Abstract
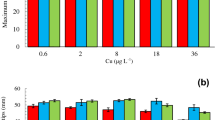
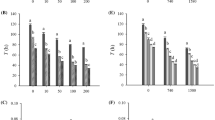
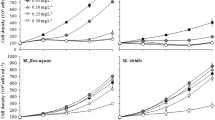
Heavy metals may interact with ecological factors such as temperature, food level and salinity, causing both mortality and reduced reproduction in organisms. Among different heavy metals, copper compounds are commonly used for eliminating algal blooms in aquaculture tanks. At certain concentrations, copper is toxic to rotifers. In the present work, we evaluated the combined effects of salt concentrations (2.5 and 5.0 g l−1 NaCl), copper levels (0, 0.03125, 0.0625, 0.125 and 0.25 mg l−1 as CuCl2) and two temperatures (20 and 25 °C) on the population growth of B. rotundiformis using Chlorella as the algal food (at 0.5 × 106 cells ml−1 for every 24 h). Regardless of salinity and temperature, copper at concentrations as low as 0.03 mg l−1 had an adverse effect on the population growth of rotifers and above 0.125 mg l−1, the populations did not grow. The effect of the toxicant on B. rotundiformis was more severe at 25° than at 20 °C at lower salinity. In general, we observed peak densities of rotifers around day 12 at 20 °C but 6–8 days earlier at 25 °C. Peak population densities of B. rotundiformis in the controls at the salinity of 2.5 g l−1 ranged from 90 to 180 ind. ml−1, depending on temperature; at a salinity of 5.0 g l−1, these were lower. The population growth rates, r, in our study varied from +0.31 to –0.12 depending on the test conditions. There was a significant impact of temperature, salinity and toxicity level on the population growth rate of B. rotundiformis. Our results suggested that even narrow changes in salinity could negatively influence the toxicity of heavy metal on the population growth rates of B. rotundiformis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous, 1985. Methods of Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents to Freshwater and Marine Organisms. US Environment Protection Agency EPA/600/4–85/013, Washington DC
M. A. Borowitzka L. J. Borowitzka (1988) Micro-algal biotechnology Cambridge University Press United Kingdom
A. I. Buikema J. Cairns SuffixJr. (1974) ArticleTitleEvaluation of Philodina (Rotifera) as a bioassay organism for heavy metals Water Resources Bulletin 10 648–661
C. Cervantes R. Moreno-Sánchez (1999) Contaminación ambiental por metales pesados AGT Editorial Mexico
C. P. Charoy C. R. Janssen G. Persoone P. Clement (1995) ArticleTitleThe swimming behaviour of Brachionus calyciflorus (rotifer) under toxic stress. 1. The use of automated trajectometry for determining sublethal effects of chemicals Aquatic Toxicology 32 271–282 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0166-445X(94)00098-B
M. D. Ferrando E. Andreu (1993) ArticleTitleFeeding behavior as an index of copper stress in Daphnia magna and Brachionus calyciflorus Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, C. Comparative Pharmacology and Toxicology 106 327–331
J. L. Gama-Flores S. S. S. Sarma M. A. F. Araiza (1999) ArticleTitleCombined effects of Chlorella density and methyl parathion concentration on the population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus (Rotifera) Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 62 769–755 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001289900938 Occurrence Handle10354003
J. Green (1993) ArticleTitleZooplankton associations in East African lakes spanning a wide salinity range Hydrobiologia 267 249–256 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00018806
U. Halbach (1984) ArticleTitlePopulation dynamics of rotifers and its consequences for ecotoxicology Hydrobiologia 109 79–96 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00006300
P. R. Hawkins D. J. Griffiths (1987) ArticleTitleCopper as an algicide in a tropical reservoir Water Research 21 475–480 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(87)90196-5
Z. He K. Qin Y. Wang W. Zhao (1993) ArticleTitleBiological resources in inland saline waters from southern Shanxi, China. Part 1. Lake Xiaochi Journal of Dalian Fisheries College 8 1–15
E. H. W. Heugens A. J. Hendriks T. Dekker N. M. Stralen Particlevan W. Admiraal (2001) ArticleTitleA review of the effects of multiple stressors on aquatic organisms and analysis of uncertainty factors for use in risk assessment Critical Reviews in Toxicology 31 247–284 Occurrence Handle10.1080/20014091111695 Occurrence Handle11405441
G. E. Hutchinson (1967) A Treatise on Limnology. 2. Introduction to Lake Biology and the Limnoplankton John Wiley New York 1115
