Abstract
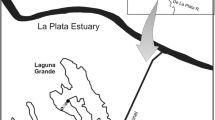
We investigated the main structuring forces driving epiphytic algae dynamics with wind disturbances and zooplankton grazing acting as potential stressors by inducing a natural 60-day epiphyton summer succession. We cleaned macrophytes in the subtropical shallow Mangueira Lake, southern Brazil, using soft sponges and sampled them randomly at short-term intervals. Simultaneously, we sampled and classified zooplankton from the littoral zone according to their particle ingestion size. Disturbance by wind was the main factor driving the epiphyton succession. Tightly attached diatoms were well adapted to the system’s high mean wind velocity (15 m s−1), whereas low wind velocity (<7 m s−1) reduced community diversity. Summer storms (46.7 mm of precipitation; 29.5 m s−1 wind velocity) caused phosphorus input and favored prostrate diatoms. Epiphyton was very productive (8028.8 mg C m−2 h−1), consistent with a heterogeneous community. Small rotifers and ciliates were abundant in the water column during the study. Our data indicate that rotifers as well as other zooplankton grazed on epiphyton, due to the positive correlation between algal diversity and rotifer abundance as well as between diatom and zooplankton biomasses, whereas Copepods and Cladocerans followed large motile diatoms in abundance. We conclude that epiphyton is an important food source for zooplankton in Mangueira Lake.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ács, E. & K. T. Kiss, 1993. Effects of the water discharge on periphyton abundance and diversity in a large river (River Danube, Hungary). Hydrobiologia 249: 125–133.
Ács, E., A. K. Borsodi, K. Kropfl, P. Vladar & G. Zarai, 2007. Changes in the algal composition, bacterial metabolic activity and element content of biofilms developed on artificial substrata in the early phase of colonization. Acta Bot Croat 66: 89–100.
Agasild, H., P. Zingel, I. Tõnno, J. Haberman & T. Nõges, 2007. Contribution of different zooplankton groups in grazing on phytoplankton in shallow eutrophic Lake Võrtsjäev (Estonia). Hydrobiologia 584: 167–177.
Agasild, H., P. Zingel, K. Karus, K. Kangro, J. Salujõe & T. Nõges, 2013. Does metazooplankton regulate the ciliate community in a shallow eutrophic lake? Freshwater Biology 58: 183–191.
American Public Health Association (APHA), 2005. Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, Washington (DC).
Ask, J., J. Karlsson, L. Persson, P. Ask, P. Byström & M. Jansson, 2009. Terrestrial organic matter and light penetration: effects on bacterial and primary production in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2034–2040.
Berthon, V., A. Bouchez & F. Rimet, 2011. Using diatom life-forms and ecological guilds to assess organic pollution and trophic level in rivers: a case of study of rivers in south-eastern France. Hydrobiologia 673: 259–271.
Biggs, B. J. F., 1996. Patterns in benthic algae of streams. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Elsevier, San Diego: 31–56.
Blukacz, E. A., W. G. Sprules, B. J. Shuter & J. P. Richards, 2010. Evaluating the effect of wind-driven patchiness on trophic interactions between zooplankton and phytoplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1590–1600.
Bottrell, H. H., A. Duncan, Z. M. Gliwicz, E. Grygierek, A. Herzig, A. Hillbricht-Ilkowska, H. Kurosawa, P. Larsson & T. Weglenska, 1976. A review of some problems in zooplankton production studies. Norwegian Journal of Zoology 24: 419–456.
Brothers, S., Y. Vadeboncoeur & P. Sibley, 2016. Benthic algae compensate for phytoplankton losses in large aquatic ecosystems. Global Change Biology. doi:10.1111/gcb.13306.
Bundy, M. H., H. A. Vanderploeg, P. J. Lavrentyev & P. A. Kovalcilk, 2005. The importance of microzooplankton versus phytoplankton to copepod populations during late winter and early spring in Lake Michigan. Canadian Journal of Fish and Aquatic Sciences 62: 2371–2385.
