Abstract
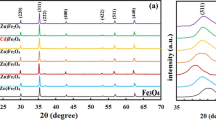
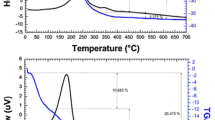
The spinel Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 was obtained via calcining Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2(C2O4)3·5H2O above 400 °C in air. The precursor and its calcined products were characterized by thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform FT-IR, X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer, and vibrating sample magnetometer. The results showed that Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 obtained at 600 °C had a specific saturation magnetization of 46.2 emu g–1. The thermal decomposition of Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2(C2O4)3·5H2O below 450 °C experienced two steps which involved, at first, the dehydration of five water molecules and then decomposition of Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2(C2O4)3 into spinel Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 in air. Based on Starink equation, the values of the activation energies associated with the thermal decomposition of Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2(C2O4)3·5H2O were determined.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marinca TF, Chicinas I, Isnard O. Influence of the heat treatment conditions on the formation of CuFe2O4 from mechanical milled precursors oxides. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:301–7.
Gabal MA, Ahmed MA. structural, electrical and magnetic properties of copper-cadmium ferrites prepared from metal oxalates. J Mater Sci. 2005;40:387–98.
Wu WW, Li YN, Zhou KW, Wu XH, Liao S, Wang Q. Nanocrystalline Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4: preparation and kinetics of thermal process of precursor. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:1143–51.
Sun ZP, Liu L, Jia DZ, Pan WY. Simple synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as gas-sensing materials. Sens Actuators B. 2007;125:144–8.
Li JJ, Yuan HM, Li GD, Liu YJ, Leng JS. Cation distribution dependence of magnetic properties of sol–gel prepared MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater. 2010;322:3396–400.
Wu XH, Wu WW, Zhou KW, Cui XM, Liao S. Products and non-isothermal kinetics of thermal decomposition of MgFe2(C2O4)3·6H2O. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:781–7.
Li FS, Wang HB, Wang L, Wang JB. Magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;309:295–9.
Wu WW. C, Wu XH, Li YN, Liao S. Magnetic properties and crystallization kinetics of Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4. Rare Met. 2011;30:621–6.
Satyanarayana L, Madhusudan Reddy K, Manorama SV. Nano-sized spinel NiFe2O4: a novel material for the detection of liquefied petroleum gas in air. Mater Chem Phys. 2003;82:21–6.
Zhang K, Holloway T, Pradhan AK. Magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline CoFe2O4. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323:1616–22.
Wu WW, Cai JC, Wu XH, Liao S, Huang AG. Co0.35Mn0.65Fe2O4 magnetic particles: preparation and kinetics research of thermal process of the precursor. Powder Technol. 2012;215–216:200–5.
John Berchmans L, Karthikeyan R, Helan M, Berchmans Sheela, Ŝepelak V, Becker KD. Mechanochemical synthesis and electrochemical characterization of nano crystalline calcium ferrite. Catal Lett. 2011;141:1451–7.
Maqsood A, Faraz A. Synthesis, structural, electrical and magnetic characterization of Mn0.5Mg0.5−x Ni x Fe2O4 spinel Nanoferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2011. doi:10.1007/s10948-011-1343-x.
Huang JW, Su P, Wu WW, Li YN, Wu XH, Liao S. Preparation of magnetic Cu0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles and kinetics of thermal process of precursor. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2012;25:1971–7.
Wang WW. Microwave-induced polyol-process synthesis of MIIFe2O4 (M = Mn, Co) nanoparticles and magnetic property. Mater Chem Phys. 2008;108:227–31.
Tromsdorf UI, Bigall NC, Kaul MG, Bruns OT, Nikolic MS, Mollwitz B, Sperling RA, Reimer R, Hohenberg H, Parak WJ, Förster S, Beisiegel U, Adam G, Weller H. Size and surface effects on the MRI, relaxivity of manganese ferrite nanoparticle contrast agents. Nano Lett. 2007;7:2422–7.
Liu XM, Yang G, Fu SY. mass synthesis of manocrystalline spinel ferrites by a polymer-pyrolysis route. Mater Sci Eng C. 2007;27:750–5.
Zhen L, He K, Xu CY, Shao WZ. Synthesis and characterization of single-crystalline MnFe2O4 nanorods via a surfactant-free hydrothermal route. J Magn Magn Mater. 2008;320:2672–5.
Wang J, Chen QW, Hou BY, Peng ZM. Synthesis and magnetic properties of single-crystals of MnFe2O4 nanorods. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2004;35:1165–8.
Ju YW, Park JH, Jung HR, Cho SJ, Lee WJ. Electrospun MnFe2O4 nanofibers: preparation and morphology. Compos Sci Technol. 2008;68:1704–9.
Zhang DE, Zhang XJ, Ni XM, Song JM, Zheng HG. Low-temperature fabrication of MnFe2O4 octahedrons: magnetic and electrochemical properties. Chem Phys Lett. 2006;426:120–3.