C. R. Janssen M. D. Ferrando G. Persoone (1994) ArticleTitleEcotoxicological studies with the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 28 244–255 Occurrence Handle10.1006/eesa.1994.1050 Occurrence Handle7525220
Koste, W. 1978. Rotatoria. Die Rädertiere Mitteleuropas. Ein Bestimmungswerk begründet von Max Voigt. Bornträger, Stuttgart. Vol. 1, Textband 673 pp., Vol. 2, Tafelband, 234 pp
C. J. Krebs (1985) Ecology. The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance EditionNumber3 Harper & Row New York
E. Lubzens G. Minkoff Y. Barr O. Zmora (1997) ArticleTitleMariculture in Israel: Past achievements and future directions in raising rotifers as food for marine fish larvae Hydrobiologia 358 13–20 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003117610203
A. Luna-Andrade R. Aguilar-Duran S. Nandini S. S. S. Sarma (2002) ArticleTitleCombined effects of copper and microalgal (Tetraselmis suecica) concentrations on the population growth of Brachionus plicatilis Müller (Rotifera) Water, Air and Soil Pollution 141 143–153
D. S. McLusky V. Bryant R. Campbell (1986) ArticleTitleThe effects of temperature and salinity on the toxicity of heavy metals to marine and estuarine invertebrates Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review 24 481–520
I. Moreno-Garrido L. M. Lubián A. M. V. M. Soares (1999) ArticleTitleGrowth differences in cultured populations of Brachionus plicatilis Müller caused by heavy metal stress as function of microalgal diet Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 63 392–398 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001289900993 Occurrence Handle10475919
R. Ortells A. Gomez M. Serra (2003) ArticleTitleCoexistence of cryptic rotifer species: ecological and genetic characterisation of Brachionus plicatilis Freshwater Biology 48 2194–2202 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01159.x
T. Nogrady R. L. Wallace T. W. Snell (1993) Rotifera. Vol. 1. Biology, Ecology and Systematics SBP Academic Publishers The Hague 142
S. S. S. Rao T. R. & Sarma (1986) ArticleTitleDemographic parameters of Brachionus patulus Müller (Rotifera) exposed to sublethal DDT concentrations at low and high food levels Hydrobiologia 139 193–200 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00028292
R. Rico-Martínez I. A. Pérez-Legaspi G. E. Quintero-Díaz M. G. Rodríguez-Martínez M. A. Hernández-Rodríguez J. E. Zaragoza-Almaraz (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of copper addition to laboratory maintained microcosms of Presidente Calles Reservoir organisms (Aguascalientes, Mexico) Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management 1 323–332
W. Salomón U. Förstner P. Mader (Eds) (1995) Heavy metals. Problems and solutions Springer-Verlag Berlin
S. S. S. Sarma N. Iyer H. J. Dumont (1996) ArticleTitleCompetitive interactions between herbivorous rotifers: importance of food concentration and initial population density Hydrobiologia 331 1–7
S. S. S. Sarma P. S. Larios-Jurado S. Nandini (2001) ArticleTitleEffect of three food types on the population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus and Brachionus patulus (Rotifera: Brachionidae) Revista de Biología Tropical 49 75–82
S.S.S. Sarma B. Elguea-Sánchez S. Nandini (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of salinity on competition between the rotifers Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff and Hexarthra jenkinae (De Beauchamp) (Rotifera) Hydrobiologia 474 183–188 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016535821741
T. W. Snell C. R. Janssen (1998) Microscale toxicity testing with rotifers P. Wells K. Lee C. Blaise (Eds) Microscale Testing in Aquatic Toxicology: Advances, Techniques, and Practice CRC Press Florida, USA 409–422
D. J. Soucek D. S. Cherry C. E. Zipper (2001) ArticleTitleAluminum-dominated acute toxicity to the cladoceran Ceriodaphnia dubia in neutral waters downstream of an acid mine drainage discharge Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58 2396–2404 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfas-58-12-2396
R. Q. Yu W X. Wang (2002) ArticleTitleTrace metal assimilation and release budget in Daphnia magna Limnology and Oceanography 47 495–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gama-Flores, J.L., Sarma, S. & Nandini, S. Interaction Among Copper Toxicity, Temperature and Salinity on the Population Dynamics of Brachionus Rotundiformis (Rotifera). Hydrobiologia 546, 559–568 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4300-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4300-5