Burkholder, J. M. & R. G. Wetzel, 1989. Epiphytic microalgae on natural substrata in a hard water lake: seasonal dynamics of community structure, biomass and ATP content. Archives of Hydrobiology 83: 1–56.
Cantonati, M. & R. L. Lowe, 2014. Lake benthic algae: toward an understanding of their ecology. Freshwater Science 33: 475–486.
Cardoso, L. S. & D. Motta Marques, 2004. Structure of the zooplankton community in a subtropical shallow lake (Itapeva Lake – South of Brazil) and its relationship to hydrodynamic aspects. Hydrobiologia 518: 123–134.
Cardoso, L. S. & D. Motta Marques, 2009. Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake. Aquatic Ecology 43: 73–84.
Cardoso, L. S., C. R. Fragoso Jr., R. S. Souza & D. Motta Marques, 2012. Hydrodynamic control of plankton spatial and temporal heterogeneity in subtropical shallow lakes. In Schulz, H. E., A. L. A. Simões & R. J. Lobosco (eds), Hydrodynamics-Natural Water Bodie. Intech Open Access Publisher, Rijeka: 27–48.
Carrias, J. F., J. P. Serre, T. S. Ngando & C. Amblard, 2002. Distribution, size, and bacterial colonization of pico- and nano-detrital organic particles (DOP) in two lakes of different trophic status. Limnology and Oceanography 47: 1202–1209.
Chen, C. C., J. E. Petersen & W. M. Kemp, 1997. Spatial and temporal scaling of periphyton growth on walls of estuarine mesocosms. Marine Ecology Pregress Series 155: 1–15.
Collos, Y., C. Descolas-Gros, M. Fontugne, A. Mortain-Bertand, M. J. Chrétiennot-Dinet & M. G. Frikha, 1992. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics during growth and degradation of phytoplankton under natural surface irradiance. Marine Biology 112: 491–496.
Connell, J. H., 1978. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 199: 1302–1310.
Crossetti, L. O., V. Becker, L. S. Cardoso, L. H. Rodrigues, L. S. Costa & D. Motta Marques, 2013. Is phytoplankton functional classification a suitable tool to investigate spatial heterogeneity in a subtropical shallow lake? Limnologica 43: 157–163.
Crossetti, L. O., F. Schneck, L. M. Freitas-Teixeira & D. Motta-Marques, 2014. The influence of environmental variables on spatial and temporal phytoplankton dissimilarity in a large shallow subtropical lake (Lake Mangueira, southern Brazil). Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 26: 111–118.
DeMott, W. R., R. D. Gulati & E. Van Donk, 2001. Daphnia food limitation in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes: evidence for exclusion of large-bodied species by interfering filaments of Cyanobacteria. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 2054–2060.
DeNicola, D. M. & M. Kelly, 2014. Role of periphyton in ecological assessment of lakes. Freshwater Science 33: 619–638.
DeYoe, H. R., R. L. Lowe & J. C. Marks, 1992. Effects of nitrogen phosphorus on the endosymbiont load of Rhopalodia gibba and Epithemia turgida (Bacillariophyta). Journal of Phycology 28: 773–777.
Dumont, H. J., I. van de Velde & S. Dumont, 1975. The dry weight estimate of biomass in a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 19: 75–97.
Elmoor-Loureiro, L. M. A. 1997. Manual de identificação de cladóceros límnicos do Brasil. Universa, Brasília. 156p.
Faria, D. M., L. S. Cardoso & D. Motta-Marques, 2015. Periphytic diatoms exhibit a longitudinal gradient in a large subtropical shallow lake. Inland Waters 5: 117–124.
Ferragut, C. & D. C. Bicudo, 2010. Periphytic algal community adaptative strategies in N and P enriched experiments in a tropical oligotrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 646: 295–309.
