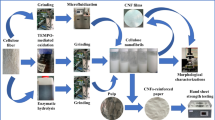
Abstract
The pursuit for sustainability in the papermaking industry calls for the elimination or reduction of synthetic additives and the exploration of renewable and biodegradable alternatives. Cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs), due to their inherent morphological and biochemical properties, are an excellent alternative to synthetic additives. These properties enable CNFs to improve the mechanical, functional, and barrier properties of different types of paper. The nanosize diameter, micrometre length, semicrystalline structure, high strength, and modulus of CNFs have a direct influence on the mechanical properties of paper, such as tensile index, burst index, Scott index, breaking length, tear index, Z-strength, E-modulus, strain at break, and tensile stiffness. This review details the role played by CNFs as an additive to improve strength properties of paper and the factors affecting the improvement in paper quality when CNFs are added as additives. The paper also includes techno-economic aspects of the process and identifies areas that need further research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Yano H (2009) Comparison of the characteristics of cellulose microfibril aggregates of wood, rice straw and potato tuber. Cellulose 16(6):1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9334-9
Abe K, Iwamoto S, Yano H (2007) Obtaining cellulose nanofibers with a uniform width of 15 nm from wood. Biomacromolecules 8(10):3276–3278. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm700624p
Adel AM, El-Gendy AA, Diab MA, Abou-Zeid RE, El-Zawawy WK, Dufresne A (2016) Microfibrillated cellulose from agricultural residues. Part I: Papermaking application. Ind Crops Prod 93:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.043
Adnan S, Azhar A, Jasmani L, Samsudin M (2018) Properties of paper incorporated with nanocellulose extracted using microbial hydrolysis assisted shear process. IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing, 012022
Afra E, Yousefi H, Hadilam MM, Nishino T (2013) Comparative effect of mechanical beating and nanofibrillation of cellulose on paper properties made from bagasse and softwood pulps. Carbohydr Polym 97(2):725–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.032
Ahola S, Österberg M, Laine J (2008) Cellulose nanofibrils—adsorption with poly (amideamine) epichlorohydrin studied by QCM-D and application as a paper strength additive. Cellulose 15(2):303–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9167-3
Alagarasi A (2013) Introduction to Nanomaterials. John Wiley & Sons, National Center for Environmental Research
Alcalá M, González I, Boufi S, Vilaseca F, Mutjé P (2013) All-cellulose composites from unbleached hardwood kraft pulp reinforced with nanofibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 20(6):2909–2921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0085-2
Ämmälä A, Liimatainen H, Burmeister C, Niinimäki J (2013) Effect of tempo and periodate-chlorite oxidized nanofibrils on ground calcium carbonate flocculation and retention in sheet forming and on the physical properties of sheets. Cellulose 20(5):2451–2460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0012-6
Ang S, Haritos V, Batchelor W (2020) Cellulose nanofibers from recycled and virgin wood pulp: a comparative study of fiber development. Carbohydr Polym 234:115900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115900
Ankerfors M, Lindström T, Söderberg D (2014) The use of microfibrillated cellulose in fine paper manufacturing—results from a pilot scale papermaking trial. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 29(3):476–483. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-03-p476-483
Bajpai P (2016) Pulp and paper industry: nanotechnology in forest industry. Elsevier, New Delhi
Balea A, Blanco Á, Monte MC, Merayo N, Negro C (2016a) Effect of bleached eucalyptus and pine cellulose nanofibers on the physico-mechanical properties of cartonboard. BioResources 11(4):8123–8138. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.4.8123-8138
Balea A, Merayo N, Fuente E, Delgado-Aguilar M, Mutje P, Blanco A, Negro C (2016b) Valorization of corn stalk by the production of cellulose nanofibers to improve recycled paper properties. BioResources 11(2):3416–3431. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.2.3416-3431
Balea A, Merayo N, De La Fuente E, Negro C, Blanco Á (2017) Assessing the influence of refining, bleaching and TEMPO-mediated oxidation on the production of more sustainable cellulose nanofibers and their application as paper additives. Ind Crops Prod 97:374–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.12.050
Balea A, Sanchez-Salvador JL, Monte MC, Merayo N, Negro C, Blanco A (2019) In situ production and application of cellulose nanofibers to improve recycled paper production. Molecules 24(9):1800. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091800
Balea A, Monte MC, Merayo N, Campano C, Negro C, Blanco A (2020) Industrial Application of nanocelluloses in papermaking: a review of challenges, technical solutions, and market perspectives. Molecules 25(3):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030526
