Abstract
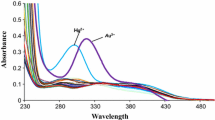
This approach disclose the selective fluorogenic ion sensing ability of 5,11,17,23-tetratertbutyl-25,27-bis((2hydroxynaphthylimino)1,2-ethylenediaminecarbonylmethoxy)-26,28 dihydroxycalix[4]arene (C4NSB). Binding property of receptor probed by using selected various cations and anions with conferring of results that demonstrates ‘turn-off’ fluorescence response and significantly high chromogenic selectivity toward Au3+ and I−. Furthermore, selective nature of receptor was investigated in the presence of different co-existing competing ions. The limit of detection (LOD) for Au3+ and I− was determined as 1.5 × 10−5 and 4.5 × 10−6 M respectively. Receptor C4NSB form (1:1) stoichiometric complex with both ions and their binding constants were calculated as 8.0 × 102 for Au3+ and 15.6 × 102 M−1 for I−. Complexes were also characterized through FT-IR spectroscopy.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Czarnik AW (1993) Fluorescent chemosensors for ion and molecule recognition. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
De Silva AP, Fox DB, Huxley AJM, Moody TS (2000) Combining luminescence, coordination and electron transfer for signaling purposes. Coord Chem Rev 205:41–57
De Silva AP, Gunaratne HQN, Gunnlaugsson T, Huxley AJM, McCoy CP, Rademacher JT, Rice TE (1997) Signaling recognition events with fluorescent sensors and switches. Chem Rev 97:1515–1566
Desvergne JP, Czarnik AW (1997) Chemosensors of ion and molecule recognition. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Tchounwou PB, Ayensu WK, Ninashvili N, Sutton D (2003) Environmental exposure to mercury and its toxicopathologic implications for public health. Environ Toxicol 18:149–175
Fleming CJ, Salisbury EL, Kirwan P, Painter DM, Barnetson RS (1996) Chrysiasis after low-dose gold and UV light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol 34:349–351
American Rheumatism Association (1973) A controlled trial of gold salt therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 16:353–358
Block WD, Knapp EL (1945) Metabolism, toxicity, and manner of action of gold compounds in the treatment of arthritis: vii. The effect of various gold compounds on the oxygen consumption of rat tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 83:275–278
Goodman CM, McCusker CD, Yilmaz T, Rotello VM (2004) Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjug Chem 15:897–900
Michael GH, Robert SG (1968) Modern nutrition in health and disease, 4th edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia
Dai G, Levy O, Carrasco N (1996) Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 379:458–460
Pearce EN (2012) Iodine-induced thyroid dysfunction: Comment on “Association between iodinated contrast media exposure and incident hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism”. Arch Intern Med 172:159–161
Steed JW, Atwood JL (2000) Supramolecular chemistry. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Schneider HJ, Yatsimirsky A (2000) Principles and methods in supramolecular chemistry. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Wang R, Bu J, Liu J, Liao S (2008) Calix[4]arene based selective fluorescent chemosensor for organic acid recognition. Front Chem Chin 3:348–352
Czarnik AW (1992) Fluorescent chemosensors for ion and molecule recognition; ACS Symposium Series 538. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
De Silva AP, Gunnlaugsson T, McCoy CP (1997) Photoionic supermolecules: mobilizing the charge and light bridges. J Chem Educ 74:53–58
Bodenant B, Weil T, Businelli-Pourcel M, Fages F, Barbe B, Pianet I, Laguerre M (1999) Synthesis and solution structure analysis of a bispyrenyl bishydroxamate calix[4]arene-based receptor, a fluorescent chemosensor for Cu2+ and Ni2+ metal ions. J Org Chem 64:7034–7039
Park SM, Kim MH, Choe JI, No KT, Chang SK (2007) Cyclams bearing diametrically disubstituted pyrenes as Cu2+ and Hg2+ selective fluoroionophores. J Org Chem 72:3550–3553
