Abstract
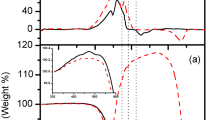
Copper powder is synthesized by hydrothermal treatment using the copper powder obtained from the chemical reduction method as a precursor. The copper powder is also treated in benzotriazole solution. The powder X-ray diffraction patterns and SEM photomicrographs exhibit that the copper powder possesses perfect crystallinity and narrow size distribution. The thermal behavior of the three kinds of copper powder is evaluated by thermogravimetry and derivative thermogravimetry. Comparing with the sample prepared by means of the chemical reduction method, the copper powder treated under hydrothermal condition displays a peak temperature of the formation of Cu2O shifting from 60.49 °C to higher temperatures, which indicates that it has strong antioxidation performance. However, the antioxidation effect of copper powder treated in benzotriazole solution shows only a little improvement at high temperature






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Yamamatsu, N. Kawano, T. Arashi, A. Sato, Y. Nakano, T. Nomura, J. Power Sources 60, 199 (1996)
H. Shin, J.-S. Park, S. Kim, H.S. Jung, K.S. Hong, Microelectron. Eng. 77, 270 (2005)
B.-H. Kim, G.-Y. Lee, W.-J. Lee, J.-H. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 113, 198 (2004)
H. Kishi, Y. Mizuno, H. Chanzono, Jpn. J. Appl. Phy. 42, 1 (2003)
M. Pollet, S. Marinel, J. Mater. Sci. 39, 1943 (2004)
J..L. Paulsen, E.K. Reed, Microelectron. Reliability 42, 815 (2002)
Y. Wang, L. Li, J. Qi, Z. Ma, J. Cao, Z. Gui, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 99, 378 (2003)
D.F.K. Hennings, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1637 (2001)
V. Rosenband, A. Gany, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 153–154, 1058 (2004)
A. Agrawal, V. Kumar, B.D. Pandey, K.K. Sahu, Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 879 (2006)
H. Zhu, C. Zhang, Y. Yin, Nanotechnology 16, 3079 (2005)
A. Sinha, S. Kumar Das, T.V. Vijaya Kumar, V. Rao, P. Ramachandrarao, J. Mater. Synth. Process. 7, 373 (1999)
J. Guilherme, R. Poco, R. Guardani, C. Shimmi, M. Giulietti, Mater. Res. 9, 131 (2006)
H.-T. Zhu, C.-Y. Zhang, Y.-S. Yin, J. Cryst. Growth 270, 722 (2004)
R.D. Van der Weijden, J. Mahabir, A. Abbadi, M.A. Reuter, Hydrometallurg 64, 131 (2002)
E. Cifti, M.N. Rahaman, J. Mater. Sci. 36, 4875 (2001)
O.O. Vasylkiv, Y. Sakka, V.V. Skorokhod, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 44, 228 (2005)
S.-F. Liu, I. R. Abothu, S. Komarneni, Mater. Lett. 38, 344 (1999)
Y.J. Ma, J.H. Cho, Y.H. Lee, B.I. Kim, Mater. Chem. Phy. 98, 5 (2006)
H. Wang, Journal of Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 471 (2003)
Yu V. Kolen’ko, V.D. Maximov, V.A. Muhanov, B.R. Churagulov, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 23, 1033 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Zhu, L., Dong, D. et al. Thermal behavior of copper powder prepared by hydrothermal treatment. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 18, 817–821 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9257-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9257-x