Abstract
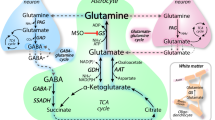
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is associated with increased ammonia levels in plasma and brain. Different treatment strategies have been developed to ameliorate the detrimental effects of the ammonia load. One such strategy is based on the finding of a low level of the branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) in plasma of patients suffering from HE and the assumption that in particular isoleucine could be beneficial to brain energy metabolism as it is metabolized to the tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediate and precursor succinyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA, respectively. This would enable de novo synthesis of glutamine via α-ketoglutarate and glutamate and at the same time stimulate oxidative metabolism. The present mini-review summarizes the metabolic basis for this hypothesis delineating studies in the brain in vivo as well as in cultured neural cells aimed at elucidating the metabolism of the BCAAs focusing on isoleucine. The conclusion is that isoleucine appears at least partially to act in this fashion albeit its metabolism is quantitatively relatively modest. In addition, a short section on the role of the BCAAs in synaptic ammonia homeostasis is included along with some thoughts on the role of the BCAAs in other pathologies such as cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams SL, Younathan ES (1971) Modulation of the kinetic properties of phosphofructokinase by ammonium ions. J Biol Chem 246(8):2464–2467
Amaral AI, Teixeira AP, Martens S, Bernal V, Sousa MF, Alves PM (2010) Metabolic alterations induced by ischemia in primary cultures of astrocytes: merging 13C NMR spectroscopy and metabolic flux analysis. J Neurochem 113(3):735–748
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98:641–653
Bak LK, Johansen ML, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2007) Among the branched-chain amino acids only valine metabolism is up-regulated in astrocytes during glutamate exposure. J Neurosci Res 86:3465–3470
Bak LK, Iversen P, Sørensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A (2009) Metabolic fate of isoleucine in a rat model of hepatic encephalopathy and in cultured neural cells exposed to ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 24:135–145
Berl S, Frigyesi TL (1968) Metabolism of [14C]leucine and [14C]acetate in sensorimotor cortex, thalamus, caudate nucleus and cerebellum of the cat. J Neurochem 15(9):965–970
Berl S, Frigyesi TL (1969) Comparison of cerebral regional metabolism of [14C]leucine following third ventricle and intravenous administration in the cat. J Neurochem 16(3):405–415
Cole JT, Mitala CM, Kundu S, Verma A, Elkind JA, Nissim I, Cohen AS (2010) Dietarybranched chain amino acids ameliorate injury-induced cognitive impairment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(1):366–371
Cooper AJ (2011) 13 N as a tracer for studying glutamate metabolism. Neurochem Int 59(4):456–464
Dadsetan S, Bak LK, Sørensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Leke R, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2011) Inhibition of glutamine synthetase induces glutamate dehydrogenase-dependent ammonia fixation into alanine in co-cultures of astrocytes and neurons. Neurochem Int 59:482–488
Dadsetan S, Sørensen M, Bak LK, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Schousboe A, Jalan R, Keiding S, Waagepetersen HS (2013) Interorgan metabolism of ornithine phenylacetate—A novel strategy for treatment of hyperammonimia. Biochem Pharmacol 85:115–123
Dam G, Keiding S, Ol M, Ott P, Buhl M, Vilstrup H, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Møller N, Sørensen M (2011) Branched-chain amino acids increase arterial blood ammonia in spite of enhanced intrinsic ammonia metabolism in patients with cirrhosis and healthy subjects. Am J Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301:G269–G277
Fischer JE, Yoshimura N, Aguirre A, James JH, Cummings MG, Abel RM, Deindoerfer F (1974) Plasma amino acids in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Effects of amino acid infusions. Am J Surg 127(1):40–47
Gjedde A, Lockwood AH, Duffy TE, Plum F (1978) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in chronically hyperammonemic rats: effect of an acute ammonia challenge. Ann Neurol 3:325–330
Hertz L, Yu ACH, Kala G, Schousboe A (2000) Neuronal-astrocytic and cytosolic-mitochondrial metabolite trafficking during brain activation, hyperammonemia and energy deprivation. Neurochem Int 37:83–102
