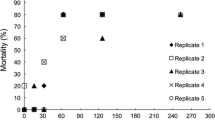
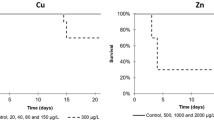
Abstract
Aquatic organisms commonly respond to harsh conditions by forming diapausing stages, which enable populations to survive adverse periods forming egg banks. Production of diapausing eggs is frequently observed in monogonont rotifers, previously changing from asexual to partial sexual reproduction (mixis). In despite that zooplankton are frequently used in ecotoxicological assessment because of their sensitivity to various toxicants and their important role in the ecosystems, toxicity evaluations often consider the directly exposed population produced by parthenogenetic reproduction, exclusively. We assessed experimentally effects of exposure to metals on mixis delay and fitness of hatchlings of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis obtained from a brackish water lagoon with high metal content, especially copper. We show that sub-lethal concentrations of copper affected traits related to sexual reproduction and diapausing egg production in the rotifer. Copper addition did not delay the start of mixis, suggesting that rapid initiation of mixis is promoted in risky environments, according to the hypothesis of mixis as an escape strategy. Higher investment in mixis was obtained when individuals were exposed to metal. Addition of copper negatively affected the hatching success of diapausing eggs and performance of hatchlings. Nevertheless, these effects were greater for individuals formed in non-metal conditions, suggesting an adaptive advantage of populations from natural sediments exposed to copper. These results highlight the ecological and evolutionary consequences of the presence of metals in freshwater environments by modulating diapause adaptive efficacy and the selective process in egg banks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agra AR, Guilhermino L, Soares AMVM, Barata C (2010) Genetic costs of tolerance to metals in Daphnia longispina populations historically exposed to copper mine drainage. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:939–946
Agra AR, Soares AMVM, Barata C (2011) Life-history consequences of adaptation to pollution. “Daphnia longispina clones historically exposed to copper”. Ecotoxicology 20:552–562
Alekseev VR, De Stasio BT, Gilbert JJ (2007) Diapause in aquatic invertebrates: theory and human use. Springer, The Netherlands, Monographiae Biologicae, Vol 84
Alvarado-Flores J, Rico-Martínez R, Ventura-Juárez J, Silva-Briano M, Rubio-Franchini I (2012) Bioconcentration and localization of lead in the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas 1677 (Rotifera: Monogononta). Aquat Toxicol 109:127–132
Alvarado-Flores J, Rico-Martínez R, Adabache-Ortíz A, Silva-Briano M (2015) Morphological alterations in the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas 1766 (Rotifera: Monogononta) caused by vinclozolin chronic exposure. Ecotoxicology 24:915–925
Aparici E, Carmona MJ, Serra M (1996) Polymorphism in bisexual reproductive patterns of cyclical parthenogens. A simulation approach using a rotifer growth model. Ecol Model 88:133–142
Aparici E, Carmona MJ, Serra M (2001) Variability for mixis initiation in Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 446/447:45–50
Aránguiz-Acuña A, Ramos-Jiliberto R (2014) Diapause may promote coexistence of zooplankton competitors. J Plankton Res 36(4):978–988
Aránguiz-Acuña A, Ramos-Jiliberto R, Serra M (2015) Zooplankton competition promotes trade‑offs affecting diapause in rotifers. Oecologia 177:273–279
Aránguiz-Acuña A, Serra M (2016) Diapause as escape strategy to exposure to toxicants: response of Brachionus calyciforus to arsenic. Ecotoxicology 25:708–719
ASTM (1991) A standard practice for performing acute toxicity tests using rotifers in the genus Brachionus. American Society of Testing and Materials, E1440(11.04):1210–1216
