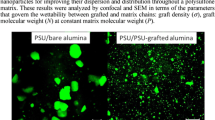
Surface-treated and untreated alumina nanoparticles were mixed with a polycarbonate matrix at different weight percentages and the mechanical properties of the nanocomposites produced were determined by subjecting them to quasi-static tension and Charpy impact tests. The results obtained showed that the surface treatment of nanoparticles had improved their mechanical properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Tehrani, A. Y. Boroujeni, T. B. Hartman, T. P. Haugh, S. W. Case, and M. S. Al-Haik, “Mechanical characterization and impact damage assessment of a woven-carbon-fiber reinforced carbon nanotube–epoxy composite,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 75, 42–48 (2013).
J. S. Park, S J Gwon, Y. M. Lim, and Y. Ch. Nho, “Influence of the stretching temperature on an alumina-filled microporous high-density polyethylene membrane,” Mater. Des., 31, 3215–3219 (2010).
S. Siengchin, J. Karger-Kocsis, and R. Thomann, “Alumina-filled polystyrene micro- and nanocomposites prepared by melt mixing with and without latex precompounding: Structure and properties,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 105, 2963–2972 (2007)..
S. Fu, Yu. Wang, and Ya. Wang, “Tension testing of polycarbonate at high strain rates,” Polym. Test., 28, 724–729 (2009)..
Q. H. Shaha and Y. A. Abkar, “Effect of distance from the support on the penetration mechanism of clamped circular polycarbonate armor plates,” Int. J. Impact Eng., 35, 1244–1250 (2008)..
Q. H. Shaha, “Impact resistance of a rectangular polycarbonate armor plate subjected to single and multiple impacts,” Int. J. Impact Eng., 36, 1128–1135 (2009).
H. Vahabi, O. Eterradossi, L. Ferry, C. Longuet, R. Sonnier, and J. M. Lopez-Cuesta, “Polycarbonate nanocomposite with improved fire behavior, physical and psychophysical transparency,” Eur. Polym. J., 49, No. 2, 319–327 (2013).
M. U. Orden, D. Pascual, A. Antelo, J. A. Andrés, V. Lorenzo, and J. M. Urreaga, “Polymer degradation during the melt processing of clay-reinforced polycarbonate nanocomposites,” Polymer Degrad. Stab., 98, No. 6, 1110–1117 (2013).
P. Jindal, S. Pande, P. Sharma, V. Mangla, A. Chaudhury, D. Patel, B. P. Singh, R. B. Mathur, and M. Goyal, “High strain rate behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotube–polycarbonate composites,” Composites: Part B: Eng., 45, No. 1, 417–422 (2013).
T. Hanemann, J. Haußelt, and E. Ritzhaupt-Kleissl, “Compounding, microinjection moulding and characterisation of polycarbonate-nanosized alumina composites for application in microoptics,” Microsyst. Technol., 15, 421–427 (2009)..
A. Chandra, L. S. Turng, P. Gopalan, R. M. Rowell, and S. Gong, “Study of utilizing thin polymer surface coating on the nanoparticles for melt compounding of polycarbonate/alumina nanocomposites and their optical properties,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 68, 768–776 (2008)..
A. Christmann, P. Ienny, J. C. Quantin, A. S. Caro-Bretelle, and J. M. Lopez-Cuesta, “Mechanical behaviour at large strain of polycarbonate nanocomposites during uniaxial tensile test,” Polym., 52, 4033–4044 (2011).
Xi. Zhang and L. C. Simon, “In situ polymerization of hybrid polyethylene-alumina nanocomposites,” Macromol. Mater. Eng., 290, 573–583 (2005)..
S. Zhao, L. S. Schadleer, R. Duncan, H. Hillborg, and T. Auletta, “Mechanisms leading to improved mechanical performance in nanoscale alumina filled epoxy,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 68, 2965–2975 (2008)..
S. C. Zunjarrao and R. P. Singh, “Characterization of the fracture behavior of epoxy reinforced with nanometer and micrometer-sized aluminum particles,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 66, 2296–2305 (2006).
L. T. Truong, Å. Larsen, B. Holme, F. K. Hansen, and J. Roots, “Morphology of syndiotactic polypropylene/alumina nanocomposites,” Polym., 52, 1116–1123 (2011).
Zh. Guo, T. Pereira, O. Choi, Y. Wang, and H. T. Hahn, “Surface-functionalized alumina nanoparticle-filled polymeric nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties,” J. Mater. Chem., 16, 2800–2808 (2006)..
URL:www.plastics.bayer.com/Products/Makrolon/ProductList/201305212210/Makrolon-2807.aspx; Bayer Materal Science AG, Polycarbonates Business Unit.August, 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 51, No. 3, pp. 491–504 , May-June, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirchakhmaghi, S., Nia, A.A., Azizpour, G. et al. The Effect of surface Treatment of Alumina NanoParticles with a Silane Coupling Agent on the Mechanical Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites. Mech Compos Mater 51, 347–358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-015-9506-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-015-9506-7