Abstract
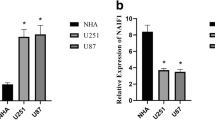
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant and common brain tumor; it is aggressive growth pattern means that GBM patients face a poor prognosis even when receiving the best available treatment modalities. In recent years, an increasing number of reports suggest that the discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) might provide a novel therapeutic target for human cancers, including GBM. One miRNA in particular, microRNA-25 (miR-25), is overexpressed in several cancers, wherein accumulating evidence indicates that it functions as an oncogene. However, the function of miR-25 in GBM has not been totally elucidated. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-25 was significantly up-regulated in astrocytoma tissues and glioblastoma cell lines. In vitro studies further demonstrated that overexpressed miR-25 was able to promote, while its antisense oligos inhibited cell proliferation and invasion in U251 cells. Moreover, we identified neurofilament light polypeptide (NEFL) as a novel target molecule of miR-25. Also of note was the fact that NEFL was down-regulated with increased levels of miR-25 expression in human astrocytoma clinical specimens. In addition, via the mTOR signaling pathway, NEFL-siRNA could significantly attenuate the inhibitory effects of knockdown miR-25 on the proliferation and invasion of U251 cells. Overall, our results showed an important role for miR-25 in regulating NEFL expression in GBM, and suggest that miR-25 could be a potential target for GBM treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu Y, Parada LF (2002) The molecular and genetic basis of neurological tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 2:616–626. doi:10.1038/nrc866
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2012) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 379:1984–1996. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61346-9
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra07081264
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838. doi:10.1038/nature03702
Liu X, Lei Q, Yu Z, Xu G, Tang H, Wang W, Wang Z, Li G, Wu M (2015) MiR-101 reverses the hypomethylation of the LMO3 promoter in glioma cells. Oncotarget 6:7930–7943
She X, Yu Z, Cui Y, Lei Q, Wang Z, Xu G, Luo Z, Li G, Wu M (2014) miR-181 subunits enhance the chemosensitivity of temozolomide by Rap1B-mediated cytoskeleton remodeling in glioblastoma cells. Med Oncol 31:892. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0892-9
She X, Yu Z, Cui Y, Lei Q, Wang Z, Xu G, Xiang J, Wu M, Li G (2014) miR-128 and miR-149 enhance the chemosensitivity of temozolomide by Rap1B-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling in glioblastoma. Oncol Rep 32:957–964. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3318
Tang H, Bian Y, Tu C, Wang Z, Yu Z, Liu Q, Xu G, Wu M, Li G (2013) The miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates oxidative apoptosis and sensitizes cells to chemotherapy in gliomas. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13:221–231. doi:10.2174/1568009611313020010
Tang H, Liu X, Wang Z, She X, Zeng X, Deng M, Liao Q, Guo X, Wang R, Li X, Zeng F, Wu M, Li G (2011) Interaction of hsa-miR-381 and glioma suppressor LRRC4 is involved in glioma growth. Brain Res 1390:21–32. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.034
Tang H, Wang Z, Liu Q, Liu X, Wu M, Li G (2014) Disturbing miR-182 and -381 inhibits BRD7 transcription and glioma growth by directly targeting LRRC4. PloS One 9:e84146. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084146
Tang H, Wang Z, Liu X, Liu Q, Xu G, Li G, Wu M (2012) LRRC4 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through a miR-185-dependent pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 12:1032–1042. doi:10.2174/156800912803251180
Wang Z, Yang J, Xu G, Wang W, Liu C, Yang H, Yu Z, Lei Q, Xiao L, Xiong J, Zeng L, Xiang J, Ma J, Li G, Wu M (2015) Targeting miR-381-NEFL axis sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by regulating stemness factors and multidrug resistance factors. Oncotarget 6:3147–3164
Yuan J, Xiao G, Peng G, Liu D, Wang Z, Liao Y, Liu Q, Wu M, Yuan X (2015) MiRNA-125a-5p inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation and promotes cell differentiation by targeting TAZ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:171–176. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.078
Zhang Z, Tang H, Wang Z, Zhang B, Liu W, Lu H, Xiao L, Liu X, Wang R, Li X, Wu M, Li G (2011) MiR-185 targets the DNA methyltransferases 1 and regulates global DNA methylation in human glioma. Mol Cancer 10:124. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-124
Li Z, Sun Y, Chen X, Squires J, Nowroozizadeh B, Liang C, Huang J (2015) p53 Mutation directs AURKA overexpression via miR-25 and FBXW7 in prostatic small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res 13:584–591. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0277-T
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, Xiao B, Zhuang Y, Mao XH, Wu C, Yang SM, Zeng H, Zou QM, Guo G (2014) MicroRNA-25 promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor survival. Oncogene 34(20):2556–2565. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.214
Feng S, Pan W, Jin Y, Zheng J (2014) MiR-25 promotes ovarian cancer proliferation and motility by targeting LATS2. Tumour Biol 35:12339–12344. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2546-0
Wang X, Wang HK, Li Y, Hafner M, Banerjee NS, Tang S, Briskin D, Meyers C, Chow LT, Xie X, Tuschl T, Zheng ZM (2014) microRNAs are biomarkers of oncogenic human papillomavirus infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:4262–4267. doi:10.1073/pnas.1401430111
