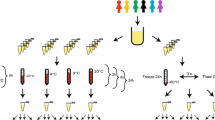
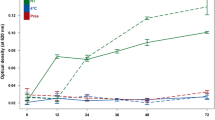
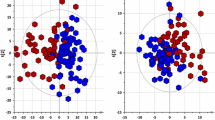
Metabolomic studies attempt to identify and profile unique metabolic differences among test populations, which may be correlated with a specific biological stress or pathophysiology. Due to the ease of collection and the metabolite-rich nature of urine, it is frequently used as a bio-fluid for human and animal metabolic studies. High-resolution 1H-NMR is an analytical tool used to qualitatively and quantitatively identify metabolites in urine. Urine samples were collected from healthy male and female subjects and prepared: raw, following centrifugation, filtration, or the addition of the bacteriostatic preservative sodium azide and analyzed by NMR. In addition, these samples were stored at room temperature (22 °C), in a refrigerator (4 °C), or in a deep-freeze (−80 °C). Samples were analyzed by NMR every week for a month and changes in concentrations of 55 easily identifiable metabolites were followed. The degree of change in metabolite concentrations following storage over a 4-week period were influenced by the different methods of sample preparation and storage. Significant changes in urine metabolites are likely due to bacterial contamination of the urine. Our study demonstrates that bacterial contamination of urine in normal individuals significantly alters the metabolic profile of urine over time and proper preparation and storage procedures must be followed to reduce these changes. By identifying appropriate methods of urine preparation and storage investigators will preserve the fidelity of the urine samples in order to better reflect the original metabolic state.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen T.A., Jones R.L., Purvance J., (1987) Microbiologic evaluation of canine urine: direct microscopic examination and preservation of specimen quality for culture J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 190: 1289–1291
Armstrong M.D., Shaw K.N., Wall P.E., (1956) The phenolic acids of human urine; paper chromatography of phenolic acids J. Biol. Chem. 218: 293–303
Bain M.D., Jones M., Borriello S.P., Reed P.J., Tracey B.M., Chalmers R.A., Stacey T.E., (1988) Contribution of gut bacterial metabolism to human metabolic disease Lancet 1: 1078–1079
Bar-Meir M., Raveh D., Yinnon A.M., Benenson S., Rudensky B., Schlesinger Y., (2005) Non-Typhi Salmonella gastroenteritis in children presenting to the emergency department: characteristics of patients with associated bacteraemia Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 11: 651–655
Bollard M.E., Stanley E.G., Lindon J.C., Nicholson J.K., Holmes E., (2005) NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition NMR Biomed. 18: 143–162
Brenner D.J., Mcwhorter A.C., Kai A., Steigerwalt A.G., Farmer J.J. 3rd (1986) Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov., a new species found in clinical specimens, and reassignment of Erwinia dissolvens and Erwinia nimipressuralis to the genus Enterobacter as Enterobacter dissolvens comb. nov. and Enterobacter nimipressuralis comb. nov J. Clin. Microbiol. 23: 1114–1120
Brewster M.A., Schedewie H., (1983) Trimethylaminuria Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 13: 20–24
Brindle J.T., Antti H., Holmes E., Tranter G., Nicholson J.K., Bethell H.W., Clarke S., Schofield P.M., Mckilligin E., Mosedale D.E., Grainger D.J., (2002) Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabolomics Nat. Med. 8: 1439–1444
Cattell W.R., Sardeson J.M., Hutchinson E., O’grady F., (1969) Creatinine content of urine and bacterial growth Br. Med. J. 3: 175–176
Chadha V., Garg U., Alon U.S., (2001) Measurement of urinary concentration: a critical appraisal of methodologies Pediatr. Nephrol. 16: 374–382
Chambers S.T., Peddie B.A., Randall K., Lever M., (1999) Inhibitors of bacterial growth in urine: what is the role of betaines? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 11: 293–296
