Abstract
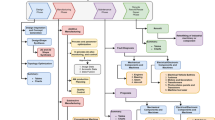
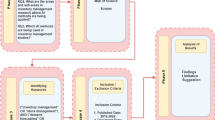
In the manufacturing section, due to limitations of specific resources (e.g., time, people, and equipment), key determinants such as process capacity, human resources supply, and equipment availability may be in uncertain or out-of-control environments, followed by decreasing production performance. Traditionally, earlier studies of related issues of production performance usually used statistical methods for handling these problems. However, these methods become more complex when relationships in the input/output dataset are nonlinear. Furthermore, statistical techniques rely on the restrictive assumption on linear separability, multivariate normality and independence of the predictive variables; unfortunately, many of the common models of production performance violate these assumptions. To remedy these existing shortcomings, the study proposes a hybrid procedure that focuses on the opinions of experts, discretization of decision attributes, and application of well-known artificial intelligent (AI) approaches, such as decision trees (DT), artificial neural networks (ANN), and DT+ANN techniques, for objectively classifying production performance to solve real-world problems that are faced by the automobile parts industry. Two practically collected datasets are employed to verify the proposed hybrid procedure. The experimental results reveal that the proposed hybrid procedure is a good alternative to classify production performance from an intelligent manufacturing perspective objectively. Moreover, the output that is created by the DT C4.5 algorithm is a set of comprehensible and meaningful rules applied readily in knowledge-based performance-evaluating systems for manufacturing managers and HR division managers. The study findings and implications are of value to academicians and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizenman J., Isard P. (1996) Production bottlenecks and congestion externalities during the transition to a market economy. International Review of Economics & Finance 5(3): 225–241 10.1016/S1059-0560(96)90031-3
Altam E.I., Macro G., Varetto F. (1994) Corporate distress diagnosis: Comparison using linear discriminant analysis and neural networks. Journal of Banking & Finance 18: 505–529. doi:10.1016/0378-4266(94)90007-8
Aytug H., Lawley M.A., McKay K., Mohan S., Uzsoy R. (2005) Executing production schedules in the face of uncertainties: A review and some future directions. European Journal of Operational Research 161(1): 86–110. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2003.08.027
Banda K., Zeid I. (2006) To disassemble or not: A computational methodology for decision making. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17(5): 621–634. doi:10.1007/s10845-006-0022-4
Barber, S. (2004). Creating effective load models for performance testing with incomplete empirical data. In Proceedings, Sixth IEEE International Workshop, pp. 51–59.
Baykasoglu A. (2006) Multi-rule multi-objective simulated annealing algorithm for straight and U type assembly line balancing problems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17(2): 217–232. doi:10.1007/s10845-005-6638-y
Beamon B.M. (1999) Measuring supply chain performance. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 19(3): 275–292. doi:10.1108/01443579910249714
Bedworth, M. D., & Lowe, D. (1988). Fault tolerance in multi-layer perceptrons: A preliminary study. RSRE: Pattern Processing and Machine Intelligence Division.
Braun, H., & Chandler, J. S. (1987). Predicting stock market behavior through rule induction: An application of the learning-from-examples approach. Decision Sciences, 415–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.1987.tb01533.x
Bishop C.M. (1991) A fast procedure for re-training the multi-layer perceptron. International Journal of Neural Systems 2(3): 229–236. doi:10.1142/S0129065791000212
Bishop C.M. (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bullinger H.J., Kühner M., Hoof A.V. (2002) Analysing supply chain performance using a balanced measurement method. International Journal of Production Research 40(15): 3533–3543. doi:10.1080/00207540210161669
Canos L., Liern V. (2008) Soft computing-based aggregation methods for human resource management. European Journal of Operational Research 189(3): 669–681. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.01.054
Chan F., Qi H.J. (2003) Feasibility of performance measurement system for supply chain: A process-based approach and measures. Integrated Manufacturing Systems 14(3): 179–190. doi:10.1108/09576060310463145
Chang Y.C., Wu C.W. (2008) Assessing process capability based on the lower confidence bound of Cpk for asymmetric tolerances. European Journal of Operational Research 190(1): 205–227. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.06.003
Chen C.C. (2008) A model for customer-focused objective-based performance evaluation of logistics service providers. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics 20(3): 309–322. doi:10.1108/13555850810890075
Chen, Y. S., Chang, J. F., & Cheng, C. H. (2008). Forecasting IPO initial returns using feature selection and entropy-based rough sets. International Journal of Innovative Computing Information and Control, 4(8), 1861–1875. IJICIC.
