Abstract
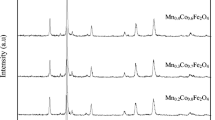
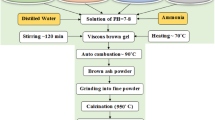
Evaluating the substitution of Cd for Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn elements in the high entropy oxide structure (Mn,Co,Ni,Cu,Zn)Fe2O4, is the primary focus in this investigation. For this purpose, five different high entropy oxides (HEOs), namely (Cd,Co,Ni,Cu,Zn)Fe2O4, (Mn,Cd,Ni,Cu,Zn) Fe2O4, (Mn,Co,Cd,Cu,Zn)Fe2O4, (Mn,Co,Ni,Cd,Zn)Fe2O4, and (Mn,Co,Ni,Cu,Cd)Fe2O4 were synthesized using combustion solution synthesis (SCS) method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), elemental mapping, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) were used to analyze the synthesized samples. The analyses confirmed the formation of single-phase (Fd-3m) nanocrystalline powders with an increased lattice parameter. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) revealed the placement of Cd element in the tetrahedral sub-lattice (A-site). Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) was employed to assess the magnetic properties. The results indicated that, in most cases, substitution of Cd for Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn leads to an increase in both the saturation magnetization (Ms) and coercivity (Hc) of the nanocrystalline powder samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data will be available upon request.
References
C.M. Rost et al., Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun. 6(1), 8485 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9485
A. Sarkar et al., High-entropy oxides: fundamental aspects and electrochemical properties. Adv. Mater. 31(26), 1806236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201806236
R. Djenadic et al., Multicomponent equiatomic rare earth oxides. Mater. Res. Lett. 5(2), 102–109 (2017)
L. Spiridigliozzi, C. Ferone, R. Cioffi, G. Accardo, D. Frattini, G. Dell’Agli, Entropy-stabilized oxides owning fluorite structure obtained by hydrothermal treatment. Materials 13(3), 558 (2020)
A. Sarkar et al., Rare earth and transition metal based entropy stabilised perovskite type oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(5), 2318–2327 (2018)
J. Dąbrowa et al., Synthesis and microstructure of the (Co, Cr, Fe, Mn, Ni) 3O4 high entropy oxide characterized by spinel structure. Mater. Lett. 216, 32–36 (2018)
C. Kinsler-Fedon et al., Synthesis, characterization, and single-crystal growth of a high-entropy rare-earth pyrochlore oxide. Physical Review Materials 4(10), 104411 (2020)
C. Zhao, F. Ding, Y. Lu, L. Chen, Y.S. Hu, High-entropy layered oxide cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(1), 264–269 (2020)
D. Vinnik et al., Correlation between entropy state, crystal structure, magnetic and electrical properties in M-type Ba-hexaferrites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40(12), 4022–4028 (2020)
A. Sarkar, R. Kruk, H. Hahn, Magnetic properties of high entropy oxides. Dalton Trans. 50(6), 1973–1982 (2021)
R. Valenzuela, Magnetic Ceramics (no. 4) (Cambridge University Press, 2005)
G. Pilania, V. Kocevski, J.A. Valdez, C.R. Kreller, B.P. Uberuaga, Prediction of structure and cation ordering in an ordered normal-inverse double spinel. Commun. Mater. 1(1), 1–11 (2020)
A. Mao, F. Quan, H.-Z. Xiang, Z.-G. Zhang, K. Kuramoto, A.-L. Xia, Facile synthesis and ferrimagnetic property of spinel (CoCrFeMnNi)3O4 high-entropy oxide nanocrystalline powder. J. Mol. Struct. 1194, 11–18 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.05.073
K. Wu, J. Li, C. Zhang, Zinc ferrite based gas sensors: a review. Ceram. Int. 45(9), 11143–11157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.086
M. Fu, X. Ma, K. Zhao, X. Li, D. Su, High-entropy materials for energy-related applications. iScience 24(3), 102177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.102177
T. Lazarova et al., Influence of the type of fuel used for the solution combustion synthesis on the structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanosized NiFe2O4. J. Alloy. Compd. 700, 272–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.055
C.-C. Hwang, J.-S. Tsai, T.-H. Huang, Combustion synthesis of Ni–Zn ferrite by using glycine and metal nitrates—investigations of precursor homogeneity, product reproducibility, and reaction mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 93(2), 330–336 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.03.056
E. Novitskaya, J.P. Kelly, S. Bhaduri, O.A. Graeve, A review of solution combustion synthesis: an analysis of parameters controlling powder characteristics. Int. Mater. Rev. 66(3), 188–214 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2020.1765603
J.C. Toniolo, A.S. Takimi, C.P. Bergmann, Nanostructured cobalt oxides (Co3O4 and CoO) and metallic Co powders synthesized by the solution combustion method. Mater. Res. Bull. 45(6), 672–676 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.03.001