Ferragut, C. & D. C. Bicudo, 2012. Effect of N and P enrichment on periphytic algal community in a succession in a tropical oligotrophic reservoir. Limnology 13: 131–141.
Fragoso Jr., C. R., D. Motta Marques, T. F. Ferreira, J. H. Janse & E. H. van Nes, 2011. Potential effects of climate change and eutrophication on a large subtropical shallow lake. Environmental Modeling & Software 26: 1337–1348.
Fraterrigo, J. M. & J. A. Rusak, 2008. Disturbance-driven changes in the variability of ecological patterns and process. Ecology Letters 11: 756–770.
Hillebrand, H., C. D. Durselen, D. Kirschtel, U. Pollinger & T. Zohary, 1999. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology 35: 403–424.
Hoagland, K. D., S. C. Roemer & J. R. Rosowski, 1982. Colonization and community structure of two periphyton assemblages, with emphasis on the diatoms (Baccillariophyceae). American Journal of Botany 69: 188–213.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1975. A treatise on Limnology. Limnological Botany, Interscience, New York.
Ilmavirta, V., 1988. Phytoflagellates and their ecology in Finnish brown-water lakes. Hydrobiologia 161: 255–270.
Jespersen, A. M. & K. Christoffersen, 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll – a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 109: 445–454.
Jeppesen, E., T. L. Lauridsen, T. Kairesalo & M. Perrow, 1998. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton interactions in lakes. In Jeppesen, E., M. S. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer, New York: 91–114.
Kahlert, M., 1998. C:N: P ratios of freshwater benthic algae. Archives of Hydrobiology 51: 105–114.
Kelly, M. G., L. King & B. NíChatháin, 2009. The conceptual basis of ecological-status assessments using diatoms. Biology and Environment: Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy 109: 175–189
Kluijver, A., J. Ning, Z. Liu, E. Jeppensen, R. D. Gulati & J. J. Middelburg, 2015. Macrophytes and periphyton carbon subsidies to bacterioplankton and zooplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake in tropical China. Limnology and Oceanography 60: 375–385.
Koste, W. 1978. Rotatoria. II Tafelband. Gebrüder Borntraeger, Berlin, Stuttgart. 234p.
Lake, P. S., 2000. Disturbance, patchiness, and diversity in streams. Journal of National American Benthological Society 19: 573–592.
Lange, K., A. Liess, J. J. Piggott, C. R. Townsend & C. D. Matthaei, 2011. Light, nutrients and grazing interact to determine stream diatom community composition and functional group structure. Freshwater Biology 56: 164–278.
Lavoie, I., P. J. Dillon & S. Campeau, 2009. The effect of excluding diatom and reducing taxonomic resolution on multivariate analysis and strem bioassessment. Ecological Indicators 9: 213–225.
Lengyel, E., J. Padisák & C. Stenger-Kovács, 2015. Establishment of equilibrium states and effect of disturbances on benthic diatom assemblages of the Torna-stream, Hungary. Hydrobiologia 750(1): 43–56.
Lewis Jr., W. M., 1976. Surface/Volume ratio: implications for phytoplankton morphology. Science 192: 885–887.
Lewis Jr., W. M., 1978. Analysis of succession in a tropical phytoplankton community and a new measure of succession rate. The American Naturalist 122: 401–414.
Liboriussen, L. & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Temporal dynamics in epipelic, pelagic and epiphytic algal production in a clear and a turbid shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 48: 418–431.
Liboriussen, L. & E. Jeppesen, 2006. Structure, biomass, production and depth distribution of periphyton on artificial substratum in shallow lakes with contrasting nutrient concentration. Freshwater Biology 51: 95–109.
Lowe, R. L., 1996. Periphyton patterns in lakes. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic. Elsevier, San Diego: 57–76.