Chenhall R.H. (1997) Reliance on manufacturing performance measures, total quality management and organization performance. Management Accounting Research 8: 187–206. doi:10.1006/mare.1996.0038
Chumakov R. (2008) An artificial neural network for fault detection in the assembly of thread-forming screws. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(3): 327–333. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0085-5
Conan-Guez, B., & Rossi, F. (2002). Multi-layer perceptrons for functional data analysis: A projection based approach, ICANN 2002 (pp. 667–672). Madrid, Spain.
Danes S.M., Stafford K., Loy J.T. (2007) Family business performance: The effects of gender and management. Journal of Business Research 60(10): 1058–1069. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.12.013
Dasgupta C.G., Dispensa G.S., Ghose S. (1994) Comparative the predictive performance of a neural network model with some traditional market response models. International Journal of Forecasting 10: 235–244. doi:10.1016/0169-2070(94)90004-3
Dolgui A., Eremeev A.V., Sigaev V.S. (2007) HBBA: Hybrid algorithm for buffer allocation in tandem production lines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 18(3): 411–420. doi:10.1007/s10845-007-0030-z
Duda R.O., Hart P.E., Stork D.G. (2001) Pattern classification (2nd eds). John Wiley and Sons, New York
Dunham, M. H. (2003). Data mining: Introductory and advanced topics. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Fan H., Mark A.E., Zhu J., Honig B. (2005) Comparative study of generalized Born models: Protein dynamics. Chemical Theory and Computation Special Feature 102(19): 6760–6764
Felix T.S., Chan N.K. (2007) Global supplier development considering risk factors using fuzzy extended AHP-based approach. Omega—The International Journal of Management Science 35: 417–431
Flamini M., Pacciarelli D. (2008) Real time management of a metro rail terminus. European Journal of Operational Research 189(3): 746–761. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.09.098
Fullerton R., McWatters S. (2002) The role of performance measures and incentive systems in relation to the degree of JIT implementation. Accounting, Organizations and Society 27: 711–736. doi:10.1016/S0361-3682(02)00012-0
Gneezy U., Niederle M., Rustichini A. (2003) Performance in competitive environments: Gender differences. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 118(3): 1049–1074. doi:10.1162/00335530360698496
Gurney K. (1997) An Introduction to Neural Networs. Routledge, London
Hall R.W. (1987) Attaining manufacturing excellence. Business One Irwin, Homewood, IL
Han J., Kamber M. (2001) Data mining: Concepts and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco
Huang Z., Chena H., Hsua C.J., Chenb W.H., Wu S. (2004) Credit rating analysis with support vector machines and neural networks: A market comparative study. Decision Support Systems 37: 543–558. doi:10.1016/S0167-9236(03)00086-1
Imhof M., Vollmeyer R., Beierlein C. (2007) Computer use and the gender gap: The issue of access, use, motivation, and performance. Computers in Human Behavior 23(6): 2823–2837. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2006.05.007
Jeong W., Nof S.Y. (2008) Performance evaluation of wireless sensor network protocols for industrial applications. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(3): 335–345. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0086-4
Karels G.V., Prakash A.J. (1987) Multivariate normality and forecasting of business bankruptcy. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting 14: 573–593. doi:10.1111/j.1468-5957.1987.tb00113.x
Kattan M.W., Cooper R.B. (2000) A simulation of factors affecting machine learning techniques: An examination of partitioning and class proportions. Omega - The International Journal of Management Science 28: 501–512
Kutschenreiter-Praszkiewicz I. (2008) Application of artificial neural network for determination of standard time in machining. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(2): 233–240. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0076-6
Lawrence J. (1994) Introduction to neural networks. Scientific Software Press, California
Lawrence S.R., Buss A.H. (1995) Economic analysis of production bottlenecks. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 1(4): 341–363. doi:10.1155/S1024123X95000202
Liu W., Cheraghi S.H. (2006) A hybrid approach to nonconformance tracking and recovery. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17(1): 149–162. doi:10.1007/s10845-005-5518-9
Mak B., Munakata T. (2002) Rule extraction from expert heuristics: A comparative study of rough sets with neural networks and ID3. European Journal of Operational Research 136: 212–229. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00062-5
Markopoulos A.P., Manolakos D.E., Vaxevanidis N.M. (2008) Artificial neural network models for the prediction of surface roughness in electrical discharge machining. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(3): 283–292. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0081-9
Milas V.F., Vouyioukas D., Moraitis N., Constantinou P. (2008) Spectrum planning and performance evaluation between heterogeneous satellite networks. European Journal of Operational Research 191(3): 1132–1138. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.07.016
