Abstract
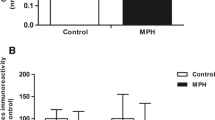
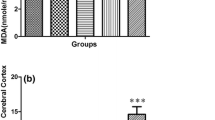
The use of psychostimulant methylphenidate has increased in recent years for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. However, the behavioral and neurochemical changes promoted by its use are not yet fully understood, particularly when used for a prolonged period during stages of brain development. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine some parameters of oxidative stress in encephalic structures of juvenile rats subjected to chronic methylphenidate treatment. Wistar rats received intraperitoneal injections of methylphenidate (2.0 mg/kg) once a day, from the 15th to the 45th day of age or an equivalent volume of 0.9% saline solution (controls). Two hours after the last injection, animals were euthanized and the encephalic structures obtained for determination of oxidative stress parameters. Results showed that methylphenidate administration increased the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase, but did not alter the levels of reactive species, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances levels and sulfhydryl group in cerebellum of rats. In striatum and hippocampus, the methylphenidate-treated rats presented a decrease in the levels of reactive species and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, but did not present changes in the sulfhydryl groups levels. In prefrontal cortex, methylphenidate promoted an increase in reactive species formation, SOD/CAT ratio, and increased the lipid peroxidation and protein damage. These findings suggest that the encephalic structures respond differently to methylphenidate treatment, at least, when administered chronically to young rats. Notably, the prefrontal cortex of juvenile rats showed greater sensitivity to oxidative effects promoted by methylphenidate in relation to other encephalic structures analyzed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Aksenov MY, Markesbery WR (2001) Changes in thiol content and expression of glutathione redox system genes in the hippocampus and cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 302:141–145
Andersen SL (2004) Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:3–18
Andreazza AC, Frey BN, Valvassori SS, Zanotto C, Gomes KM, Comim CM et al (2007) DNA damage in rats after treatment with methylphenidate. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:1282–1288
Arnsten AF (2009) Toward a new understanding of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder pathophysiology: an important role for prefrontal cortex dysfunction. CNS Drugs 23:33–41
Aylward EH, Reiss AL, Reader MJ, Singer HS, Brown JE, Denckla MB (1996) Basal ganglia volumes in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Child Neurol 11:112–115
Baez S, Segura-Aguilar J, Widersten M, Johansson AS, Mannervick B (1997) Glutathione transferases catalyse the detoxication of oxidized metabolites (o-quinones) of catecholamines and may serve as an antioxidant system preventing degenerative cellular processes. Biochem J 324:25–28
Benes FM (1998) Brain development, VII. Human brain growth spans decades. Am J Psychiatry 155:1489
Biederman J, Mick E, Faraone SV (2000) Age-dependent decline of symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: impact of remission definition and symptom type. Am J Psychiatry 157:816–818
Biederman J, Spencer T, Wilens T (2004) Evidence-based pharmacotherapy for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7:77–97
Bowler RP, Crapo JD (2002) Oxidative stress in airways: is there a role for extracellular superoxide dismutase? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:38–43
Brown MF, Yamamoto S (2003) Effects of amphetamine on mitochondrial function: role of free radicals and oxidative stress. Pharmacol & Terap 99:45–53
Castellanos FX (1997) Toward a pathophysiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin Pediatr 36:381–393
Castellanos FX, Giedd JN, Marsh WL, Hamburger SD, Vaituzis AC, Dickstein DP et al (1996) Quantitative brain magnetic resonance imaging in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:607–616
Challman TD, Lipsky JJ (2000) Methylphenidate: its pharmacology and uses. Mayo Clin Proc 75:711–721
Chase TD, Brown RE, Carrey N, Wilkinson M (2003) Daily methylphenidate administration attenuates c-fos expression in the striatum of prepubertal rats. Neuroreport 14:769–772
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dove R, Rozalski R, Gackowski D, Siomek A et al (2005) DNA repair is responsible for the presence of oxidatively damaged DNA lesions in urine. Mutat Res 574:58–66
Culmsee C, Mattson MP (2005) p53 in neuronal apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:761–777
Dinn WM, Robbins NC, Harris CL (2001) Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: neuropsychological and clinical presentation. Brain Cogn 46:114–121
Dougherty DD, Bonab AA, Spencer TJ, Rauch SL, Madras BK, Fischaman AJ (1999) Dopamine transporter density in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 354:2132–2133
Drouin C, Page M, Waterhouse B (2006) Methylphenidate enhances noradrenergic transmission and suppresses mid- and long-latency sensory responses in the primary somatosensory cortex of awake rats. J Neurophysiol 96:622–632
