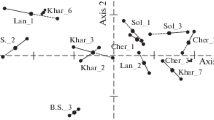
Abstract
Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was used to test the hypothesis that the wind-governed hydrodynamics of a shallow coastal lake is responsible for the spatial and temporal gradients of biotic and abiotic variables. Certain environmental variables, such as turbidity, suspended solids, and water level, formed seasonal spatial gradients in Itapeva Lake, southern Brazil, in response to wind action. Physical variables formed gradients more easily than did most of the plankton community, although the densities of certain species did respond to wind-driven oscillations. The results of this analysis indicate that the spatial and temporal gradients experienced by the physical, chemical, and biological descriptors displayed a characteristic property of this type of wind-driven environment. Moreover, CCA revealed that water dynamics may govern the plankton community of Itapeva Lake.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1992) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. APHA, Washington D.C.
Agbeti MD, Kingston JC, Smol JP, Watters C (1997) Comparison of phytoplankton succession in two lakes of different mixing regimes. Arch Hydrobiol 140:37–69
Antunes SC, Abrantes N, Gonçalves F (2003) Seasonal variation of the abiotic parameters and the cladoceran assemblage of Lake Vela: comparison with previous studies. Ann Limnol Int J Limnol 39:255–264
Attayde JL, Bozelli RL (1998) Assessing the indicator properties of zooplankton groups to disturbance gradients by canonical correspondence analysis. Ann Limnol – Int J Limnol 55:1789–1797
Becker V, Motta Marques D da (2004) Water dynamics, phytoplankton biomass and size structure of a shallow freshwater subtropical lake (Itapeva lake, south of Brazil). Acta Limnol Bras 16:163–174
Becker V, Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2004) Development of Anabaena Bory ex Bornet, Flahault (Cyanobacteria) blooms in a shallow, subtropical lake in southern Brazil. Acta Limnol Bras 16:306–317
Bruce LC, Hamilton D, Imberger J, Gal G, Gophen M, Zohary T, Hambright KD (2006) A numerical simulation of the role of zooplankton in C, N and P cycling in Lake Kinneret, Israel. Ecol Modell 193:412–436
Cardoso L de S (2001) Variações da estrutura planctônica da Lagoa Itapeva (Sistema Lagunar Costeiro do Rio Grande do Sul) em função da hidrodinâmica. PhD thesis. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre
Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2002) Evaluation of phytoplankton pigments in a shallow coastal lake submitted to strong hydrodynamics: comparative analysis of spectrophotometric methods. Acta Limnol Bras 14:1–16
Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2003) Rate of change of the phytoplankton community at Itapeva Lake (North Coast of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil), based on the wind driven hydrodynamic regime. Hydrobiologia 497:1–12
Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2004a) Structure of the zooplankton community in a subtropical shallow lake (Itapeva Lake—South of Brazil) and its relationship to hydrodynamic aspects. Hydrobiologia 528:123–134
Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2004b) The influence of hydrodynamics on the spatial and temporal variation of phytoplankton pigments in a large, sub-tropical coastal lake (Brazil). Braz Arch Biol Technol 47:587–600
Cardoso L de S, Motta Marques D da (2004c) Seasonal composition of the phytoplankton community in Itapeva Lake (north coast of Rio Grande do Sul - Brazil) in function of hydrodynamic aspects. Acta Limnol Bras 16:401–416
Cardoso L de S, Silveira ALL da, Motta Marques D da (2003) A ação do vento como gestor da hidrodinâmica na Lagoa Itapeva (Litoral Norte do Rio Grande do Sul-Brasil). Rev Bras Rec Hid 8:5–15
Carrick HJ, Aldridge FJ, Schelske CL (1993) Wind influences phytoplankton biomass and composition in a shallow, productive lake. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1179–1192
Cristofor S, Vadineanu A, Ignat G, Ciubuc C (1994) Factors affecting light penetration in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 275/276:493–498
Dejen E, Vijverberg J, Nagelkerke LAJ, Sibbing FA (2004) Temporal and spatial distribution of microcrustacean zooplankton in relation to turbidity and other environmental factors in a large tropical lake (L Tana, Ethiopia). Hydrobiologia 513:39–49
Dokulil MT, Padisák J (1994) Long-term compositional response of phytoplankton in a shallow, turbid environment, Neusiedlersee (Austria/Hungary). Hydrobiologia 275/276:125–137
Flores LN, Barone R (1998) Phytoplankton dynamics in two reservoirs with different trophic state (Lake Rosamarina and Lake Arancio, Sicily, Italy). Hydrobilogia 370:163–178
