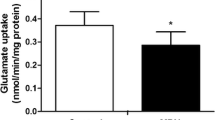
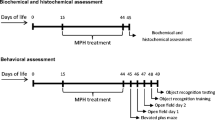
Abstract
Methylphenidate is a central nervous system stimulant used for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Na+, K+-ATPase is a membrane-bound enzyme necessary to maintain neuronal excitability. Considering that methylphenidate effects on central nervous system metabolism are poorly known and that Na+, K+-ATPase is essential to normal brain function, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of this drug on Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the cerebrum of young and adult rats. For acute administration, a single injection of methylphenidate (1.0, 2.0, or 10.0 mg/Kg) or saline was given to rats on postnatal day 25 or postnatal day 60, in the young and adult groups, respectively. For chronic administration, methylphenidate (1.0, 2.0, or 10.0 mg/Kg) or saline injections were given to young rats starting at postnatal day 25 once daily for 28 days. In adult rats, the same regimen was performed starting at postnatal day 60. Our results showed that acute methylphenidate administration increased Na+, K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and striatum of young and adult rats. In young rats, chronic administration of methylphenidate also enhanced Na+, K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, but not in striatum. When tested in adult rats, Na+, K+-ATPase activity was increased in all cerebral structures studied. The present findings suggest that increased Na+, K+-ATPase activity may be associated with neuronal excitability caused by methylphenidate.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achat-Mendes C, Anderson KL, Itzhak Y (2003) Methylphenidate and MDMA adolescent exposure in mice: long-lasting consequences on cocaine-induced reward and psychomotor stimulation in adulthood. Neuropharmacology 45:106–115
Adriani W, Leo D, Greco D, Rea M, di Porzio U, Laviola G, Perrone-Capano C (2006) Methylphenidate administration to adolescent rats determines plastic changes on reward-related behavior and striatal gene expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1946–1956
Andersen SL (2005) Stimulants and the developing brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:237–243
Arnsten AF, Steere JC, Hunt RD (1996) The contribution of alpha 2-noradrenergic mechanisms of prefrontal cortical cognitive function. Potential significance for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:448–455
Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Santosh P, Zuddas A, Asherson P, Buitelaar J, Danckaerts M, Döpfner M, Faraone SV, Rothenberger A, Sergeant J, Steinhausen HC, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Taylor E (2006) Long-acting medications for the hyperkinetic disorders: a systematic review and European guideline. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 15:476–498
Biederman J, Faraone SV (2005) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 366:237–248
Bock N, Quentin DJ, Hüther G, Moll GH, Banaschewski T, Rothenberger A (2005) Very early treatment with fluoxetine and reboxetine causing long lasting changes of the serotonin but not the noradrenaline transporter in the frontal cortex of rats. World J Biol Psychiatry 6:107–112
Bolanos CA, Barrot M, Berton O, Wallace-Black D, Nestler EJ (2003) Methylphenidate treatment during pre- and periadolescence alters behavioral responses to emotional stimuli at adulthood. Biol Psychiatry 54:1317–1329
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of micrograms quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-die-binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bush G, Valera EM, Seidman LJ (2005) Functional neuroimaging of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and suggested future directions. Biol Psychiatry 57:1273–1284
Carageorgiou H, Zarros A, Tsakiris S (2003) Selegiline long-term effects on brain acetylcholinesterase, Na+, K+-ATPase activities, antioxidant status and learning performance of aged rats. Pharmacol Res 48:245–251
Carlezon WA Jr, Mague SD, Andersen SL (2003) Enduring behavioral effects of early exposure to methylphenidate in rats. Biol Psychiatry 54:1330–1337
Castellanos FX, Tannock R (2002) Neuroscience of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: the search for endophenotypes. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:617–628