Fagundes AO, Rezin GT, Zanette F, Grandi E, Assis LC, Dal-Pizzol F et al (2007) Chronic administration of methylphenidate activates mitochondrial respiratory chain in brain of young rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 25:47–51
Faraone SV (2004) Genetics of adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. In: Spencer T (ed) Psychiatric clinics of North America. PA. Sauders Press, Philadelphia, pp 3030–321
Faraone SV, Sergeant J, Gillberg C, Biederman J (2003) The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: is it an American condition? World Psychiatry 2:104–113
Fukami G, Hashimoto K, Koike K, Okamura N, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2004) Effect of antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine on behavioral changes and neurotoxicity in rats after administration of metahnphetamine. Brain Res 1016:90–95
Garland EJ (1998) Pharmacotherapy of adolescent attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: challenges, choice and caveats. J Psychopharmacology 12:385–395
Gerasimov MR, Franceschi M, Volkow ND, Gifford A, Gatley SJ, Marsteller D et al (2000) Comparison between intraperitoneal and oral methylphenidate administration: A microdialysis and locomotor activity study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:51–57
Goldman LS, Genel M, Bezman RJ, Slanetz PJ (1998) Diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. JAMA 279:1100–1107
Goldman-Rakic PS, Muly EC, Williams GV (2000) D(1) receptors in prefrontal cell and circuits. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:295–301
Gomes KM, Petronilho FC, Mantovani M, Garbelotto T, Boeck CR, Dal-Pizzol F et al (2008) Antioxidant enzyme activities following acute and chronic methylphenidate treatment in young rats. Neurochem Res 33:1024–1027
Gomes KM, Inácio CG, Valvassori SS, Réus GZ, Boeck CR, Dal-Pizzol F et al (2009) Superoxide production after acute and chronic treatment with methylphenidate in young and adult rats. Neurosci Lett 465:95–98
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Greenhill LL (2001) Clinical effects of stimulant medication in attention-deficti/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In: Solanto MV, Arnsten AFT, Castellanos FX (eds) Stimulant drugs and ADHD: basic and clinical neuroscience. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 31–71
Gutteridge JMC (2001) Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 4th edn. Oxford University Press Inc, New York, p 851
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007) Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 851
Husson I, Mesplès B, Medja F, Leroux P, Kosofsky B, Gressens P (2004) Methylphenidate and Mk-801, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist: shared biological properties. Neuroscience 125:163–170
Ignarro LJ, Fukuto JM, Griscavage JM, Rogers NE, Byrns RE (1993) Oxidation of nitric oxide in aqueous solution to nitrite but not nitrate: comparison with enzymatically formed nitric oxide from L-arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8103–8107
Ikai Y, Takada M, Shinonaga Y, Mizuno N (1992) Dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area of the rat project, respectively, to the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei. Neuroscience 51:719–728
Ikai Y, Takada M, Mizuno N (1994) Single neurons in the ventral tegmental area that project to both the central and cerebellar cortical areas by way of axon collaterals. Neuroscience 61:925–934
Issy AC, Salum C, Del Bel EA (2009) Nitric oxide modulation of methylphenidate-induced disruption of prepulse inhibiton in Swiss mice. Behav Brain Res 205:475–481
Itzhak Y, Ali SF (2006) Role of nitrergic system in behavioral and neurotoxic effects of amphetamine analogs. Pharmacol Ther 109:246–262
Kirby K, Rutman LE, Bernstein H (2002) Attention-deficit/hiperactivity disorder: a therapeutic update. Curr Opin Pediatr 14:236–246
Kuczenski R, Segal DS (2001) Locomotor effects of acute and repeated threshold doses of amphetamine and methylphenidate: relative roles of dopamine and norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:876–883
Kuczenski R, Segal DS (2002) Exposure of adolescent rats to oral methylphenidate: preferential effects on extracellular norepinephrine and absence of sensitization and cross-sensitization to methamphetamine. J Neurosci 22:7264–7271
LeBel CP, Ali SF, McKee M, Bondy SC (1990) Organometal-induced increases in oxygen reactive species: the potential of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate as an index of neurotoxic damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 104:17–24
Lou H (1996) Etiology and pathogenesis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): significance of prematurity and perinatal hypoxic-haemodynamic encephalopathy. Acta Paediatr 85:1266–1271
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Machado A (2004) Neuroanatomia Funcional, 2nd edn. Atheneu, São Paulo, pp 1993–2000
Marklund SL (1985) Pyrogallol autoxidation. In: Handbook for Oxygen Radical Research. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 243–247
Martins MR, Reinke A, Petronilho FC, Gomes KM, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J (2006) Methylphenidate treatment induces oxidative stress in young rat brain. Brain Res 1078:189–197
Matés JM, Pérez-Gómez C, Núñez de Castro I (1999) Antioxidant enzymes and human diseases. Clin Biochem 32:595–603