Mariazzi, A., V. Conzonno, R. Echenique & H. Labollita, 1991. Physical and chemical characters, phytoplankton and primary production of Ezequiel Ramos Mexíareresvoir (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 209: 107–116.
Mackereth, F. J. H., J. Heron & J. F. Talling, 1989. Water Analysis: Some Revised Methods for Limnologists. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication, Ambleside.
Malley, D. F., S. G. Lawrence, M. A. Maclver & W. J. Findlay, 1989. Range of variation in estimates of dry weight for planktonic Crustacea and Rotifera from temperate North American lakes. Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 1666: 1–49.
McCormick, P. V., M. B. O’Dell, R. B. E. Shuford II, J. G. Backus & W. C. Kennedy, 2001. Periphyton responses to experimental phosphorus enrichment in a subtropical wetland. Aquatic Botany 71: 119–139.
McCune, B. & M. J. Mefford, 2011. PC-ORD Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data.Version 6.0 MjM Software. Gleneden Beach, Oregon.
Ogden, C. G. & R. H. Hedley, 1980. An atlas of freshwater testate amoebae. British Museum (Natural History), Oxford University, Oxford. 222p.
Pappas, J. L. & E. F. Stoermer, 1996. Quantitative method for determining a representative algal sample count. Journal of Phycology 32: 693–696.
Passy, S. I., 2007. Diatom ecological guilds display distinct and predictable behavior along nutrient and disturbance gradients in running waters. Aquatic Botany 86: 171–178.
Patrick, R. & C. W. Reimer, 1966. The diatoms of United States. Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia.
Pellegrini, B. G. & C. Ferragut, 2012. Seasonal and successional variation of a periphytic algal community on natural substrate in a tropical mesotrophic reservoir. Acta Botânica Brasilica 26: 807–818.
Peterson, C. G., 1987. Gut passage and insect grazer selectivity of lotic diatoms. Freshwater Biology 18: 455–460.
Peterson, C. G. & J. R. Stevenson, 1992. Resistance and resilience of lotic algal communities: importance of disturbance timing and current. Ecology 73: 1445–1461.
Pip, E. & G. G. C. Robinson, 1984. A comparison of algal periphyton composition on eleven species of submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiological Bulletin 18: 109–118.
Power, M., R. Lowe, P. Furey, J. Welter, M. Limm, J. Finlay, C. Bode, S. Chang, M. Goodrich & J. Sculley, 2009. Algal mats and insect emergence in rivers under Mediterranean climates: towards photogrammetric surveillance. Freshwater Biology. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02163.x.
Rimet, F. & A. Bouchez, 2011. Use of diatom life-form and ecological guilds to assess pesticide contamination in rivers: lotic mesocosm approaches. Ecological Indicators 11: 489–499.
Rimet, F. & A. Bouchez, 2012. Life-forms, cell-sizes and ecological guilds of diatoms in European Rivers. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 406: 01.
Rimet, F., A. Bouchez & B. Montuelle, 2015. Benthic diatoms and phytoplankton to assess nutrients in a large lake: complementary of their use in Lake Geneva (France-Switzerland). Ecological Indicators 53: 231–239.
Rimet, F., A. Bouchez & K. Tapolczai, 2016. Spatial heterogeneity of littoral benthic in a large lake: monitoring implications. Hydrobiologia 771: 179–193.
Rodrigues, L. H. R., N. F. Fontoura & D. Motta Marques, 2014. Food web structure in a subtropical coastal lake: how phylogenetic constraints may affect species linkages. Marine & Freshwater Research 65: 453–465.
Rodrigues dos Santos, T. & C. Ferragut, 2013. The successional phases of a periphytic algal community in a shallow tropical reservoir during the dry and rainy seasons. Limnetica 32: 337–352.
Rosa, L. M., L. S. Cardoso, L. O. Crossetti & D. Motta-Marques, 2016. Spatial and temporal variability of zooplankton–phytoplankton interactions in a large subtropical shallow lake dominated by non-toxic cyanobacteria. Marine and Freswater Research. doi:10.1071/MF15356.