ASTM (2013) Standard practice for the preparation of substitute ocean water. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Borowitzka MA, Borowitzka LJ (1988) Micro-algal biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Brendonck L, De Meester L (2003) Egg banks in freshwater zooplankton: evolutionary and ecological archives in the sediment. Hydrobiologia 491:65–84
Brock MA, Nielsen DL, Shiel RJ, Green JD, Langley JD (2003) Drought and aquatic community resilience: the role of eggs and seeds in sediments of temporary wetlands. Freshwater Biol 48:1207–1218
Cáceres C (1997) Temporal variation, dormancy, and coexistence: a field test of the storage effect. Ecology 94:9171–9175
Cáceres CE, Tessier AJ (2004) To sink or swim: variable diapause strategies among Daphnia species. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1333–1340
Campillo S, García-Roger EM, Carmona MJ, Serra M (2011) Local adaptation in rotifer populations. Evol Ecol 25:933–947
de Wet CB, Godfrey L, de Wet AP (2015) Sedimentology and stable isotopes from a lacustrine-to-palustrine limestone deposited in an arid setting, climatic and tectonic factors: Miocene–Pliocene Opache formation, Atacama Desert, Chile. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeocl 426:46–67
Declerck SAJ, Malo A, Diehl S, Waasdorp D, Lemmen KD, Proios K, Papakostas S (2015) Rapid adaptation of herbivore consumers to nutrient limitation: eco-evolutionary feedbacks to population demography and resource control. Ecol Lett 18:553–562
Díaz-Palma P, Stegen S, Queirolo F, Arias D, Araya S (2012) Biochemical profile of halophilous microalgae strains from high-andean extreme ecosystems (NE-Chile) using methodological validation approaches. J Biosci Bioeng 113:730–736
Dittmar T (2004) Hydrochemical process controlling arsenic and heavy metal contamination in the Elqui river system (Chile). Sci Total Environ 325:193–207
Fernández-González MA, González-Barrientos J, Carter MJ, Ramos-Jiliberto R (2011) Parent-to-offspring transfer of sublethal effects of copper exposure: metabolic rate and life-history traits of Daphnia. Rev Chil Hist Nat 84:195–201
Folmer O, Black M, Hoen W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Ecol 10:1743–1750
Fussmann GF, Ellner SP, Hairston Jr NG (2003) Evolution as a critical component of plankton dynamics. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 270:1015–1022
Fussmann GF, Kramer G, Labib M (2007) Incomplete induction of mixis in Brachionus calyciflorus: patterns of reproduction at the individual level. Hydrobiologia 593:111–119
Fussmann GF (2011) Rotifers: excellent subjects for the study of macro- and microevolutionary change. Hydrobiologia 662:11–18
Gabaldón C, Montero-Pau J, Serra M, Carmona MJ (2013) Morphological similarity and ecological overlap in two rotifer species. PLoS One 8(2):e57087
Gabaldón C, Carmona MJ, Montero-Pau J, Serra M (2015) Long-term competitive dynamics of two cryptic species: diapause and fluctuating conditions. PLoS One 10(4):e0124406
Gama-Flores JL, Sarma SSS, Nandini S (2005) Interaction among copper toxicity, temperature and salinity on the population dynamics of Brachionus rotundiformis (Rotifera). Hydrobiologia 546:559–568
García-Roger EM, Carmona MJ, Serra M (2006) Patterns in rotifer diapausing egg banks: density and viability. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 336:198–210
Gardeström J, Dahl U, Kotsalainen O, Maxson A, Elfwing T, Grahn M, Bengtsson B-E, Breitholtz M (2008) Evidence of population genetic effects of long-term exposure to contaminated sediments. A multi-endpoint study with copepods. Aquat Toxicol 86:426–436
Gilbert JJ (2002) Endogenous regulation of environmentally induced sexuality in a rotifer: a multigenerational parental effect induced by fertilization. Freshw Biol 47:1633–1641
Gilbert JJ (2003) Specificity of crowding response that induce sexuality in the rotifer Brachionus. Limnol Oceanogr 48:1297–1303