Melchitzky DS, Lewis DA (2000) Tyrosine hydroxylase- and dopamine transporter-immunoreactive axons in the primate cerebellum. Evidence for a lobular- and laminar-specific dopamine innervation. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:466–472
Mick E, Biederman J, Prince J, Fischer MJ, Faraone SV (2002) Impact of low birth weight on attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Dev Behav Pediatr 23:16–22
Miller KJ, Castellanos FX (1998) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders. Pediatr Rev 19:373–384
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Radi R, Cassiana A, Hodara R, Quijano C, Castro L (2002) Peroxynitrite reactions and formation in mitochondria. Free Radic Biol Med 33:1451–1464
Rice D, Barone S Jr (2000) Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ Health Perspect 108:511–533
Rowland SA, Lesesne CA, Abramowitz AJ (2002) The epidemiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a public health view. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 8:162–170
Rubia K, Overmeyer S, Taylor E, Brammer M, Williams SC, Simmons A et al (1999) Hypofrontality in attention deficit hyperactivity during higher-order motor control: a study with functional MRI. Am J Psychiatry 156:891–896
Rubia K, Taylor E, Smith AB, Oksanen H, Overmeyer S, Newman S (2001) Neuropsychological analyses of impulsiveness in childhood hyperactivity. Br J Psychiatry 179:138–143
Safer DJ, Allen RP (1989) Absence of tolerance to the behavioral effects of methylphenidate in hyperactive and inattentive children. J Pediatr 115:1003–1008
Sarkar A, Bhaduri A (2001) Black tea is a powerful chemopreventor of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: comparison with its individual catechin constituents and green tea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:173–178
Scherer EB, Matté C, Ferreira AG, Gomes KM, Comim CM, Mattos C et al (2009) Methylphenidate treatment increases Na(+), K (+)-ATPase activity in the cerebrum of young and adult rats. J Neural Transm 116:1681–1687
Scherer EB, da Cunha MJ, Matté C, Schmitz F, Netto CA, Wyse AT (2010) Methylphenidate affects memory, brain-derived neurotrophic factor immunocontent and brain acetylcholinesterase activity in the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94:247–253
Schmitz F, Scherer EB, da Cunha MJ, da Cunha AA, Lima DD, Delwing D et al (2012) Chronic methylphenidate administration alters antioxidant defenses and butyrylcholinesterase activity in blood of juvenile rats. Mol Cell Biochem 361:281–288
Schweri MM, Skolnick P, Rafferty MF, Rice KC, Janowsky AJ, Paul SM (1985) [3H] Treo-(+/−)-methylphenidate binding to 3,4-dihidroxyphenylethylamine uptake sites in corpus striatum: correlation with the stimulant properties of ritalinic acid esters. J Neurochem 45:1062–1070
Sunohara GA, Malone MA, Rovet J, Humphries T, Roberts W, Taylor MJ (1999) Effect of methylphenidate on attention in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): ERP evidence. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:218–228
Swanson JM, Volkow ND (2002) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of stimulants: implications for the design of new treatments for ADHD. Behav Brain Res 130:73–78
Swanson J, Castellanos FX, Murias M, LaHoste G, Kennedy J (1998) Cognitive neuroscience of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and hyperkinetic disorder. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8:263–271
Taylor FB, Russo J (2001) Comparing guanfacine and dextroamphetamine for the treatment of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21:223–228
Vaidya C, Austin G, Kirkorian G, Ridlehuber HW, Desmond JE, Glover GH et al (1998) Selective effects methylphenidate in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a functional magnetic resonance study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14494–14499
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Gatley SJ, Logan J, Ding YS et al (1998) Dopamine transporter occupancies in the human brain induced by therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate. Am J Psychiatry 155:1325–1331
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D et al (2001) Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am J Psychiatry 158:377–382
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Ding YS (2005) Imaging the effects of methylphenidate on brain dopamine: new model on its therapeutic actions for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57:1410–1415
Wendel A (1981) Glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 77:325–333
Wigal T, Swanson JM, Regino R, Lerner MA, Soliman I, Steinhoff K (1999) Stimulant medications for the treatment of ADHD: efficacy and limitations. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 5:215–224
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Spencer TJ (2002) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Annu Rev Med 53:113–131
Zito JM, Safer DJ, dosReis S, Gardner JF, Boles M, Lynch F (2000) Trends in the prescribing of psychotropic medications to preschoolers. JAMA 283:1025–1030
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq–Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, F., Scherer, E.B.S., Machado, F.R. et al. Methylphenidate induces lipid and protein damage in prefrontal cortex, but not in cerebellum, striatum and hippocampus of juvenile rats. Metab Brain Dis 27, 605–612 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-012-9335-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-012-9335-5