Abstract
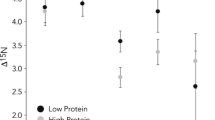
The vital role of body protein as an energy reserve has received little focus in studies of wild primates. Owing to the relatively low protein content of fruit, some frugivorous primates could face a protein deficit if body protein is catabolized for energy during periods of low fruit availability. Such an imbalance can be detected if fatty acids, amino acids, and nitrogen (N) catabolites are reincorporated or recycled back to tissues. Here we describe a method to quantify protein recycling by measuring standardized urea concentration and N isotope signatures from urine samples collected from wild Bornean orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus wurmbii). Our overall goal was to explore if concentrations of urea and δ15N values could be used as indicators of the amount of protein consumed and the degree of protein recycling, respectively, in wild, free-ranging primates. We examine the relationships between urea concentration, δ15N values, protein intake, and fruit availability. Urea concentration increased with fruit availability, reflecting a slight increase in protein consumption when fruit was abundant. However, we found no relationship between δ15N values and fruit availability, suggesting that orangutans avert a negative protein balance during periods of low fruit availability. These noninvasive methods complement recent advances in primate energy balance research and will contribute to our understanding of adaptations of primates during periods of fruit shortage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann, J. (1974). Observational study of behavior: sampling methods. Behaviour, 49, 227–265.
Anonymous. (1977). Human protein-deficiency—biochemical changes and functional implications. Nutrition Reviews, 35(11), 294–296.
Barboza, P. S., & Parker, K. L. (2006). Body protein stores and isotopic indicators of N balance in female reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) during winter. Physiological Biochemical Zoology, 79(3), 628–644.
Barboza, P. S., & Parker, K. L. (2008). Allocating protein to reproduction in Arctic reindeer and caribou. Physiological Biochemical Zoology, 81(6), 835–855.
Bastian, M. L., Zweifel, N., Vogel, E. R., Wich, S. A., & van Schaik, C. P. (2010). Diet traditions in wild orangutans. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 143(2), 175–187.
Bergstrom, J., Furst, P., Alvestrand, A., & Lindholm, B. (1993). Protein and energy intake, nitrogen balance and ntirogen losses in patients treated with continuous ambulatory peridoneal dialysis. Kidney International, 4, 1048–1057.
Campbell, J. L., Eisemann, J. H., Glander, K. E., & Crissey, S. D. (1999). Intake, digestibility, and passage of a commercially designed diet by two Propithecus species. American Journal of Primatology, 48(3), 237–246.
Cannon, C. H., & Leighton, M. (2004). Tree species distributions across five habitats in a Bornean rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 15(2), 257–266.
Cannon, C. H., Curran, L. M., Marshall, A. J., & Leighton, M. (2007a). Beyond mast-fruiting events: community asynchrony and individual dormancy dominate woody plant reproductive behavior across seven Bornean forest types. Current Science, 93(11), 1558–1566.
Cannon, C. H., Curran, L. M., Marshall, A. J., & Leighton, M. (2007b). Long-term reproductive behaviour of woody plants across seven Bornean forest types in the Gunung Palung National Park (Indonesia): suprannual synchrony, temporal productivity and fruiting diversity. Ecology Letters, 10(10), 956–969.
Chapman, C. A., Chapman, L. J., Naughton-Treves, L., Lawes, M. J., & McDowell, L. R. (2004). Predicting folivorous primate abundance: validation of a nutritional model. American Journal of Primatology, 62(2), 55–69.
Charnov, E. L. (1976). Optimal foraging: the marginal value theorem. Theoretical Population Biology, 9, 129–136.
Codron, J., Codron, D., Lee-Thorp, J. A., Sponheimer, M., Bond, W. J., de Ruiter, D., et al. (2005). Taxonomic, anatomical, and spatio-temporal variations in the stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of plants from an African savanna. Journal of Archaeological Science, 32, 1757–1772.
Conklin-Brittain, N. L., Wrangham, R. W., & Hunt, K. D. (1998). Dietary response of chimpanzees and cercopithecines to seasonal variation in fruit abundance. II. Macronutrients. International Jornal of Primatology, 19(6), 971–998.
Conklin-Brittain, N. L., Dierenfeld, E. S., Wrangham, R. W., Norconk, M., & Silver, S. C. (1999). Chemical protein analysis: a comparison of Kjeldahl crude protein and total ninhydrin protein from wild, tropical vegetation. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 25(12), 2601–2622.