Gilbert JJ (2007) Induction of mictic females in the rotifer Brachionus: oocytes of amictic females respond individually to population-density signal only during oogenesis shortly before oviposition. Freshw Biol 52:1417–1426
Gilbert JJ, Diéguez MC (2010) Low crowding threshold for induction of sexual reproduction and diapause in a Patagonian rotifer. Freshw Biol 55:1705–1718
Gómez A, Carvalho GR (2000) Sex, parthenogenesis and genetic structure of rotifers microsatellite analysis of contemporary and resting egg bank populations. Mol Ecol 9:203–214
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Gyllström M, Hansson L-A (2004) Dormancy in freshwater zooplankton: Induction, termination and the importance of benthic-pelagic coupling. Aquat Sci 66:274–295
Hagiwara A, Hino A (1989) Effect of incubation and preservation on resting egg hatching and mixis in the derived clones of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 186:415–421
Hairston Jr NG (1998) Time travelers: what’s timely in diapause research? Arch Hydrobiol 52:1–15
Hairston Jr NG, Cáceres C (1996) Distribution of crustacean diapause: micro- and macroevolutionary pattern and process. Hydrobiologia 320:27–44
Hairston Jr NG, Ellner S, Kearns CM (1996) Overlapping generations: the storage effect and the maintenance of biotic diversity. In: Rhodes Jr OE, Chessner RK & Smith MH (eds) Population dynamics in ecological space and time. University of Chicago Press, Illinois, pp 109–145
Hairston Jr NG, Perry LJ, Bohonak AJ, Fellows MQ, Kearns CM, Engstrom DM (1999) Population biology of a failed invasion: paleolimnology of Daphnia exilis in upstate New York. Limol Oceanogr 44:477–486
Jiang X, Wang G, Li S, He J (2007) Heavy metal exposure reduces hatching success of Acartia pacifica resting eggs in sediment. J Environ Sci 19(6):733–737
Karstens S, Buczko U, Jurasinski G, Peticzka R, Glatzel S (2016) Impact of adjacent land use on costal wetland sediments. Sci Total Environ 550:337–348
Kerfoot WC, Robbins JA, Weider LJ (1999) A new approach to historical reconstruction: Combining descriptive and experimental paleolimnology. Limnol Oceanogr 44:1232–1247
Kotani T, Ozaki M, Matsuoka K, Snell TW, Hagiwara A (2001) Reproductive isolation among geographically and temporally isolated marine Brachionus strains. Hydrobiologia 446/447:283–290
Landis W, Yu M (2005) Introduction to environmental toxicology: impacts of chemicals upon ecological systems, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Larios R, Fernández-Martínez R, Silva V, Rucandio I (2013) Chemical availability of arsenic and heavy metals in sediments from abandoned cinnabar mine tailings. Environ Earth Sci 68:535–546
Latorre C, Betancourt JL, Arroyo MTK (2006) Late Quaternary vegetation and climate history of a perennial river canyon in the Río Salado basin (22°S) of Northern Chile. Quat Res 65:450–466
Laurent B, Marticorena B, Bergametti G, León JF, Mahowald NM (2008) Modeling mineral dust emissions from the Sahara desert using new surface properties and soil database. J Geophys Res 113:D14218
Lennon JT, Jones SE (2011) Microbial seed banks: the ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nature 9:119–130
Luna-Andrade A, Aguilar-Durán R, Nandini S, Sarma SSS (2002) Combined effects of copper and microalgal (Tetraselmis suecica) concentrations on the population growth of Brachionus plicatilis Müller (Rotifera). Water Air Soil Pollut 141:143–153
Marcus NH, Lutz R, Burnett W, Cable P (1994) Age, viability and vertical distribution of zooplankton resting eggs from an anoxic basin: evidence of an egg bank. Limnol Oceanogr 39:154–158
Marín-Guirao L, Lloret J, Marin A (2008) Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes and metal concentration in food webs from a mining-impacted coastal lagoon. Sci Total Environ 393:118–130
Marshall DJ (2008) Transgenerational plasticity in the sea: context-dependent maternal effects across the life history. Ecology 89:418–427
Marcial HS, Hagiwara A, Snell TW (2005) Effect of some pesticides on reproduction of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller. Hydrobiologia 546:569–575