Bonacchi S, Genovese D, Juris R, Montalti M, Prodi L, Rampazzo E, Sgarzi M, Zaccheroni N (2011) Luminescent chemosensors based on silica nanoparticles. Top Curr Chem 300:93–138
Subrata P, Ravi G, Lo R, Suresh E, Bishwajit G, Parimal P (2012) Cation-induced fluorescent excimer emission in calix[4]arene-chemosensors bearing quinoline as a fluorogenic unit: experimental, molecular modeling and crystallographic studies. New J Chem 36:988–1002
Gutsche CD (1989) Calixarenes. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
An WT, Jiao Y, Sun XH, Zhang XL, Dong C, Shuang SM, Xia PF, Wong MS (2009) Synthesis and binding properties of carboxylphenyl-modified calix[4]arenes and cytochrome c. Talanta 79:54–61
Matthews SE, Beer PD (2005) Calixarene-based anion receptors. Supramol Chem 17:411–435
Tabakci M, Tabakci B, Yilmaz M (2005) Design and synthesis of new chiral calix[4]arenes as liquid phase extraction agents for α-amino acid methylesters and chiral α-amines. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 53:51–56
Tabakci B, Beduk AD, Tabakci M, Yilmaz M (2006) Synthesis and binding properties of two polymeric Thiacalix[4]arenes. React Funct Polym 66:379–386
Yilmaz A, Tabakci B, Tabakci M (2009) New diamino derivatives of p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene for oxyanion recognition: synthesis and complexation studies. Supramol Chem 21:435–441
Yilmaz A, Tabakci B, Akceylan E, Yilmaz M (2007) Synthesis and dichromate anion extraction ability of p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene diamide derivatives with different binding sites. Tetrahedron 63:5000–5005
Mathew VJ, Khopkar SM (1997) Hexaacetato calix(6)arene as the novel extractant for palladium. Talanta 44:1699–1703
Sirit A, Karakucuk A, Memon S, Kocabas E, Yilmaz M (2004) Synthesis and characterization of a novel chiral chromogenic calix[4](azoxa)crown-7. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 15:3595–3600
Bozkurt S, Karakucuk A, Sirit A, Yilmaz M (2005) Synthesis of two calix[4]arene diamide derivatives for extraction of chromium(VI). Tetrahedron 61:10443–10448
Vázquez M, Fabbrizzi L, Taglietti A, Pedrido RM, González-Noya AM, Bermejo MR (2004) A colorimetric approach to anion sensing: a selective chemosensor of fluoride ions, in which color is generated by anion-enhanced π delocalization. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:1962–1965
Ediz O, Tabakci M, Memon S, Yilmaz M, Roundhill DM (2004) A convenient approach towards the synthesis of a “proton switchable” chromium(vi) extractant based on calix4arene. Supramol Chem 16:199–204
Ocak U, Ocak M, Surowiec K, Bartsch RA, Gorbunova MG, Tu C, Surowiec MA (2009) Metal ion complexation in acetonitrile by di-ionized calix[4]arenes bearing two dansyl fluorophores. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 63:131–139
Hu J, Yu Y, Brooks JC, Godwin LA, Somasundaram S, Torabinejad F, Kim J, Shannon C, Easley CJ (2014) A reusable electrochemical proximity assay for highly selective, real-time protein quantitation in biological matrices. J Am Chem Soc 136:8467–8474
Hu J, Wang T, Kim J, Shannon C, Easley CJ (2012) Quantitation of femtomolar protein levels via direct readout with the electrochemical proximity assay. J Am Chem Soc 134:7066–7072
Li X, Yu M, Yang F, Liu X, Wei L, Li Z (2013) A dual-model and on–off fluorescent Al3+/Cu2+ chemosensor and the detection of F/Al3+ with ‘in situ’ prepared Al3+/Cu2+ complexes. New J Chem 37:2257–2260
Jou MJ, Chen X, Swamy KMK, Kim HN, Kim HJ, Lee S, Yoon J (2009) Highly selective fluorescent probe for Au3+ based on cyclization of propargylamide. Chem Commun 46:7218–7220
Dong M, Wang YW, Peng Y (2010) Highly selective ratiometric fluorescent sensing for Hg2+ and Au3+ respectively, in aqueous media. Org Lett 12:5310–5313