Conklin-Brittain, N. L., Knott, C. D., & Wrangham, R. W. (2006). Energy intake by wild chimpanzees and orangutans: Methodological considerations and a preliminary comparison. In G. Hohmann, M. Robbins & C. Boesch (Eds.), Feeding ecology in apes and other primates: Ecological, physiological and behavioural aspects. Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology 48 (pp. 445–471). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Curran, L. M., & Leighton, M. (2000). Vertebrate responses to spatiotemporal variation in seed production of mast-fruiting Dipterocarpaceae. Ecological Monographs, 70(1), 101–128.
DeNiro, M. J., & Epstein, S. (1981). Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 341–351.
Deschner, T., Fuller, B. T., Oelze, V., Ortmann, S., Richard, M. P., & G., H. (2010). Monitoring nutritional stress with urinary delta15N and C/N ratios in captive bonobos. American Journal of Physical Anthropology (Supplement), 50, 93.
Edozien, J. C., Khan, M. A. R., & Waslien, C. I. (1976). Human protein-deficiency— results of a Nigerian village study. Journal of Nutrition, 106(3), 312–328.
Emery Thompson, M., & Knott, C. D. (2008). Urinary C-peptide of insulin as a non-invasive marker of energy balance in wild orangutans. Hormones and Behavior, 53(4), 526–535.
Felton, A. M., Felton, A., Raubenheimer, D., Simpson, S. J., Foley, W. J., Wood, J. T., et al. (2009a). Protein content of diets dictates the daily energy intake of a free-ranging primate. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 20(4), 685–690.
Felton, A. M., Felton, A., Wood, J. T., Foley, W. J., Raubenheimer, D., Wallis, I. R., et al. (2009b). Nutritional ecology of Ateles chamek in lowland Bolivia: how macronutrient balancing influences food choices. International Journal of Primatology, 30(5), 675–696.
Ganzhorn, J. U. (1992). Leaf chemistry and the biomass of folivorous primates in tropical forests—test of a hypothesis. Oecologia, 91(4), 540–547.
Ganzhorn, J. U., Arrigo-Nelson, S., Boinski, S., Bollen, A., Carrai, V., Derby, A., et al. (2009). Possible fruit protein effects on primate communities in Madagascar and the Neotropics. PLoS One, 4(12).
Glander, K. E. (1981). Feeding patterns in mantled howling monkeys. In A. Kamil & T. D. Sargent (Eds.), Foraging behavior: Ecological, ethological and psychological perspectives. New York: Garland Press.
Goeyens, L., Kindermans, N., Yusuf, M. A., & Elskens, M. (1998). A room temperature procedure for the manual determination of urea in seawater. Estuarine, Coastal, and Shelf Science, 47(4), 415–418.
Harrison, M. E., Morrogh-Bernard, H. C., & Chivers, D. J. (2010). Orangutan energetics and the influence of fruit availability in the nonmasting peat-swamp forest of Sabangau, Indonesian Borneo. International Journal of Primatology, 31(4), 585–607.
Heiman, M. L., Chen, Y. Y., & Caro, J. F. (1998). Leptin participates in the regulation of glucocorticoid and growth hormone axes. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 9(10), 553–559.
Hobson, K. A., Alisauskas, R. T., & Clark, R. G. (1993). Stable-nitrogen isotope enrichment in avian-tissues due to fasting and nutritional stress—implications for isotopic analyses of diet. Condor, 95(2), 388–394.
Hyodo, F., Matsumoto, T., Takematsu, Y., Kamoi, T., Fukuda, D., Nakagawa, M., et al. (2010). The structure of a food web in a tropical rain forest in Malaysia based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 26, 205–214.
Izhaki, I. (1993). Influence of nonprotein nitrogen on estimation of protein from total nitrogen in fleshy fruits. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 19(11), 2605–2615.
Jackson, A. A., Danielsen, M. S., & Boyes, S. (1993). A noninvasive methods for measuring urea kinetcs with a single-dose of [N15 N15] urea in free-living humans. Journal of Nutrition, 123(12), 2129–2136.
Kempster, B., Zanette, L., Longstaffe, F. J., MacDougall-Shackleton, S. A., Wingfield, J. C., & Clinchy, M. (2007). Do stable isotopes reflect nutritional stress? Results from a laboratory experiment on song sparrows. Oecologia, 151(3), 365–371.
Knott, C. D. (1997). Field collection and preservation of urine in orangutans and chimpanzees. Tropical Biodiversity, 4, 95–102.