Iyer R, Desai R, Upadhyay RV. Low temperature synthesis of nanosized Mn1–xZnxFe2O4 ferrites and their characterizations. Bull Mater Sci. 2009;32:141–7.
Faraz A, Saqib M, Ahmad NM, Fazal-ur-Rehman, Maqsood A, Usman M, Mumtaz A, Hassan MA. Synthesis, structural, and magnetic characterization of Mn1−xNixFe2O4 spinel nanoferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2011. doi: 10.1007/s10948-011-1212-7.
Sharma SK, Ravi Kumar, Siva Kumar VV, Knobel M, Reddy VR, Gupta A, Singh M. Role of electronic energy loss on the magnetic properties of Mg0.95Mn0.05Fe2O4 nanoparticles. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 2006;248:37–41.
Mansour SF, Elkestawy MA. A comparative study of electric properties of nano-structured and bulk Mn–Mg spinel ferrite. Ceram Int. 2011;37:1175–80.
Mansour SF. Structural and magnetic investigations of sub-nano Mn–Mg ferrite prepared by wet method. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323:1735–40.
Okasha N. Enhancement of magnetization of Mg–Mn nanoferrite by γ-irradiation. J Alloys Compd. 2010;490:307–10.
Maqsood A, Faraz A. Synthesis, structural, electrical and magnetic characterization of Mn0.5Mg0.5−xNixFe2O4 spinel nanoferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2012;25:1025–33.
Msomi JZ, Moyo T, Abdallah HMI. Magnetic properties of MgxMn1−xFe2O4 nanoferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2012. doi:10.1007/s10948-011-1235-0.
Starink MJ. The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. 2003;404:163–76.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Vlaev L, Nedelchev N, Gyurova K, Zagorcheva M. A comparative study of non-isothermal kinetics of decomposition of calcium oxalate monohydrate. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2008;81:253–62.
Liqing L, Donghua C. Application of iso-temperature method of multiple rate to kinetic analysis: Dehydration for calcium oxalate monohydrate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2004;78:283–93.
Jiang HY, Wang JG, Wu SQ, Wang BS, Wang ZZ. Pyrolysis kinetics of phenol–formaldehyde resin by non-isothermal thermogravimetry. Carbon. 2010;48:352–8.
Wu XH, Wu WW, Cui XM, Liao S. Preparation of nanocrystalline BiFeO3 via a simple and novel method and its kinetics of crystallization. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:625–32.
Boonchom B, Danvirutai C, Youngme S, Maensiri S. Simple synthesis, magnetic properties, and nonisothermal decomposition kinetics of Fe(H2PO4)2·2H2O. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2008;47:7642–7.
Deb N. Solid-state thermal decomposition of heterobimetallic oxalate coordination compounds, zinc(II) tetraaquatris (oxalato) lanthanate(III)hexahydrate and cadmium(II) heptaaquatris(oxalato)lanthanate(III)tetrahydrate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2437-9.
Deb N. Some heterobimetallic oxalate coordination precursors of lanthanum(III) of the type, M3[La(C2O4)3(H2O) m ]2·nH2O (M = Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II)). J Thermal Anal Calorim. 2012;107:561–71.
Donia AM. Synthesis, identification and thermal analysis of coprecipitates of silver-(cobalt, nickel, copper and zinc) oxalate. Polyhedron. 1997;16:3013–31.
Goel SP, Mehrotra PN. IR and thermal studies on lithium oxomolybdenum (VI) oxalate. J Therm Anal. 1985;30:145–51.
Berbenni V, Milanese C, Bruni G, Girella A, Marini A. Synthesis of YFeO3 by thermal decomposition of mechanically activated mixtures Y(CH3COO)3·4H2O–FeC2O4·2H2O. Thermochim Acta. 2011;521:218–23.
Jiang CT, Liu RJ, Shen XQ, Zhu L, Song FZ. Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties and adsorption of bovine serum albumin. Powder Technol. 2011;211:90–4.
Budrugeac P, Muşat V, Segal E. Non-isothermal kinetic study on the decomposition of Zn acetate-based sol-gel precursor. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;88:699–702.
Chaiyo N, Muanghlua R, Niemcharoen S, Boonchom B, Seeharaj P, Vittayakorn N. Non-isothermal kinetics of the thermal decomposition of sodium oxalate Na2C2O4. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:1023–9.
Huang JW, Su P, Wu WW, Li YN, Wu XH, Tao L. Preparation of nanocrystalline BiFeO3 and kinetics of thermal process of precursor. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;. doi:10.1007/s10973-012-2524-y.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21161002) and the Guangxi Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 2011GXNSFA018036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Wu, W., Li, Y. et al. Preparation of magnetic nanocrystalline Mn0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 and kinetics of thermal decomposition of precursor. J Therm Anal Calorim 114, 205–212 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2927-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2927-9