Egorova OA, Seo H, Chatterjee A, Ahn KH (2010) Reaction-based fluorescent sensing of Au(I)/Au(III) species: mechanistic implications on vinyl gold intermediates. Org Lett 12:401–403
Song Z, Xiao C, Dai Y, Fei Q, Huan Y, Feng G (2012) Fluorescence quenching amplification in silica nanosensors for Au3+. Nanotechnology 23:425501
Çubuk S, Kahraman MV, Yetimoğlu EK, Kenan S (2014) Photocured thiol-ene based optical fluorescence sensor for determination of gold (III). Anal Chim Acta 812:215–221
Joseph R, Chinta JP, Rao CP (2010) Benzothiazole appended lower rim 1,3-di-amido-derivative of calix[4]arene: synthesis, structure, receptor properties towards Cu2+, iodide recognition and computational modeling. Inorg Chim Acta 363:2833–2839
Kim JS, Park SY, Kim SH, Thuéry P, Souane R, Matthews SE, Vicens J (2010) A pyrenyl-appended triazole-based calix[4]arene as a fluorescent sensor for iodide ion. Bull Kor Chem Soc 31:624–629
Joseph R, Gupta A, Ali A, Rao CP (2007) Fluorescent and absorption studies on the selective recognition of iodide by lower rim 1,3 bis(aminoethoxy)-p-tertbutylcalix[4]arene derivative. Indian J Chem 46:1095–1100
Ocak Ü, Ocak M, Surowiec K, Liu X, Bartsch RA (2009) Metal ion complexation in acetonitrile by upper-rim allyl-substituted, di-ionized calix[4]arenes bearing two dansyl fluorophores. Tetrahedron 65:7038–7047
Qazi MA, Ocak Ü, Ocak M, Memon S (2013) An excellent copper selective chemosensor based on calix [4] arene framework. Anal Chim Acta 761:157–168
Qazi MA, Qureshi I, Memon S (2011) Analytical evaluation of Cu2+ selective behavior of calix [4] arene derivative. J Fluoresc 21:1703–1711
Solangi IB, Bhatti AA, Qazi MA, Memon S, Bhanger MI (2012) Selective cation recognition by p-tetranitrocalix [4] arene. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 13:129–136
Qazi MA, Qureshi I, Memon S (2011) Hg(II) selective complexation by chromoionophoric calix[4]arene derivative. J Fluoresc 21:1231–1238
Qazi MA, Ocak Ü, Ocak M, Memon S, Solangi IB (2013) Bifunctional calix [4] arene sensor for Pb(II) and Cr2O7 2− ions. J Fluoresc 23:575–590
Gutsche CD, Iqbal M, Stewart D (1986) Calixarenes. 19. Syntheses procedures for p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene. J Org Chem 51:742–745
Maity D, Chakraborty A, Gunupuru R, Paul P (2011) Calix[4]arene based molecular sensors with pyrene as fluoregenic unit: effect of solvent in ion selectivity and colorimetric detection of fluoride. Inorg Chim Acta 372:126–135
Chen X, Dings RPM, Nesmelova I, Debbert S, Haseman JR, Maxwell J, Hoye TR, Mayo KH (2006) Topomimetics of amphipathic â-sheet and helix-forming bactericidal peptides neutralize lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. J Med Chem 49:7754–7765
Liang Z, Liu Z, Gao Y (2007) Synthesis, characterization and photochromic studies of three novel calix[4]arene–Schiff bases. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 68:1231–1235
Izatt RM, Bradshaw JS, Nielsen SA, Lamb JD, Christian JJ, Sen D (1985) Thermodynamic and kinetic data for cation-macrocycle interaction. Chem Rev 85:271–339
Izatt RM, Bradshaw JS, Pawlak K, Bradshaw JS, Bruening RL (1991) Thermodynamic and kinetic data for macrocycle interactions with cations and anions. Chem Rev 91:1721–2085
Benesi HA, Hildebrand JH (1949) A spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc 71:2703–2707
Harris DC (1995) Quantitative Chemical Analysis 4th edn. W.H. Freeman & Company, New York
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Center of Excellence in Analytical Chemistry, University of Sindh, Jamshoro/Pakistan and Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK, B.02.1.TBT.0.06.01-216.01/895–6391) for the financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Memon, S., Bhatti, A.A., Bhatti, A.A. et al. Calix[4]arene Based Highly Efficient Fluorescent Sensor for Au3+ and I− . J Fluoresc 25, 1507–1515 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1642-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1642-x