope using a nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller. Complexity Article no.5246074 (2018)
Rahmani, M., Komijani, H., Ghanbari, A., Ettefagh, M.M.: Optimal novel super-twisting PID sliding mode control of a MEMS gyroscope based on multi-objective bat algorithm. Microsyst. Technol. 24(11), 2835–2846 (2018)
Xu, B., Zhang, R., Li, S., He, W., Shi, Z.: Composite neural learning-based nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(4), 1375–1386 (2020)
Xu, B., Shi, Z., Sun, F., He, W.: Barrier lyapunov function based learning control of hypersonic flight vehicle with AOA constraint and actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(3), 1047–1057 (2018)
Jin, X.: Adaptive fixed-time control for MIMO nonlinear systems with asymmetric output constraints using universal barrier functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64(7), 3046–3053 (2019)
Jin, X.: Fault tolerant nonrepetitive trajectory tracking for MIMO output constrained nonlinear systems using iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(8), 3180–3190 (2019)
Jin, X.: Nonrepetitive leader-follower formation tracking for multiagent systems with LOS range and angle constraints using iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(5), 1748–1758 (2019)
Jing, C., Xu, H., Niu, X.: Adaptive sliding mode disturbance rejection control with prescribed performance for robotic manipulators. ISA Trans. 91, 41–51 (2019)
Si, H., Shao, X., Zhang, W.: MLP-based neural guaranteed performance control for MEMS gyroscope with logarithmic quantizer. IEEE Access 8, 38596–38605 (2020)
Zhu, Y., Qiao, J., Guo, L.: Adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer-based composite control with prescribed performance of space manipulators for target capturing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(3), 1973–1983 (2019)
Pishrobat, M.H., Keighobadi, J.: Robust output regulation of a triaxial MEMS gyroscope via nonlinear active disturbance rejection. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 28, 1830–1851 (2018)
Yang, Y., Hua, C., Guan, X.: Finite time control design for bilateral teleoperation system with position synchronization error constrained. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(3), 609–619 (2016)
Yu, S., Yu, X., Shirinzadeh, B., Man, Z.: Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica 41(11), 1957–1964 (2005)
Li, S., Ahn, C.K., Xiang, Z.: Command filter based adaptive fuzzy finite-time control for switched nonlinear systems using state-dependent switching method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2965917
Ding, S.H., Chen, W.H., Mei, K.Q., Smith, D.M.: Disturbance observer design for nonlinear systems represented by input–output models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(2), 1222–1232 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This work was supported in part by the Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality under Grant JCYJ20190806154612782, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61933010 and in part by the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University under Grant CX201954.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Xu, B. & Zhao, W. Finite-time prescribed performance control of MEMS gyroscopes. Nonlinear Dyn 101, 2223–2234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05959-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05959-y