Ruttner-Kolisko, A., 1977. Suggestions for biomass calculation of plankton rotifers. Archiv für Hydrobiologie-Beiheft Ergebnisse der Limnologie 8: 71–76.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman and Hall, London.
Schneck, F. & A. S. Mello, 2012. Hydrological disturbance overrides the effect of substratum roughness on the resistance and resilience of stream benhtic algae. Freshwater Biology 57: 1678–1688.
Seiji, D. & S. M. F. Gianesella-Galvão, 1991. Pigment chromatic adaptation in Cyclotella caspia Grunow (Bacillariophyta). Boletim do Instituto de Oceanografia 39: 123–130.
Sommer, U. & F. Sommer, 2006. Cladocerans versus copepods: the cause of contrasting top-down controls on freshwater and marine phytoplankton. Oecologia 147: 183–194.
Sommer, U., J. Padisák, C. S. Reynolds & P. Juhász-Nagy, 1993. Hutchinson’s heritage: the diversity-disturbance relationship in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 249: 1–7.
Sommer, U., F. Sommer, B. Santer, E. Zöllner, K. Jürgens, C. Jamieson, M. Boersma & K. Gocke, 2003. Daphinia versus copepod impact on summer phytoplankton: functional compensation at both trophic levels. Oecologia 135: 639–647.
Stevenson, R. J., 1996. An introduction to algal ecology in freshwater benthic habitats. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Elsevier, San Diego: 3–30.
Stoecker, D. K., D. E. Gustafson, C. T. Baier & M. M. D. Black, 2000. Primary production in the upper sea ice. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21: 274–287.
Szlauer-Łukaszewska, A., 2007. Succession of periphyton developing on artificial substrate immersed in polysaprobic wastewater reservoir. Polish Journal of Envinronmental Studies 16: 753–762.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton Methodik. Mitteilungen des International Verein Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., G. Peterson, M. J. V. Zanden & J. Kalff, 2008. Benthic algal production across lake size gradients: interactions among morphometry, nutrients and light. Ecology 89: 2542–2552.
Villar, C., L. Cabot & C. A. Bonetto, 1996. Macrophytic primary production and nutrient concentration in a deltic floodplain marsh of the Lower Paraná River. Hydrobiologia 330: 59–66.
Wall, D. & F. Briand, 1979. Response of lake phytoplankton communities to in situ manipulations of light intensity and colour. Journal of Plankton Research 1: 103–111.
Wallen, D. G. & G. H. Geen, 1971. Light quality in relation to growth, photosynthetic rates and carbon metabolism in two species of marine plankton algae. Marine Biology 10: 34–43.
Wehr, J. D. & R. G. Sheath, 2003. Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification. Elsevier, San Diego.
Wetzel, R. G., 1990. Land-water interfaces: metabolic and limnological regulators. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 24: 6–24.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. E. Likens, 2000. Limnological analysis. Springer, New York.
Zhu, G., B. Qin & G. GAO, 2005. Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in large shallow lake cause by strong wind wave disturbance. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 577–582.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the CAPES (Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) for the doctoral grant awarded to the first author. We are grateful to CNPq and Dr. Lucia H.R. Rodrigues for logistical support; the IPH (Hydraulic Research Institute, at UFRGS) technicians for sampling support; Gustavo F. Hartmann for zooplankton counting; and Professors Carla Ferragut, Lezilda C. Torgan, Lucia H.R. Rodrigues, and Luciane de O. Crossetti, and the two unknown referees for constructive comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. The English language was reviewed by Cary Collett.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Luigi Naselli-Flores
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Faria, D.M., Cardoso, L.S. & da Motta Marques, D. Epiphyton dynamics during an induced succession in a large shallow lake: wind disturbance and zooplankton grazing act as main structuring forces. Hydrobiologia 788, 267–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3002-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3002-5