Bardet R, Bras J (2014) Cellulose nanofibers and their use in paper industry. In: Sain M (ed) Handbook of green materials: bionanomaterials: separation processes, characterization and properties. World Scientific, pp 207–232
Bossu J, Czibula CV, Winter A, Gindl-Altmutter W, Eckhart R, Zankel A, Bauer W (2019) Combined effect of the morphology and rate of addition of fine cellulosic materials produced from chemical pulp on paper properties. International paper physics conference 247–259
Boufi S, González I, Delgado-Aguilar M, Tarrès Q, Mutjé P (2017) Nanofibrillated cellulose as an additive in papermaking process. Carbohydr Polym 154:153–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.117
Brodin FW, Gregersen ØW, Syverud K (2014) Cellulose nanofibrils: challenges and possibilities as a paper additive or coating material—a review. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 29(1):156–166. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-01-p156-166
Campano C, Merayo N, Balea A, Tarrés Q, Delgado-Aguilar M, Mutjé P, Negro C, Blanco Á (2018) Mechanical and chemical dispersion of nanocelluloses to improve their reinforcing effect on recycled paper. Cellulose 25(1):269–280
Cao D, Xing Y, Tantratian K, Wang X, Ma Y, Mukhopadhyay A, Cheng Z, Zhang Q, Jiao Y, Chen L (2019) 3D printed high-performance lithium metal microbatteries enabled by nanocellulose. J Adv Mater 31(14):1807313. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201807313
Charani PR, Dehghani-Firouzabadi M, Afra E, Blademo Å, Naderi A, Lindström T (2013) Production of microfibrillated cellulose from unbleached kraft pulp of Kenaf and Scotch Pine and its effect on the properties of hardwood kraft: microfibrillated cellulose paper. Cellulose 20(5):2559–2567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9998-z
Cowie J, Bilek ET, Wegner TH, Shatkin JA (2014) Market projections of cellulose nanomaterial-enabled products-Part 2: volume estimates. Tappi J 13(6):57–69. https://doi.org/10.32964/tj13.6.57
Das AK, Islam MN, Ashaduzzaman M, Nazhad MM (2020) Nanocellulose: its applications, consequences and challenges in papermaking. Package Technol Res 1–8
De Assis CA, Houtman C, Phillips R, Bilek E, Rojas OJ, Pal L, Peresin MS, Jameel H, Gonzalez R (2017) Conversion economics of forest biomaterials: risk and financial analysis of CNC manufacturing. Biofuel Bioprod Biorefin 11(4):682–700. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1782
De Assis CA, Iglesias MC, Bilodeau M, Johnson D, Phillips R, Peresin MS, Bilek E, Rojas OJ, Venditti R, Gonzalez R (2018) Cellulose micro-and nanofibrils (CMNF) manufacturing-financial and risk assessment. Biofuel Bioprod Biorefin 12(2):251–264. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1835
De Oliveira MH, Maric M, Van De Ven TG (2008) The role of fiber entanglement in the strength of wet papers. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 23(4):426–431. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2008-23-04-p426-431
Delgado Aguilar M, González Tovar I, Tarrés Farrés Q, Alcalà Vilavella M, Pèlach Serra MÀ, Mutjé Pujol P (2015) Approaching a low-cost production of cellulose nanofibers for papermaking applications. BioResources. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.10.3.5345-5355
Delgado-Aguilar M, González I, Pèlach M, De La Fuente E, Negro C, Mutjé P (2015) Improvement of deinked old newspaper/old magazine pulp suspensions by means of nanofibrillated cellulose addition. Cellulose 22(1):789–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0473-2
Diab M, Curtil D, El-Shinnawy N, Hassan ML, Zeid IF, Mauret E (2015) Biobased polymers and cationic microfibrillated cellulose as retention and drainage aids in papermaking: comparison between softwood and bagasse pulps. Ind Crops Prod 72:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.01.072
Ding Q, Zeng J, Wang B, Gao W, Chen K, Yuan Z, Xu J, Tang D (2018) Effect of retention rate of fluorescent cellulose nanofibrils on paper properties and structure. Carbohydr Polym 186:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.040
Eriksen Ø, Syverud K, Gregersen Ø (2008) The use of microfibrillated cellulose produced from kraft pulp as strength enhancer in TMP paper. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 23(3):299–304. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2008-23-03-p299-304
Espinosa E, Tarrés Q, Delgado-Aguilar M, González I, Mutjé P, Rodríguez A (2016) Suitability of wheat straw semichemical pulp for the fabrication of lignocellulosic nanofibres and their application to papermaking slurries. Cellulose 23(1):837–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0807-8
Fotie G, Limbo S, Piergiovanni L (2020) Manufacturing of food packaging based on nanocellulose: current advances and challenges. Nanomaterials 10(9):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091726
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24(11):4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
González I, Boufi S, Pèlach MA, Alcalà M, Vilaseca F, Mutjé P (2012) Nanofibrillated cellulose as paper additive in eucalyptus pulps. BioResources 7(4):5167–5180. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.7.4.5167-5180