Marcial HS, Hagiwara A (2007) Effect of diazinon on life stages and resting egg hatchability of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 593(1):219–225
Medina MH, Correa JA, Barata C (2007) Micro-evolution due to pollution: Possible consequences for ecosystem responses to toxic stress. Chemosphere 67:2105–2114
Montero-Pau J, Gómez A, Muñoz J (2008) Application of an inexpensive and high-throughput genomic DNA extraction method for the molecular ecology of zooplanktonic diapausing eggs. Limnol Oceanogr 6:218–222
Montero-Pau J, Serra M (2011) Life-Cycle switching and coexistence of species with no niche differentiation. PLoS One 6:e20314
Navis S, Waterkeyn A, Voet T, De Meester L, Brendonck L (2013) Pesticide exposure impacts not only hatching of dormant eggs, but also hatchling survival and performance in the water flea Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 22:803–814
Navis S, Waterkeyn A, Putman A, De Meester L, Vanermen G, Brendonck L (2015) Timing matters: Sensitivity of Daphnia magna dormant eggs to fenoxycarb exposure depends on embryonic developmental stage. Aquat Toxicol 159:176–183
Nielsen DL, Smith D, Petrie R (2012) Resting egg banks can facilitate recovery of zooplankton communities after extended exposure to saline conditions. Freshw Biol 57:1306–1314
Pell A, Márquez A, López-Sánchez JF, Rubio R, Barbero M, Stegen S, Queirolo F, Díaz-Palma P (2013) Ocurrence of arsenic species in algae and freshwater plants of an extreme arid region in northern Chile, the Loa River Basin. Chemosphere 90:556–564
Piscia R, Tabozzi S, Bettinetti R, Nevalainen L, Manca MM (2016) Unexpected increases in rotifer resting egg abundances during the period of contamination of Lake Orta. J Limnol 75(s2):76–85
Posthuma L, Hogervorst RF, Joosse ENG, Van Straalen NM (1993) Genetic variation and covariation for characteristics associated with cadmium tolerance in natural populations of the springtail Orchesella cincta. Evolution 47:619–631
Preston BJ, Snell TW (2001) Direct and indirect effects of sublethal toxicant exposure on population dynamics of freshwater rotifers: a modeling approach. Aquat Toxicol 52:87–99
Queirolo F, Stegen S, Mondaca J, Cortés R, Rojas R, Contreras C, Munoz L, Schwuger MJ, Ostapczuk P (2000) Total arsenic, lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc in some salt rivers in the northern Andes of Antofagasta, Chile. Sci Total Environ 255:85–95
R Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, http://www.R-project.org/
Rogalski MA (2015) Tainted resurrection: metal pollution is linked with reduced hatching and high juveniles mortality in Daphnia egg banks. Ecology 96:1166–1173
Romero L, Alonso H, Campano P, Fanfani L, Cidu R, Dadea C et al. (2003) Arsenic enrichment in waters and sediments of the Río Loa (Second Region, Chile). Appl Geochem 18:1399–1416
Sarabia R, Ramo JD, Varó I, Díaz-Mayans J, Torreblanca A (2008) Sublethal zinc exposure has a detrimental effect on reproductive performance but not on the cyst hatching success of Artemia parthenogenetica. Sci Total Environ 398:48–52
Scheuerl T, Stelzer C-P (2013) Patterns and dynamics of rapid local adaptation and sex in varying habitat type in rotifers. Ecol Evol 3:4253–4264
Schröeder T (2005) Diapause in monogonont rotifers. Hydrobiologia 546:291–306
Schröeder T, Gilbert JJ (2004) Transgenerational plasticity for sexual reproduction and diapause in the life cycle of monogonont rotifers: intraclonal, intraspecific and interspecific variation in the response to crowding. Funct Ecol 18:458–466
Schröeder T, Howard S, Arroyo ML, Walsh EJ (2007) Sexual reproduction and diapause of Hexarthra sp. (Rotifera) in short-lived ponds in the Chihuahuan Desert. Freshw Biol 52:1033–1042
Serra M, Snell TW, King CE (2004) The timing of sex in cyclically parthenogenetic rotifers. In: Moya A & Font E (eds) Evolution: from molecules to ecosystems. Oxford University Press, London, pp 135–146