Knott, C. D. (1998). Changes in orangutan caloric intake, energy balance, and ketones in response to fluctuating fruit availability. International Journal of Primatolology, 19, 1061–1079.
Knott, C. D. (1999). Reproductive, physiological and behavioral responses of orangutans in Borneo to fluctuations in food availability. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, Harvard University.
Knott, C. D. (2005a). Energetic responses to food availability in the great apes: inplications for hominin evolution. In D. K. Brockman & C. P. van Schaik (Eds.), Seasonality in primates: Studies of living and extinct human and non-human primates (pp. 351–378). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Knott, C. D. (2005b). Radioimmunoassay of estrone conjugates from urine dried on filter paper. American Journal of Primatology, 67(1), 121–135.
Knott, C. D., Thompson, M. E., Stumpf, R. M., & McIntyre, M. H. (2010). Female reproductive strategies in orangutans: evidence for female choice and counterstrategies to infanticide in a species with frequent sexual coercion. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277(1678), 105–113.
Koch, P. L. (2007). Isotopic study of the biology of modern and fossil vertebrates. In R. Michener & K. Lajtha (Eds.), Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental Science (2nd ed., pp. 99–154). Boston: Blackwell.
Lechtig, A., Martorell, R., Yarbrough, C., Delgado, H., & Klein, R. E. (1976). The urea/creatinine ratio: is it useful for field studies? Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 22(3), 121–128.
Lechtig, A., Martorell, R., Yarbrough, C., Delgado, H., & Klein, R. E. (1981). Influence of food supplementation on the urinary urea-creatinine (U-C) ratio of the child. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 27(3), 144–149.
Lee, K. P., Simpson, S. J., & Wilson, K. (2008). Dietary protein-quality influences melanization and immune function in an insect. Functional Ecology, 22(6), 1052–1061.
Leighton, M., & Wirawan, N. (1986). Catastrophic drought and fire in Borneo tropical rain forest associated with the 1982–1983 El Nino Southern Oscillation event. AAAS (American Association for the Advancement of Science) Selected Symposium, 101, 75–102.
Leonard, W. R. (2000). Human nutritional evolution. In S. Stinson, B. Bogin, R. Huss-Ashmore, & D. O'Rourke (Eds.), Human biology: An evolutionary and biocultural perspective (pp. 295–343). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Marshall, A. J. (2009). Are montane forests demographic sinks for Bornean white-bearded gibbons, Hylobates albibarbis ? Biotropica, 41(2), 257–267.
Martínez del Rio, C., & Wolf, B. O. (2005). Mass-balance models for animal isotopic ecology. In J. M. Starck & T. Wang (Eds.), Physiological and ecological adaptations to feeding in vertebrates. Enfield, NH: Science Publishers.
Martínez del Rio, C., Wolf, N., Carleton, S. A., & Gannes, L. Z. (2009). Isotopic ecology ten years after a call for more laboratory experiments. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 84, 91–111.
McCue, M. D., & Pollock, E. D. (2008). Stable isotopes may provide evidence for starvation in reptiles. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 22(15), 2307–2314.
McKey, D. B., Gartlan, J. S., Waterman, P. G., & Choo, G. M. (1981). Food selection by black colobus monkeys (Colobus satanus) in relation to plant chemistry. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 16, 115–146.
Meling, T. R., & Nylen, E. S. (1996). Growth hormone deficiency in adults: a review. American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 311(4), 153–166.
Millward, D. J. (1999). Optimal intakes of protein in the human diet. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 58(2), 403–413.
Milton, K. (1979). Factors influencing leaf choice by howler monkeys: a test of some hypotheses of food selection by generalist herbivores. American Naturalist, 114, 362–378.
Milton, K. (1981). Food choice and digestive strategies of 2 sympatric primate species. American Naturalist, 117(4), 496–505.
Milton, K., & Dintzis, F. R. (1981). Nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for tropical plant-samples Biotropica, 13(3), 177–181.
Miyoshi, H., Okuda, T., Fujita, Y., Ichikawa, M., Kajiwara, N. M., Miyatani, S., et al. (1986). Effect of dietary protein levels on urea utilization in Papua New Guinea highlanders. Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36(4), 761–771.
Morrogh-Bernard, H. C., Husson, S. J., Knott, C. D., Wich, S. A., van Schaik, C. P., van Noordwijk, M. A., et al. (2009). Orangutan activity budgets and diet: A comparison between species, populations and habitats. In S. A. Wich, S. Utami Atmoko, T. Mitra Setia, & C. P. van Schaik (Eds.), Orangutans: Geographic variation in behavioral ecology and conservation (pp. 119–133). New York: Oxford University Press.