González I, Vilaseca F, Alcalá M, Pèlach M, Boufi S, Mutjé P (2013) Effect of the combination of biobeating and NFC on the physico-mechanical properties of paper. Cellulose 20(3):1425–1435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9927-1
Gullichsen J, Fogelholm C-J, Fapet O (2000) Chemical pulping-papermaking science and technology. Fapet Oy, Jyväskylä
Hai LV, Seo YB (2018) Properties of nanofibrillated cellulose prepared by mechanical means. Cellul Chem Technol 52(9–10):741–747
He M, Yang G, Cho B-U, Lee YK, Won JM (2017) Effects of addition method and fibrillation degree of cellulose nanofibrils on furnish drainability and paper properties. Cellulose 24(12):5657–5669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1495-3
Hii C, Gregersen ØW, Chinga-Carrasco G, Eriksen Ø (2012) The effect of MFC on the pressability and paper properties of TMP and GCC based sheets. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 27(2):388. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2012-27-02-p388-396
Hu F, Zeng J, Cheng Z, Wang X, Wang B, Zeng Z, Chen K (2021) Cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) produced by different mechanical methods to improve mechanical properties of recycled paper. Carbohydr Polym 254:117474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117474
Hubbe MA (2014) Prospects for maintaining strength of paper and paperboard products while using less forest resources: a review. BioResources 9(1):1634–1763. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.9.1.1634-1763
Ishii D, Saito T, Isogai A (2011) Viscoelastic evaluation of average length of cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Biomacromolecules 12:548–550. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm1013876
Jawaid M, Boufi S, Khalil A (2017) Cellulose-Reinforced nanofibre composites: Production, properties and applications. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge
Johansson A (2011) Correlations between fibre properties and paper properties. Dissertation, KTH Royal Institute of Technology
Johnson DA, Paradis MA, Bilodeau M, Crossley B, Foulger M, Gelinas P (2016) Effects of cellulosic nanofibrils on papermaking properties of fine papers. Tappi J 15(6):395–402. https://doi.org/10.32964/TJ15.6.395
Jowkarderis L, Van De Ven TG (2014) Intrinsic viscosity of aqueous suspensions of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 21(4):2511–2517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0292-5
Kajanto I, Kosonen M (2012) The potential use of micro-and nanofibrillated cellulose as a reinforcing element in paper. Forest Sci Technol 2(6):42–48
Karlsson H (2007) Some aspects on strength properties in paper composed of different pulps. Dissertation, Karlstad University
Khalil HA, Davoudpour Y, Islam MN, Mustapha A, Sudesh K, Dungani R, Jawaid M (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.069
Kim KM, Lee JY, Jo HM, Kim SH (2019) Cellulose nanofibril grades’ effect on the strength and drainability of security paper. BioResources 14(4):8364–8375
Kumar A, Singh S, Singh A (2016) Comparative study of cellulose nanofiber blending effect on properties of paper made from bleached bagasse, hardwood and softwood pulps. Cellulose 23(4):2663–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0954-6
Kumar V, Pathak P, Bhardwaj NK (2020) Facile chemo-refining approach for production of micro-nanofibrillated cellulose from bleached mixed hardwood pulp to improve paper quality. Carbohydr Polym 238:116186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116186
Kumar V, Pathak P, Bhardwaj NK (2021) Micro-nanofibrillated cellulose preparation from bleached softwood pulp using chemo-refining approach and its evaluation as strength enhancer for paper properties. Appl Nanosci 11(1):101–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01575-9
Laitinen O, Suopajärvi T, Liimatainen H (2020) Enhancing packaging board properties using micro-and nanofibers prepared from recycled board. Cellulose 27:7215–7225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03264-w
Latifah J, Nurrul-Atika M, Sharmiza A, Rushdan I (2020) Extraction of nanofibrillated cellulose from Kelempayan (Neolamarckia cadamba) and its use as strength additive in papermaking. J Trop For Sci 32(2):170–178. https://doi.org/10.26525/jtfs32.2.170
Lee H, Sundaram J, Mani S (2017) Production of cellulose nanofibrils and their application to food: a review. J Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-4678-0_1
Lengowski EC, Júnior EaB, Kumode MMN, Carneiro ME, Satyanarayana KG (2019) Nanocellulose in the paper making. Sustainable polymer composites and nanocomposites. Springer, 1027–1066
Li Q, Mcginnis S, Sydnor C, Wong A, Renneckar S (2013) Nanocellulose life cycle assessment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1(8):919–928. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc4000225
Lindstrom T, Naderi A, Wiberg A (2015) Large scale applications of nanocellulosic materials—a comprehensive review. J Korea TAPPI 47(6):5–21. https://doi.org/10.7584/KTAPPI.2015.47.6.005
Lourenço AF, Gamelas JA, Nunes T, Amaral J, Mutjé P, Ferreira P (2017) Influence of TEMPO-oxidised cellulose nanofibrils on the properties of filler-containing papers. Cellulose 24(1):349–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1121-9