Hart RC (1978) Horizontal distribution of the copepod Pseudodiaptomus hessei in subtropical Lake Sibaya. Freshw Biol 8:415–421
Hart RC (1990) Zooplankton distribution in relation to turbidity and related environmental gradients in a large subtropical reservoir: patterns and implications. Freshw Biol 24:241–263
Havens KE, Phlips EJ, Cichra MF, Li BL (1998) Light availability as a possible regulator of cyanobacteria species composition in a shallow subtropical lake. Freshw Biol 39:547–556
Izaguirre I, O’Farrell I, Unrein F, Sinistro R, Afonso MD, Tell G (2004) Algal assemblages across a wetland, from a shallow lake to relictual oxbow lakes (Lower Parana River, South America). Hydrobiologia 511:25–36
Jongman RH, Ter Braak CJF, Van Tongeren OFR (1987) Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Pudoc, Wageningen
Komárková J, Komárek O, Hejzlar J (2003) Evaluation of the long term monitoring of phytoplankton assemblages in a canyon-shape reservoir using multivariate statistical methods. Hydrobiologia 504:143–157
Lacroix G, Lescher-Moutoué F (1995) Spatial patterns of planktonic microcrustaceans in a small shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 300/301:205–217
Legendre L, Demers S (1984) Towards dynamic biological oceanography and limnology. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 41:2–19
Lopardo N (2002) Estudo hidrodinâmico e correlação com sólidos suspensos e turbidez na Lagoa Itapeva do litoral norte do estado do Rio Grande do Sul. MSc thesis. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre
McCune B, Mefford MJ (1999) PC-ORD multivariate analysis of ecological data – version 4. MJM Software Design, Gleneden Beach
Mengitsu S, Fernando CH (1991) Seasonality and abundance of some dominant crustacean zooplankton in Lake Awassa, a tropical roft valley lake in Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 226:137–152
Millet B, Cecchi P (1992) Wind-induced hydrodynamic control of the phytoplankton biomass in a lagoon ecosystem. Limnol Oceanogr 37:140–146
Padisák J (1993) The influence of different disturbance frequencies on the species richness, diversity and equitability of phytoplankton in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 249:135–156
Padisák J, Dokulil M (1994) Meroplankton dynamics in a saline, turbulent, turbid shallow lake (Neusiedlersee, Austria and Hungary). Hydrobiologia 289:23–42
Padisák J, Tóth LG, Rajczy M (1988) The role of storms in the summer succession of the phytoplankton community in a shallow lake (Lake Balanton, Hungary). J Plankton Res 10:249–265
Padisák J, Tóth LG, Rajczy M (1990) Stir-up effect of wind on a more-or-less stratified shallow lake phytoplankton community, Lake Balanton, Hungary. Hydrobiologia 191:249–254
Pinel-Alloul B (1995) Spatial heterogeneity as a multiscale characteristics of zooplankton community. Hydrobiologia 300/301:17–42
Pinel-Alloul B, Guay C, Angeli N, Legendre P, Dutilleul P, Balvay G, Gerdeaux D, Guillard J (1999) Large-scale spatial heterogeneity of macrozooplankton in Lake of Geneva. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:1437–1451
Pinel-Alloul B, Niyonsenga T, Legendre P (1995) Spatial and environmental components of fresh-water zooplankton structure. Ecoscience 2:1–19
Silva CA da, Train S, Rodrigues LC (2005) Phytoplankton assemblages in a Brazilian subtropical cascading reservoir system. Hydrobiologia 537:99–109
Thackeray S J, Glen George D, Jones RJ, Winfield IJ (2004) Quantitative analysis of the importance of wind-induced circulation for the spatial structuring of planktonic populations. Freshw Biol 49:1091–1102
Tell G, O’Farrell I, Lombardo RJ (2005) Euglenoid morphospecies replacement along a hydraulic gradient of the Lower Parana Basin (Argentina). Freshw Biol 50:616–626
Ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67:1167–1179
Vincent WF (1992) The daily pattern of nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton in dynamic mixed layer environments. Hydrobiologia 238:37–52
Vollenweider RA (ed) (1974) A manual on methods for measuring primary production in aquatic environments. 2nd edn. IBP Handbook no. 12. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Brazilian agencies FAPERGS (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa no Rio Grande do Sul) and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for grants in support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza Cardoso, L., da Motta Marques, D. Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake. Aquat Ecol 43, 73–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-007-9151-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-007-9151-x