Mulvenna, P. F., & Savidge, G. (1992). A modified manual method for the determination of urea in seawater using diacetylmonoxime reagent. Estuarine, Coastal, and Shelf Science, 34(5), 429–438.
N'Guessan, A. K., Ortmann, S., & Boesch, C. (2009). Daily energy balance and protein gain among Pan troglodytes verus in the Tai National Park, Cote d'Ivoire. International Journal of Primatology, 30(3), 481–496.
Oates, J. F., Whitesides, G. H., Davies, A. G., Waterman, P. G., Green, S. M., Dasilva, G. L., et al. (1990). Determinants of variation in tropical forest primate biomass - new evidence from west-Africa. Ecology, 71(1), 328–343.
Oftedal, O. T. (1991). The nutritional consequences of foraging in primates - the relationship of nutrient intakes to nutrient-requirements. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 334(1270), 161–170.
Ortmann, S., Bradley, B. J., Stolter, C., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2006). Estimating the quality and composition of wild animal diets—a critical survery of methods. In . Hohmann, M. Robbins & C. Boesch (Eds.), Feeding ecology in apes and other primates: Ecological, physiological and behavioural aspects. Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology 48 (pp. 397–420). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Parker, K. L., Barboza, P. S., & Stephenson, T. R. (2005). Protein conservation in female caribou (Rangifer tarandus): effects of decreasing diet quality during winter. Journal of Mammalogy, 86(3), 610–622.
Pierce, W. C., & Haenisch, E. L. (1947). Quantitative analysis. London: Wiley.
Pinheiro, J., Bates, D., DebRoy, S., Sarkar, D., & Team*, the R Core Development Team. (2011). nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version, 3, 1–100.
Price, N. M., & Harrison, P. J. (1987). Comparison of methods for the analysis of dissolved urea in seawater. Marine Biology, 94(2), 307–317.
Rikimaru, T., Fujita, Y., Okuda, T., Kajiwara, N., Date, C., Heywood, P. F., et al. (1985). Utilization of urea nitrogen in Papua New Guinea highlanders. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 31, 393–402.
Rothman, J. M., Chapman, C. A., & Pell, A. N. (2008). Fiber-bound nitrogen in gorilla diets: implications for estimating dietary protein intake of primates. American Journal of Primatology, 70(7), 690–694.
Rothman, J. M., Chapman, C. A., Hansen, J. L., Cherney, D. J. R., & Pell, A. N. (2009). Rapid assessment of the nutritional value of foods eaten by mountain gorillas: applying near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy to primatology. International Journal of Primatology, 30(5), 729–742.
Rothman, J. M., Van Soest, P. J., & Chapman, C. A. (this issue). Methods in primate nutritional ecology: A user's guide. International Journal of Primatology
Sare, D. T. J., Millar, J. S., & Longstaffe, F. J. (2005). Tracing dietary protein in red-backed voles (Clethrionomys gapperi) using stable isotopes of nitrogen and carbon. Canadian Journal of Zoology-Revue Canadienne de Zoologie, 83(5), 717–725.
Saude, E. J., & Sykes, B. D. (2007). Urine stability for metabolic studies: effects of preparation and storage. Metabolomics, 3(1), 19–27.
Schuelke, O., Chalise, M. K., & Koenig, A. (2006). The importance of ingestion rates for estimating food quality and energy intake. American Journal of Primatology, 68(10), 951–965.
Sherry, D. S., & Ellison, P. T. (2007). Potential applications of urinary C-peptide of insulin for comparative energetics research. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 133(1), 771–778.
Sick, H., Roos, N., Saggau, E., Haas, K., Meyn, V., Walch, B., et al. (1997). Amino acid utilization and isotope discrimination of amino nitrogen in nitrogen metabolism of rat liver in vivo. Zeitschrift Fur Ernahrungswissenschaft, 36(4), 340–346.
Simmons, W. K. (1972). Urinary urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio as indicator of recent protein intake in field studies. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 25, 539–542.
Sponheimer, M., Robinson, T. F., Roeder, B. L., Passey, B. H., Ayliffe, L. K., Cerling, T. E., et al. (2003). An experimental study of nitrogen flux in llamas: is N-14 preferentially excreted? Journal of Archaeological Science, 30(12), 1649–1655.
Steele, K. W., & Daniel, R. M. (1978). Fractionation of nitrogen isotopes by animals: a further complication of the use of variations in the natural abundance of 15 N for tracer studies. Journal of Agricultural Science, 90, 7–9.