Hindfelt B, Plum F, Duffy TE (1977) Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J Clin Invest 59:386–396
Hutson SM, Islam MM, Zaganas I (2011) Interaction between glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and L-leucine catabolic enzymes: intersecting metabolic pathways. Neurochem Int 59(4):518–524
Islam MM, Nautiyal M, Wynn RM, Mobley JA, Chuang DT, Hutson SM (2010) Branched-chain amino acid metabolon: interaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with the mitochondrial branched-chain aminotransferase (BCATm). J Biol Chem 285(1):265–276
Islam MM, Wallin R, Wynn RM, Conway M, Fujii H, Mobley JA, Chuang DT, Hutson SM (2007) A novel branched-chain amino acid metabolon. Protein-protein interactions in a supramolecular complex. J Biol Chem 282(16):11893–11903
Jalan R, Wright G, Davies NV, Hodges SJ (2007) L-Ornithine phenylacetate (OP): a novel treatment for hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy. Med Hypotheses 69:1064–1069
Johansen ML, Bak LK, Schousboe A, Iversen P, Sørensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Gjedde A, Ott P, Waagepetersen HS (2007) The metabolic role of isoleucine in detoxification of ammonia in cultured mouse neurons and astrocytes. Neurochem Int 50:1042–1051
Kala G, Hertz L (2005) Ammonia effects on pyruvate/lactate production in astrocytes-Interaction with glutamate. Neurochem Int 47:4–12
Laj JC, Cooper AJ (1986) Brain alpha-ketogkutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors. J Neurochem 47:1376–1386
Leke R, Bak LK, Anker M, Melø TM, Sørensen M, Keiding S, Vilstrup H, Ott P, Portela LV, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2011) Detoxification of ammonia in mouse cortical GABAergic cell cultures increases neuronal oxidative metabolism and reveals an emerging role for release of glucose-derived alanine. Neurotox Res 19:496–510
Lieth E, LaNoue KF, Berkich DA, Xu B, Ratz M, Taylor C, Hutson SM (2001) Nitrogen shuttling between neurons and glial cells during glutamate synthesis. J Neurochem 76:1712–1723
McKhann GM, Tower DB (1961) Ammonia toxicity and cerebral oxidative metabolism. Am J Physiol 200:420–424
Müting D, Wortmann V (1956) Über den aminosäurenhaushalt bei leberkrankheiten. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 45:1853–1856
Obel LF, Andersen KMH, Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2012) Effects of adrenergic agents on intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and metabolism of glucose in astrocytes with emphasis on pyruvate carboxylation, oxidative decarboxylation and recycling: Implications for glutamate neurotransmission and excitotoxicity. Neurotox Res 21:405–417
Olde Damink SW, Deutz NE, Dejong CH, Soeters PB, Jalan R (2002) Interorgan ammonia metabolism in liver failure. Neurochem Int 41(2–3):177–188
Ott P, Clemmesen O, Larsen FS (2005) Cerebral metabolic disturbances in the brain during acute liver failure: From hyperammonemia to energy failure and proteolysis. Neurochem Int 47:13–18
Sheen JH, Zoncu R, Kim D, Sabatini DM (2011) Defective regulation of autophagy upon leucine deprivation reveals a targetable liability of human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell 19(5):613–628
Yu ACH, Schousboe A, Hertz L (1984) Influence of pathological concentrations of ammonia on metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem 42:594–597
Yudkoff M (1997) Brain metabolism of branched-chain amino acids. Glia 21(1):92–98
Zwingmann C, Richter-Landsberg C, Brand A, Leibfritz D (2000) NMR spectroscopic study on the metabolic fate of [13C]alanine in astrocytes, neurons, and cocultures. Implications for neuron-glia interactions in neurotransmitter metabolism. Glia 32:386–303
Zwingmann C, Chatauret N, Leibfritz D, Butterworth RF (2003) Selective increase of brain lactate synthesis in experimental acute liver failure. Results of a [H-C] nuclear magnetic resonance study. Hepatology 37:420–428
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2000) A possible role of alanine for ammonia transfer between astrocytes and glutamatergic neurons. J Neurochem 75(2):471–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bak, L.K., Waagepetersen, H.S., Sørensen, M. et al. Role of branched chain amino acids in cerebral ammonia homeostasis related to hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 28, 209–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9381-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9381-7