Coen M., O’sullivan M., Bubb W.A., Kuchel P.W., Sorrell T., (2005) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics for rapid diagnosis of meningitis and ventriculitis Clin Infect Dis 41: 1582–1590
D’Argenio G., Mazzacca G., (1999) Short-chain fatty acid in the human colon. Relation to inflammatory bowel diseases and colon cancer Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 472: 149–158
Dunn W.B., Bailey N.J., Johnson H.E., (2005) Measuring the metabolome: current analytical technologies Analyst 130: 606–625
Dyer A., Elliott P., Chee D., Stamler J., (1997) Urinary biochemical markers of dietary intake in the INTERSALT study Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65: 1246S–1253S
Funfstuck R., Stein G., Fuchs M., Bergner M., Wessel G., Keil E., Suss J., (1987) The influence of selected urinary constituents on the adhesion process of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells Clin. Nephrol. 28: 244–9
Goodwin B.L., Ruthven C.R., Sandler M., (1994) Gut flora and the origin of some urinary aromatic phenolic compounds Biochem. Pharmacol. 47: 2294–7
Griffith D.P., Musher D.M., Itin C., (1976) Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones Invest. Urol. 13: 346–50
Griffiths L., Irwing A.M. (1998) Assay by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: quantification limits Analyst 123: 1061–1068
Guneral F., Bachmann C., (1994) Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population Clin Chem 40: 862–866
Hansen S., Perry T.L., Lesk D., Gibson L., (1972) Urinary bacteria: potential source of some organic acidurias Clin Chim Acta 39: 71–74
Holmes E., Nicholls A.W., Lindon J.C., Connor S.C., Connelly J.C., Haselden J.N., Damment S.J., Spraul M., Neidig P., Nicholson J.K., (2000) Chemometric models for toxicity classification based on NMR spectra of biofluids Chem Res Toxicol 13: 471–478
Hoult D.I., (1976) Solvent peak saturation with single phase and quadrature Fourier transformation J. Magn. Reson. 21: 337–347
Jones J.D., Burnett P.C., (1972) Implication of creatinine and gut flora in the uremic syndrome: induction of “creatininase” in colon contents of the rat by dietary creatinine Clin Chem 18: 280–284
Kaya S., Poyraz O., Gokce G., Kilicarslan H., Kaya K., Ayan S., (2003) Role of genital mycoplasmata and other bacteria in urolithiasis Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 35: 315–317
Kaye D., (1968) Antibacterial activity of human urine J. Clin. Invest. 47: 2374–2390
Lenz E.M., Bright J., Wilson I.D., Hughes A., Morrisson J., Lindberg H., Lockton A., (2004) Metabonomics, dietary influences and cultural differences: a 1H NMR-based study of urine samples obtained from healthy British and Swedish subjects J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 36: 841–849
Lenz E.M., Bright J., Wilson I.D., Morgan S.R., Nash A.F., (2003) A 1H NMR-based metabonomic study of urine and plasma samples obtained from healthy human subjects J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 33: 1103–1115
Lindon J.C., Holmes E., Bollard M.E., Stanley E.G., Nicholson J.K., (2004) Metabonomics technologies and their applications in physiological monitoring, drug safety assessment and disease diagnosis Biomarkers 9: 1–31
Lutsar I., Gontmacher A., Narska M., Ruutel V., Topman M., Ilves P., Siirde T., Beilmann A., (1995) Five days of antibacterial therapy for bacterial meningitis in children? Infection 23: 113–118
Macfarlane S., Macfarlane G.T., (2003) Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production Proc Nutr Soc 62: 67–72
Moolenaar S.H., Engelke U., Wevers R.A. (2003) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of body fluids in the field of inborn errors of metabolism Ann Clin Biochem 40: 16–24
Nazifi S., Rezakhani A., Badran M., (1997) Evaluation of hematological, serum biochemical and cerebrospinal fluid parameters in experimental bacterial meningitis in the calf Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 44: 55–63