Taussky, H. (1954). A microcolorimetric determination of creatinine in urine by the Jaffe reaction. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 208, 853–861.
Tsuji, Y., Kazahari, N., Kitahara, M., & Takatsuki, S. (2008). A more detailed seasonal division of the energy balance and the protein balance of Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata) on Kinkazan Island, northern Japan. Primates, 49(2), 157–160.
van Schaik, C. P., Terborgh, J. W., & Wright, S. J. (1993). The phenology of tropical forests: adaptive significance and consequences for primary consumers. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 24, 353–377.
Vogel, E. R., van Woerden, J. T., Lucas, P. W., Atmoko, S. S. U., van Schaik, C. P., & Dominy, N. J. (2008). Functional ecology and evolution of hominoid molar enamel thickness: Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii and Pongo pygmaeus wurmbii. Journal of Human Evolution, 55(1), 60–74.
Vogel, E. R., Haag, L., Mitra-Setia, T., van Schaik, C. P., & Dominy, N. J. (2009). Foraging and ranging behavior during a fallback episode: Hylobates albibarbis and Pongo pygmaeus wurmbii compared. American Journal of Physical Anthopology, 140(4), 716–726.
Wagenmakers, A. J. M. (1998). Protein and amino acid metabolism in human muscle. In E. A. Richter, B. Kiens, H. Galbo & B. Saltin (Eds.), Skeletal muscle metabolism in exercise and diabetes (Vol. 441, pp. 307–319).
Wheatley, B. P. (1987). The evolution of large body size in orangutans: a model for hominoid divergence. American Journal of Primatology, 13(3), 313–324.
White, F. J. (1998). Seasonality and socioecology: the importance of variation in fruit abundance to bonobo sociality. International Journal of Primatology, 19(6), 1013–1027.
Wich, S. A., & van Schaik, C. P. (2000). The impact of El Niño on mast fruiting in Sumatra and elsewhere in Malesia. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 16, 563–577.
Wich, S. A., Utami-Atmoko, S. S., Setia, T. M., Djoyosudharmo, S., & Geurts, M. L. (2006). Dietary and energetic responses of Pongo abelii to fruit availability fluctuations. International Journal of Primatology, 27(6), 1535–1550.
Withers, P. C. (1998). Urea: diverse functions of a "waste" product. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 25(9), 722–727.
Worman, C. O., & Chapman, C. A. (2005). Seasonal variation in the quality of a tropical ripe fruit and the response of three frugivores. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 21, 689–697.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Directorate of Nature Conservation (PHKA), the Gunung Palung National Park office (BTNGP), the Indonesian Institute of Sciences (LIPI), the Center for Research and Development in Biology (PPPB), and the State Ministry of Research and Technology (RISTEK) for their sponsorship and for granting permission to conduct research in Gunung Palung National Park. We thank Dr. Raphael Kudela and Dr. Paul Koch for fruitful discussions in the early stages of this research project and for providing us with access to their laboratories and supplies for our analyses. We thank the University of Santa Cruz Stable Isotope Laboratory and Dyke Andreasen for the use of the facility. We are grateful to Brett Walker, Dr. Sora Kim, and Dr. Nancy Conklin-Brittain for their advice on sample preparation for our analyses and the interpretation of our results. We also thank all of the dedicate field assistants, research assistants, field managers, and students who assisted with data and sample collection. This research was supported by L. S. B. Leakey Foundation grants (E. R. Vogel, N. J. Dominy, and C. D. Knott), The George Washington University Selective Excellence Fund (to the Center for the Advanced Study of Hominid Paleobiology for E. R. Vogel and to the Department of Statistics and the Biostatistics Center for M. D. Larsen), David and Lucile Packard Foundation Fellowship in Science and Engineering (no. 2007–31754, N. J. Dominy), National Geographic Society (C. D. Knott), The National Science Foundation no. BCS-0643122 (E. R. Vogel, N. J. Dominy, and C. D. Knott), U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (C. D. Knott), the Wenner-Gren Foundation (C. D. Knott), Harvard University (C. D. Knott), and The Mellon Foundation (C. D. Knott). This research was approved by UCSC CARC IACUC (no. 20061056–122204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 113 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, E.R., Crowley, B.E., Knott, C.D. et al. A Noninvasive Method for Estimating Nitrogen Balance in Free-Ranging Primates. Int J Primatol 33, 567–587 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-011-9543-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-011-9543-6