A. Mao, H.-Z. Xiang, Z.-G. Zhang, K. Kuramoto, H. Zhang, Y. Jia, A new class of spinel high-entropy oxides with controllable magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 497, 165884 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165884
S. Dai, M. Li, X. Wang, H. Zhu, Y. Zhao, Z. Wu, Fabrication and magnetic property of novel (Co, Zn, Fe, Mn, Ni)3O4 high-entropy spinel oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 536, 168123 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168123
H. Zhu, H. Xie, Y. Zhao, S. Dai, M. Li, X. Wang, Structure and magnetic properties of a class of spinel high-entropy oxides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 535, 168063 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168063
F. Hosseini Mohammadabadi, S.M. Masoudpanah, S. Alamolhoda, H.R. Koohdar, Electromagnetic microwave absorption properties of high entropy spinel ferrite ((MnNiCuZn)1−xCoxFe2O4)/graphene nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 1099–1111 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.018
A.R. Abbasian, M. Shafiee Afarani, One-step solution combustion synthesis and characterization of ZnFe 2 O 4 and ZnFe 1.6 O 4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 125, 1–12 (2019)
A.K. Zak, W.A. Majid, M.E. Abrishami, R. Yousefi, X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13(1), 251–256 (2011)
A.R. Abbasian, A. Mahvary, S. Alirezaei, Salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis of NiFe2O4: Effect of salt type. Ceram. Int. 47(17), 23794–23802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.086
A.M. Vasilica Tucureanu, A.M. Avram, FTIR spectroscopy for carbon family study. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 46, 502–520 (2016)
M.S.A.F. Paborji, A.M. Arabi, M. Ghahari, Phase transformation of FeCr2O4 to (Fe, Cr)2O3 solid solution pigment powders: effect of post-heating temperature. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 20, 281–293 (2023)
F. Paborji, M. Shafiee Afarani, A.M. Arabi, M. Ghahari, Solution combustion synthesis of FeCr2O4 powders for pigment applications: effect of fuel type. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 19(5), 2406–2418 (2022)
S.A.M.F. Paborji, A.M. Arabi, M. Ghahari, Synthesis of (Fe, Cr)2O3 solid solution pigment powders for ink application. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 20, 1154–1166 (2023)
S. Bedanta, A. Barman, W. Kleemann, O. Petracic, T. Seki, Magnetic nanoparticles: a subject for both fundamental research and applications. J. Nanomater. 2013, 169–169 (2013)
H.K. Ulrich Meisen, The influence of particle size, shape and particle size distribution on properties of magnetites for the production of toners. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 6, 508–513 (2000). https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2000.44.6.art00007
H. Iida, K. Takayanagi, T. Nakanishi, T. Osaka, Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with various sizes and magnetic properties by controlled hydrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 314(1), 274–280 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.05.047
C.W.K. Qing Li, S. Horie, T. Ogi, T. Iwaki, K. Okuyama, Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 7, 9894 (2017)
SMa.S.M. Mritunjoy Prasad Ghosh, Correlations between microstructural and magnetic properties of Gd3+ doped spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Eur. Phys. J. Plus (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00112-5
T.S. Mondal et al., NiFe2O4 nanorod: porosity effect on spin canting, quadrupole splitting and hyperfine magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Express 2(4), 046102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/2/4/046102
A. Hunyek, C. Sirisathitkul, C. Mahaphap, U. Boonyang, W. Tangwatanakul, Sago starch: chelating agent in Sol-gel synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 53(1), 173–176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0022-1
Acknowledgements
We express our high gratitude to the University of Sistan and Baluchestan for generously providing the necessary laboratory facilities for the successful execution of this research. Additionally, our sincere thanks go to Fereydoun Oukti Sadeq and Mahdi Shafiee Afrani from the Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, and Abbas Rahdar from the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Zabol University, for their valuable assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors equally contributed to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khosravi, M., Sharafi, S. & Irannejad, A. Investigating the effect of Cd on the structure and magnetic properties of (Mn,Co,Ni,Cu,Zn)Fe2O4 high entropy spinel oxide. Appl. Phys. A 130, 335 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07507-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07507-6