Chan KM, Delfer D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colorimetric assay for Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 157:375–380
Chase TD, Brown RE, Carrey N, Wilkinson M (2003) Daily methylphenidate administration attenuates c-fos expression in the striatum of prepubertal rats. Neuroreport 14:769–772
Chase T, Carrey N, Soo E, Wilkinson M (2007) Methylphenidate regulates activity regulated cytoskeletal associated but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in the developing rat striatum. Neuroscience 144:969–984
Choi DW (1988) Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity: relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage. Trends Neurosci 11:465–469
Deisseroth K, Singla S, Toda H, Monje M, Palmer TD, Malenka RC (2004) Excitation-neurogenesis coupling in adult neural stem/progenitor cells. Neuron 42:535–552
Dinn WM, Robbins NC, Harris CL (2001) Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: neuropsychological correlates and clinical presentation. Brain Cogn 46:114–121
Erecinska M, Silver IA (1994) Ions and energy in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 43:37–71
Fagundes AO, Rezin GT, Zanette F, Grandi E, Assis LC, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J, Streck EL (2007) Chronic administration of methylphenidate activates mitochondrial respiratory chain in brain of young rats. Int J Devl Neuroscience 25:47–51
Faraone SV, Sergeant J, Gillberg C, Biederman J (2003) The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: is it an American condition? World Psychiatry 2:104–113
Ferris RM, Tang FLM, Maxwell RA (1972) A comparison of the capacities of isomers of amphetamine, deoxypipradrol and methylphenidate to inhibit the uptake of tritiated catecholamine into rat cerebral cortex slices, synaptosomal preparations of rat cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and striatum and into adrenergic nerves of rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 181:407–416
Gamaro GD, Streck EL, Matté C, Prediger ME, Wyse AT, Dalmaz C (2003) Reduction of hippocampal Na+, K+-ATPase activity in rats subjected to an experimental model of depression. Neurochem Res 28:1339–1344
Gerasimov MR, Franceschi M, Volkow ND, Rice O, Schiffer WK, Dewey SL (2000) Synergistic interactions between nicotine and cocaine or methylphenidate depend on the dose of dopamine transporter inhibitor. Synapse 38:432–437
Goldman LS, Genel M, Bezman RJ, Slanetz PJ (1998) Diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. JAMA 279:1100–1107
Goldstein I, Levy T, Galili D, Ovadia H, Yirmiya R, Rosen H, Lichtstein D (2006) Involvement of Na+, K+-ATPase and endogenous digitalis-like compounds in depressive disorders. Biol Psychiatry 60:491–499
Hattori N, Kitagawa K, Higashida T, Yagyu K, Shimohama S, Wataya T, Perry G, Smith MA, Inagaki C (1998) Cl–ATPase and Na+, K+-ATPase activities in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurosci Lett 254:141–144
Heiligenstein E, Conyers LM, Berns AR, Miller MA (1998) Preliminary normative data on DSM-IV attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in college students. J Am Coll Health 46:185–188
Hernandez JR (1992a) Na+, K+-ATPase regulation by neurotransmitters. Neurochem Int 20:1–10
Hernandez JR (1992b) Na+, K+-ATPase regulation by serotonin in normal and kindled rats. Brain Res 593:239–244
Kuczenski R, Segal DS (1997) Effects of methylphenidate on extracellular dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine: comparison with amphetamine. J Neurochem 68:2032–2037
Kurup AR, Kurup PA (2002) Membrane Na+-K+-ATPase mediated cascade in bipolar mood disorder, major depressive disorder, and schizophrenia-relationship to hemispheric dominance. Int J Neurosci 112:965–982
Miller KJ, Castellanos FX (1998) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorders. Pediatr Rev 19:373–384
Moll GH, Hause S, Rüther E, Rothenberger A, Huether G (2001) Early methylphenidate administration to young rats causing a persistent reduction in the density of striatal dopamine transporters. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 11:15–24
Munhoz CD, Glezer I, Kawamoto EM, Araújo AP, Lepscha LB, Planeta CS, DeLucia R, Scavone C (2003) Changes in sodium, potassium-ATPase induced by repeated fencamfamine: the roles of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and the nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway. Neuropharmacology 45:1151–1159