Mukherjee S., Chatterjee A.K. (2007) On the representation of the one machine sequencing problem in the shifting bottleneck heuristic. European Journal of Operational Research 182(1): 475–479. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.07.024
Ozturk A., Arslan A. (2007) Classification of transcranial Doppler signals using their chaotic invariant measures. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 86(2): 171–180. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.02.004
Panek S., Stursberg O., Engell S. (2006) Efficient synthesis of production schedules by optimization of timed automata. Control Engineering Practice 14(10): 1183–1197. doi:10.1016/j.conengprac.2006.02.014
Petroni A., Braglia M. (2000) Vendor selection using principal component analysis. Journal of Supply Chain Management 36(2): 63–69. doi:10.1111/j.1745-493X.2000.tb00078.x
Pi W.N., Low C. (2005) Supplier evaluation and selection using Taguchi loss functions. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 26(1–2): 155–160. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1975-5
Quinlan J.R. (1986) Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning 1: 81–106
Quinlan J.R. (1993) C4.5: Programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA
Radwan A. (2000) A practical approach to a process planning expert system for manufacturing processes. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 11(1): 75–84. doi:10.1023/A:1008956125515
Raman R., Marefat M.M. (2004) Integrated process planning using tool/process capabilities and heuristic search. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 15(2): 141–174. doi:10.1023/B:JIMS.0000018030.40309.e0
Ravi A., Kurniawan H., Thai P.N.K., Ravi Kumar P. (2008) Soft computing system for bank performance prediction. Applied Soft Computing 8: 305–315. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2007.02.001
Ravi Kumar P., Ravi V. (2007) Bankruptcy prediction in banks and firms via statistical and intelligent techniques—a review. European Journal of Operational Research 180: 1–28. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.08.043
Rossi, F., Conan-Guez, B., & Fleuret, F.(2002). Functional data analysis with multi layer perceptrons, IJCNN 2002 (part of WCCI) proceeding, Honolulu, Hawaii, (pp. 2843–2848).
Sexton R.S., Dorsey R.E. (2000) Reliable classification using neural networks: A genetic algorithm and backpropagation comparison. Decision Support Systems 30: 11–22. doi:10.1016/S0167-9236(00)00086-5
Shang K.C., Marlow P.B. (2005) Logistics capability and performance in Taiwan’s major manufacturing firms. Transportation Research Part E 41: 217–234. doi:10.1016/j.tre.2004.03.002
Sheu J.B. (2008) A hybrid neuro-fuzzy analytical approach to mode choice of global logistics management. European Journal of Operational Research 189(3): 971–986. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.082
Sim K.L., Killough L.N. (1998) The performance effects of complementarities between manufacturing practices and management accounting systems. Management Accounting Research 10: 325–346
Skianis C. (2008) Performance evaluation of QoS-aware heterogeneous systems. European Journal of Operational Research 191(3): 1056–1058. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.07.010
Steinpreis R.E., Anders K.A., Ritzke D. (1999) The impact of gender on the review of the curricula vitae of job applicants and tenure candidates: A national empirical study. Sex Roles 41: 509–528. doi:10.1023/A:1018839203698
Tam K.Y., Kiang M. (1992) Predicting bank faiures: A neural network approach. Decision Sciences 23: 926–947
Thomassey S., Happiette M. (2007) A neural clustering and classification system for sales forecasting of new apparel items. Applied Soft Computing 7: 1177–1187. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2006.01.005
Wang K. (2007) Applying data mining to manufacturing: The nature and implications. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 18(4): 487–495. doi:10.1007/s10845-007-0053-5
Witten I.H., Frank E. (2005) Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques (2nd ed). Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, USA
Xie J., Zhao X., Lee T.S. (2003) Freezing the master production schedule under single resource constraint and demand uncertainty. International Journal of Production Economics 83(1): 65–84. doi:10.1016/S0925-5273(02)00262-1
Yu Y., Chen H., Chu F. (2008) A new model and hybrid approach for large scale inventory routing problems pp. European Journal of Operational Research 189(3): 1022–1040. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.02.061
Zadeh L.A. (1994) Soft computing and fuzzy logic. IEEE Software 11(6): 48–56. doi:10.1109/52.329401
Zopounidis C., Doumpos M. (2002) Multicriteria classification and sorting methods: A literature review. European Journal of Operational Research 138: 229–246. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(01)00243-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YS., Cheng, CH. & Lai, CJ. A hybrid procedure for extracting rules of production performance in the automobile parts industry. J Intell Manuf 21, 423–437 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-008-0190-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-008-0190-5