Abstract
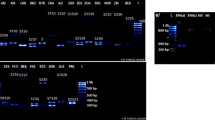
Apple plants are self-incompatible because a genetic mechanism allows the female reproductive organ to recognize and reject self-pollen or pollen from genetic related individuals and allows non-self pollen to effect fertilization. Thus, there are implications to both breeding strategies and orchard management for fruit production. The purpose of this study was to identify and to characterize the S-RNase alleles of the gametophytic incompatibility among apple cultivars developed in Brazil, seeking to give support for choosing right combinations of parent in the apple breeding programs. It also sought to identify correct combinations of scion/pollinator cultivars of commercial apple orchards. A total of 16 specific S-RNase alleles primers were tested against DNA extracted from 12 Brazilian cultivars and their parents. The molecular analysis confronted to the reference cultivars, showed that the cultivars Daiane, Imperatriz and Princesa have the same incompatibility S3 and S5 alleles, while ‘Lisgala’ showed the alleles S2 and S5; ‘Suprema’, S1 and S9; ‘Catarina’, S1 and S19; ‘Joaquina’ and ‘Fred Hough’, S5 and S19; ‘Baronesa’, S3 and S9; ‘Duquesa’, S2 and S3. For ‘Primícia’ and ‘Condessa’ it was only possible to identify one of the S-alleles, namely S24 and S2, respectively, with the second allele remaining to be identified. Progeny test indicated the Mendelian inheritance for RNase alleles. Results of this study will be helpful to judiciously choose parents in apple breeding programs to improve compatibility.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broothaerts W (2003) New findings in apple S-genotype analysis resolve previous confusion and request the re-numbering of some S-alleles. Theor Appl Genet 106:703–714
Broothaerts W (2004) Update on and review of the incompatibility (S-) genotypes of apple cultivars. HortScience 39:943–947
Broothaerts W, Janssens GA, Proost P, Brokaert WF (1995) cDNA cloning and molecular analysis of two self-incompatibility alleles from apple. Plant Mol Biol 27:499–511
Carrera L, Sanzol J, Herrero M, Hormaza JI (2009) Genomic characterization of self-incompatibility ribonucleases (S-RNases) in loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) (Rosaceae, Pyrinae). Mol Breeding 23:539–551
de Nettancourt D (1977) Incompatibility in angiosperms. In: Frankel R, Gal GAE, Linskens HF (eds) Monographs on theoretical and applied genetics. Springer, Berlin, pp 28–57
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Dressen RSG, Vanholme BTM, Luyten K, Wynsberghe LV, Fazio G, Roldán-Ruiz I, Keulemans J (2010) Analysis of Malus S-Rnase gene diversity based on a comparative study of old and modern apple cultivars and European wild apple. Mol Breeding 26:693–709
Ishimizu T, Inoue K, Shimonaka M, Saito T, Terai O, Norioka S (1999) PCR-based method for identifying the S-genotypes of Japanese pear cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:961–967
Janssens GA, Goderis IJ, Broekaert WF, Broothaerts W (1995) A molecular method for S-allele identification in apple based on allele-specific PCR. Theor Appl Genet 91:691–698
Kim H, Kakui H, Kotoda N, Hirata Y, Koba T, Sassa H (2009) Determination of partial genomic sequences and development of a CAPS system of the S-RNase gene for the identification of 22 S-haplotypes of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh). Mol Breeding 23:463–472
Kitahara KM, Matsumoto S (2002) Sequence of the S10 cDA from ‘McIntosh’ apple and a PCR-digestion identification method. HosrtScience 37:187–190
Kitahara K, Soejima J, Komatsu H, Fukui H, Matsumoto S (2000) Complete sequences of the S-genes ‘Sd’ and ‘Sh-RNase’ cDNA in apple. HortScience 35:712–715
Kobel F, Steinegger P, Anliker J (1939) Weitere Untersuchungen uber die Befruchtungsverhaltnisse der Apfel- und Birnsorten. Landw Jahrb Schweiz 53:160–191
Manganaris AG, Alston FH (1987) Inheritance and linkage relationships of glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase isozymes in apple. 1. The gene Got-1, a maker for the S incompatibility locus. Theor Appl Genet 74:154–161
Matsumoto S, Kitahara K (2000) Discovery of a new selfincompatibility allele in apple. HortScience 35:1329–1332
Matsumoto S, Kitara K, Komori S, Soejima J (1999) A new S-allele inapple, ‘Sg’, and its similarity to the ‘Sf’ allele from ‘Fuji’. HortScience 34:708–710
Noiton D, Shelbourne CJA (1992) Quantitative genetics in an apple breeding strategy. Euphytica 60:213–219
Okuno T (2000) S-RNase from Malus domestica, cultivar Starking. Delicious. GenBank submission no. AB017636
Ortega E, Bosković RI, Sargent DA, Tobutt KR (2006) Analysis of S-RNAse alleles of almond (Prunus dulcis): characterization of new sequences, resolution of synonyms and evidence of intragenic recombination. Mol Genet Genom 276:413–426
Richman AD, Broothaerts W, Kohn JR (1997) Self-incompatibility RNases from three plant families: homology or convergence? Am J Bot 84:912–917
Sakurai K, Brown SK, Weeden NF (1997) Determining the self-incompatibility alleles of Japanese apple cultivars. HortScience 32:1258–1259
Sakurai K, Brown SK, Weeden NF (2000) Self-incompatibility alleles of apple cultivars and advanced selections. HortScience 35:116–119
Sassa H, Mase N, Hirano H, Ikehashi H (1994) Identification of self-incompatibility-related glycoproteins in styles of apple (Malus × domestica). Theor Appl Genet 89:201–205
Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano H, Koba T, Ikehashi H (1996) Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of the Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250:547–557
Takayama S, Isogai A (2005) Self-incompatibility in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:467–489
Van Nerum I, Geerts M, Van Haute A, Keulemans J, Broothaerts W (2001) Re-examination of the self-incompatibility genotype of apple cultivars containing putative ‘new’ S-alleles. Theor Appl Genet 103:584–591
Verdoodt L, Van Haute A, Goderis IJ, De Witte K, Keulemans J, Broothaerts W (1998) Use of the multi-allele self-incompatibility gene in apple to assess homozygosity in shoots obtained through haploid induction. Theor Appl Genet 96:294–300
Vieira J, Morales-Hojas R, Santos RAM, Vieira CP (2007) Different positively selected sites at the gametophytic self-incompatibility pistil S-RNase gene in the Solanaceae and Rosaceae. (Prunus Pyrus and Malus) J Mol Evol 65:175–185. doi:10.1007/s00239-006-0285-6
Vieira J, Ferreira PG, Aguiar B, Fonseca NA, Vieira CP (2010) Evolutionary patterns at the RNase based gametophytic self-incompatibility system in two divergent Rosaceae groups (Maloideae and Prunus). BMC Evol Biol 10:200. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-200
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Research Council (CNPq) UNISUL, and PRODETAB for a research grant. The Brazilian CNPq provided scholarships to RON and Brazilian agency CAPES to ACMD. The authors also would like to acknowledge the anonymous reviewers, which suggestions improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Albuquerque, C.L., Denardi, F., de Mesquita Dantas, A.C. et al. The self-incompatible RNase S-alleles of Brazilian apple cultivars. Euphytica 181, 277–284 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0431-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0431-0