Overtoom CC, Verbaten MN, Kemner C, Kenemans JL, van Engeland H, Buitelaar JK, van der Molen MW, van der Gugten J, Westenberg H, Maes RA, Koelega HS (2003) Effects of methylphenidate, desipramine, and L-dopa on attention and inhibition in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Behav Brain Res 145:7–15
Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA (2007) The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry 164:942–948
Robinson TE, Kolb B (2004) Structural plasticity associated with exposure to drugs of abuse. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):33–46
Scaini G, Fagundes AO, Rezin GT, Gomes KM, Zugno AI, Quevedo J, Streck EL (2008) Methylphenidate increases creatine kinase activity in the brain of young and adult rats. Life Sci 83:795–780
Shaw P, Sharp WS, Morrison M, Eckstrand K, Greenstein DK, Clasen LS, Evans AC, Rapoport JL (2009) Psychostimulant treatment and the developing cortex in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 166:58–63
Stanwood GD, Levitt P (2004) Drug exposure early in life: functional repercussions of changing neuropharmacology during sensitive periods of brain development. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:65–71
Taylor E, Doepfner M, Sergeant J, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Coghill D, Danckaerts M, Rothenberger A, Sonuga Barke E, Steinhausen HC, Zuddas A (2004) European Clinical Guidelines for Hyperkinetic Disorder—first update. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 13(Suppl 1):7–30
Valvassori SS, Frey BN, Martins MR, Réus GZ, Schimidtz F, Inácio CG, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J (2007) Sensitization and cross-sensitization after chronic treatment with methylphenidate in adolescent Wistar rats. Behav Pharmacol 18:205–212
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Gatley SJ, Logan J, Ding YS, Hitzemann R, Pappas N (1998) Dopamine transporter occupancies in the human brain induced by therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate. Am J Psychiatry 155:1325–1331
Volkow ND, Wang G, Fowler JS, Ding YS (2005) Imaging the effects of methylphenidate on brain dopamine: new model on its therapeutic actions for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57:1410–1415
Wood AJ, Elphick M, Grahame-Smith DG (1989) Effect of lithium and of other drugs used in the treatment of manic illness on the cation-transporting properties of Na+, K+-ATPase in mouse brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem 52:1042–1049
Wyse ATS, Streck EL, Worm P, Wajner M, Ritter F, Netto CA (2000a) Preconditioning prevents the inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity after brain ischemia. Neurochem Res 25:971–975
Wyse AT, Streck EL, Barros SV, Brusque AM, Zugno AI, Wajner M (2000b) Methylmalonate administration decreases Na+, K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex of rats. Neuroreport 11:2331–2334
Xie Z, Askari A (2002) Na+, K+-ATPase as a signal transducer. Eur J Biochem 269:2434–2439
Yang ZJ, Torbey M, Li X, Bernardy J, Golden WC, Martin LJ, Koehler RC (2007) Dopamine receptor modulation of hypoxic-ischemic neuronal injury in striatum of newborn piglets. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1339–1351
Yano M, Steiner H (2005) Methylphenidate (Ritalin) induces Homer 1a and zif 268 expression in specific corticostriatal circuits. Neuroscience 132:855–865
Zanatta LM, Nascimento FC, Barros SV, Silva GR, Zugno AI, Netto CA, Wyse AT (2001) In vivo and in vitro effect of imipramine and fluoxetine on Na+, K+-ATPase activity in synaptic plasma membranes from the cerebral cortex of rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:1265–1269
Zugno AI, Valvassori SS, Scherer EBS, Mattos C, Matté C, Ferreira CL, Rezin GT, Wyse AT, Quevedo J, Streck EL (2009) Na+, K+-ATPase activity in an animal model of mania. J Neural Transm 116:431–436
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scherer, E.B.S., Matté, C., Ferreira, A.G.K. et al. Methylphenidate treatment increases Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the cerebrum of young and adult rats. J Neural Transm 116, 1681–1687 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0306-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0306-x