Nicholls A.W., Mortishire-Smith R.J., Nicholson J.K., (2003) NMR spectroscopic-based metabonomic studies of urinary metabolite variation in acclimatizing germ-free rats Chem. Res. Toxicol. 16: 1395–1404
Nickander K.K., Shanholtzer C.J., Peterson L.R., (1982) Urine culture transport tubes: effect of sample volume on bacterial toxicity of the preservative J. Clin. Microbiol. 15: 593–595
Pathak C.M., Bhasin D.K., Khanduja K.L., (2004a) Urea breath test for Helicobacter pylori detection: present status Trop. Gastroenterol. 25: 156–161
Pathak C.M., Bhasin D.K., Pramod K.A., Khanduja K.L., (2004b) 14C-urea breath test as a ‘gold standard’ for detection of Helicobacter pylori infection Med Sci Monit 10: LE14–LE15
Peddie B.A., Chambers S.T., Lever M., (1996) Is the ability of urinary tract pathogens to accumulate glycine betaine a factor in the virulence of pathogenic strains? J. Lab. Clin. Med. 128: 417–422
Sabatine M.S., Liu E., Morrow D.A., Heller E., Mccarroll R., Wiegand R., Berriz G.F., Roth F.P., Gerszten R.E., (2005) Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial ischemia Circulation 112: 3868–3875
Schiwara H.W., Siegel H., Goebel A., (1992) Increase and decrease in formic acid concentration in urine samples stored at room temperature Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 30: 75–79
Stenina M.A., Voevodin D.A., Stakhanov V.D., Kisilevich O.N., Rozanova G.N., (2003) Tissue hypoxia and intestinal dysbiosis in children with tuberculosis Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 135: 178–180
Symanski E., Greeson N.M., (2002) Assessment of variability in biomonitoring data using a large database of biological measures of exposure AIHA J (Fairfax Va) 63: 390–401
Tal S., Guller V., Levi S., Bardenstein R., Berger D., Gurevich I., Gurevich A., (2005) Profile and prognosis of febrile elderly patients with bacteremic urinary tract infection J. Infect. 50: 296–305
Tate A.R., Damment S.J., Lindon J.C., (2001) Investigation of the metabolite variation in control rat urine using 1H NMR spectroscopy Anal. Biochem. 291: 17–26
Udert K.M., Larsen T.A., Biebow M., Gujer W., (2003a) Urea hydrolysis and precipitation dynamics in a urine-collecting system Water. Res. 37: 2571–2582
Udert K.M., Larsen T.A., Gujer W., (2003b) Estimating the precipitation potential in urine-collecting systems Water Res. 37: 2667–2677
Utine G.E., Ozcelik U., Yalcin E., Dogru D., Kiper N., Aslan A., Kanra G., (2005) Childhood parapneumonic effusions: biochemical and inflammatory markers Chest 128: 1436–1441
Weckwerth W., Morgenthal K., (2005) Metabolomics: from pattern recognition to biological interpretation Drug Discov. Today 10: 1551–1558
Zeisel S.H., Dacosta K.A., Fox J.G., (1985) Endogenous formation of dimethylamine Biochem. J. 232: 403–408
Zeisel S.H., Dacosta K.A., Youssef M., Hensey S., (1989) Conversion of dietary choline to trimethylamine and dimethylamine in rats: dose–response relationship J. Nutr. 119: 800–804
Zuppi C., Messana I., Forni F., Rossi C., Pennacchietti L., Ferrari F., Giardina B., (1997) 1H NMR spectra of normal urines: reference ranges of the major metabolites Clin Chim Acta 265: 85–97
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Genome Prairie, Genome Canada, the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the University of Alberta.
The authors would like to thank Angela Thiessen for her assistance in sample preparation. We would also like to thank Carolyn Slupsky for her helpful discussions. This research was supported by the Canadian Institues of Health Research (CIHR), Genome Prairie, and Genome Canada. We would like to thank the Canadian National High Field NMR Centre (NANUC) for their assistance and use of the facilities. Operation of NANUC is funded by CIHR, the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the University of Alberta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saude, E.J., Sykes, B.D. Urine stability for metabolomic studies: effects of preparation and storage. Metabolomics 3, 19–27 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0042-2