Li X, Yang C, Wang X, Zhang J, Zhang R, Liu R (2014) The expression of miR-25 is increased in colorectal cancer and is associated with patient prognosis. Med Oncol 31:781. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0781-7
Kishikawa T, Otsuka M, Yoshikawa T, Ohno M, Takata A, Shibata C, Kondo Y, Akanuma M, Yoshida H, Koike K (2013) Regulation of the expression of the liver cancer susceptibility gene MICA by microRNAs. Sci Rep 3:2739. doi:10.1038/srep02739
Xu X, Chen Z, Zhao X, Wang J, Ding D, Wang Z, Tan F, Tan X, Zhou F, Sun J, Sun N, Gao Y, Shao K, Li N, Qiu B, He J (2012) MicroRNA-25 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 421:640–645. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.048
Razumilava N, Bronk SF, Smoot RL, Fingas CD, Werneburg NW, Roberts LR, Mott JL (2012) miR-25 targets TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor-4 and promotes apoptosis resistance in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 55:465–475. doi:10.1002/hep.24698
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Riccardi L, Fornari A, Song MS, Hobbs RM, Sportoletti P, Varmeh S, Egia A, Fedele G, Rameh L, Loda M, Pandolfi PP (2010) Identification of the miR-106b ~25 microRNA cluster as a proto-oncogenic PTEN-targeting intron that cooperates with its host gene MCM7 in transformation. Sci Signal 3:a29. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000594
Yang T, Chen T, Li Y, Gao L, Zhang S, Wang T, Chen M (2015) Downregulation of miR-25 modulates non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting CDC42. Tumour Biol 36:1903–1911. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2793-0
Haddad LA, Smith N, Bowser M, Niida Y, Murthy V, Gonzalez-Agosti C, Ramesh V (2002) The TSC1 tumor suppressor hamartin interacts with neurofilament-L and possibly functions as a novel integrator of the neuronal cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 277:44180–44186. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207211200
Chen B, Chen J, House MG, Cullen KJ, Nephew KP, Guo Z (2012) Role of neurofilament light polypeptide in head and neck cancer chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Res 10:305–315. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0300
Costa PM, Cardoso AL, Nobrega C, Pereira DAL, Bruce JN, Canoll P, Pedroso DLM (2013) MicroRNA-21 silencing enhances the cytotoxic effect of the antiangiogenic drug sunitinib in glioblastoma. Hum Mol Genet 22:904–918. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds496
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Geng WM, Wu YG, Qin CK (2014) Upregulation of microRNA-25 associates with prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 9:47. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-47
Macoska JA, Trybus TM, Benson PD, Sakr WA, Grignon DJ, Wojno KD, Pietruk T, Powell IJ (1995) Evidence for three tumor suppressor gene loci on chromosome 8p in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res 55:5390–5395
Knowles MA, Shaw ME, Proctor AJ (1993) Deletion mapping of chromosome 8 in cancers of the urinary bladder using restriction fragment length polymorphisms and microsatellite polymorphisms. Oncogene 8:1357–1364
Kang S, Kim B, Park SB, Jeong G, Kang HS, Liu R, Kim SJ (2013) Stage-specific methylome screen identifies that NEFL is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 43:1659–1665. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.2094
Coon SW, Savera AT, Zarbo RJ, Benninger MS, Chase GA, Rybicki BA, Van Dyke DL (2004) Prognostic implications of loss of heterozygosity at 8p21 and 9p21 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 111:206–212. doi:10.1002/ijc.20254
Zhang M, Wang X, Li W, Cui Y (2015) miR-107 and miR-25 simultaneously target LATS2 and regulate proliferation and invasion of gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 460:806–812. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.03.110
Murakami H, Mizuno T, Taniguchi T, Fujii M, Ishiguro F, Fukui T, Akatsuka S, Horio Y, Hida T, Kondo Y, Toyokuni S, Osada H, Sekido Y (2011) LATS2 is a tumor suppressor gene of malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res 71:873–883. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2164
Li W, Wang L, Katoh H, Liu R, Zheng P, Liu Y (2011) Identification of a tumor suppressor relay between the FOXP3 and the Hippo pathways in breast and prostate cancers. Cancer Res 71:2162–2171. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3268
Yao F, Liu H, Li Z, Zhong C, Fang W (2015) Down-regulation of LATS2 in non-small cell lung cancer promoted the growth and motility of cancer cells. Tumour Biol 36:2049–2057. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2812-1
Yu T, Bachman J, Lai ZC (2015) Mutation analysis of large tumor suppressor genes LATS1 and LATS2 supports a tumor suppressor role in human cancer. Protein Cell 6:6–11. doi:10.1007/s13238-014-0122-4
Kodack DP, Askoxylakis V, Ferraro GB, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2015) Emerging strategies for treating brain metastases from breast cancer. Cancer Cell 27:163–175. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.01.001
Gulati S, Ytterhus B, Granli US, Gulati M, Lydersen S, Torp SH (2010) Overexpression of c-erbB2 is a negative prognostic factor in anaplastic astrocytomas. Diagn Pathol 5:18. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-5-18
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Zeyou Wang for his precious suggestions and generous help in carrying out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, G., Yuan, X., Yuan, J. et al. miR-25 promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting NEFL. Mol Cell Biochem 409, 103–111 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2516-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2516-x