Serra M, Snell TW, Gilbert JJ (2005) Delayed mixis in rotifers: an adaptive response to the effects of density dependent sex on population growth. J Plankton Res 27:37–45
Serra M, Snell TW (2009) Sex Loss in Monogonont Rotifers. In: Schön I, Martens K & van Dijk P (eds) Lost sex: the evolutionary biology of parthenogenesis. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 281–294
Slusarczyk M, Pietrzak B (2008) To sink or float: the fate of dormant offspring is determined by maternal bahaviour in Daphnia. Freshw Biol 53:569–576
Snell TW, Carmona MJ (1995) Comparative toxicant sensitivity of sexual and asexual reproduction in the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:415–420
Snell TW, Serra M, Carmona MJ (1999) Toxicity and sexual reproduction in rotifers: reduced resting egg production and heterozygosity loss. In: Forbes VE (ed) Genetics and Ecotoxicology. Taylor & Francis, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. pp 169–185
Stelzer CP, Snell TW (2003) Induction of sexual reproduction in Brachionus plicatilis (Monogononta, Rotifera) by a density dependent chemical cue. Limnol Oceanogr 48:939–943
Tapia J, Audry S (2013) Control of early diagenesis processes on trace metal (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and U) and metalloid (As, Sb) behaviors in mining- and smelting-impacted lacustrine environments of the Bolivian Altiplano. Appl Geochem 31:60–78
Technelysium (2016) DNA Sequencing Software. http://technelysium.com.au/wp/chromas
Tortajada AM, Carmona MJ, Serra M (2009) Does haplodiploidy purge inbreeding depression in rotifer populations?. PLoS One 4:e8195
Turko P, Sigg L, Hollender J, Spaak P (2016) Rapid evolutionary loss of metal resistance revealed by hatching decades-old eggs. Evolution 70:398–407
USEPA (2012) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms, 5th edn. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Van Straalen NM, Hoffmann A (2000) Review of experimental evidence of physiological costs of tolerance to toxicants. In: Kammenga J & Laskowski R (eds) Demography in ecotoxicology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 147–161
Varó I, Amat F, Navarro JC, Barreda M, Pitarch E, Serrano R (2006) Assessment of the efficacy of Artemia sp. (Crustacea) cysts chorion as barrier to chlorpyrifos (organophosphorus pesticide) exposure. Effect on hatching and survival. Sci Total Environ 366:148–153
Wallace RL, Snell TW, Ricci C, Nogrady T (2006) Rotifera 1: biology, ecology and systematics. Backhuys, Leiden
Woelfl S, Óvari M, Nimptsch J, Neu TR, Mages M (2016) Determination of trace elements in freshwater rotifers and ciliates by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 116:28–33
Wyn B, Sweetman JN, Laevitt PR, Donald DB (2007) Historical metal concentrations in lacustrine food webs revealed using fossil ephippia from Daphnia. Ecol Appl 17:754–764
Xu X-P, Xi Y-L, Huang L, Xiang X-L (2015) Effects of multi-metal (Cu, Zn, Cd, Cr, and Mn) mixtures on the reproduction of freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:714–720
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Dr. Manuel Serra for helpful comments that improved the manuscript. We also thank Ana de la Fuente for her assistance in the laboratory, Dr. Jorge Valdés and Dr. Mauricio Cerda for their support in the field, and Dr. Martha Hengst and her laboratory staff for their support in molecular analysis. Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico, (11130653), Dr. Adriana Aránguiz-Acuña. This study was funded by Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico FONDECYT 11130653 to A.A-A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aránguiz-Acuña, A., Pérez-Portilla, P. Metal stress in zooplankton diapause production: post-hatching response. Ecotoxicology 26, 329–339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1766-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1766-7