Lourenço AF, Gamelas JA, Sarmento P, Ferreira PJ (2019a) Enzymatic nanocellulose in papermaking—the key role as filler flocculant and strengthening agent. Carbohydr Polym 224:115200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115200
Lourenço AF, Godinho D, Gamelas JA, Sarmento P, Ferreira PJ (2019b) Carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils in papermaking: influence on filler retention and paper properties. Cellulose 26(5):3489–3502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02303-5
Lourenço AF, Gamelas JA, Sarmento P, Ferreira PJ (2020) A comprehensive study on nanocelluloses in papermaking: the influence of common additives on filler retention and paper strength. Cellulose 27(9):5297–5309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03105-w
Manninen M, Kajanto I, Happonen J, Paltakari J (2011) The effect of microfibrillated cellulose addition on drying shrinkage and dimensional stability of wood-free paper. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 26(3):297–305. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2011-26-03-p297-305
Mashkour M, Afra E, Resalati H, Mashkour M (2015) Moderate surface acetylation of nanofibrillated cellulose for the improvement of paper strength and barrier properties. RSC Adv 5(74):60179–60187. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08161K
Merayo N, Balea A, De La Fuente E, Blanco Á, Negro C (2017a) Interactions between cellulose nanofibers and retention systems in flocculation of recycled fibers. Cellulose 24(2):677–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1138-0
Merayo N, Balea A, De La Fuente E, Blanco Á, Negro C (2017b) Synergies between cellulose nanofibers and retention additives to improve recycled paper properties and the drainage process. Cellulose 24(7):2987–3000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1302-1
Miller J (2019) Nanocellulose: market perspectives. Tappi J 18(5):313–316
Moodley RS (2018) Evaluation of paper substrates for microfluidic application in medical diagnostic kits. Dissertation, University of KwaZulu-Natal
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40(7):3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00108B
Mörseburg K, Chinga-Carrasco G (2009) Assessing the combined benefits of clay and nanofibrillated cellulose in layered TMP-based sheets. Cellulose 16(5):795–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9290-4
Nagarajan K, Ramanujam N, Sanjay M, Siengchin S, Surya Rajan B, Sathick Basha K, Madhu P, Raghav G (2021) A comprehensive review on cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibers: pretreatment, preparation, and characterization. Polym Compos 42(4):1588–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25929
Naz S, Ali JS, Zia M, Manufacturing, (2019) Nanocellulose isolation characterization and applications: a journey from non-remedial to biomedical claims. Bio-Des Manuf 2(3):187–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-019-00049-4
Nechyporchuk O, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2016) Production of cellulose nanofibrils: a review of recent advances. Ind Crops Prod 93:2–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.016
Osong SH, Norgren S, Engstrand P (2014) Paper strength improvement by inclusion of nano-ligno-cellulose to chemi-thermomechanical pulp. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 29(2):309–316. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-02-p309-316
Osong SH, Norgren S, Engstrand P (2016) Processing of wood-based microfibrillated cellulose and nanofibrillated cellulose, and applications relating to papermaking: a review. Cellulose 23(1):93–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0798-5
Ottesen V (2018) Cellulose nanofibrils as paper additive and coating material: properties, distribution and interaction effects. Dissertation, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Page D (1969) A theory for the tensile strength of paper. Tappi J 52:674–681
Park TU, Lee JY, Jo HM, Kim KM (2018) Utilization of cellulose micro/nanofibrils as paper additive for the manufacturing of security paper. BioResources 13(4):7780–7791. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.13.4.7780-7791
Petroudy SRD, Syverud K, Chinga-Carrasco G, Ghasemain A, Resalati H (2014) Effects of bagasse microfibrillated cellulose and cationic polyacrylamide on key properties of bagasse paper. Carbohydr Polym 99:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.073
Phipps J, Larson T, Ingle D, Eaton H (2017) The effect of microfibrillated cellulose on the strength and light scattering of highly filled papers. Advances in Pulp and Paper Research. Trans of the XVIth Fund Res Symp Oxford
Potulski DC, Viana LC, Da Fonte AN, Carneiro ME, De Muniz GIB, Klock U (2020) Nanofibrillated cellulose applied as reinforcement for short-fiber paper. Floresta 50(3):1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.5380/rf.v50i3.59251
Ru J, Tong C, Chen N, Shan P, Zhao X, Liu X, Chen J, Li Q, Liu X, Liu H (2019) Morphological and property characteristics of surface-quaternized nanofibrillated cellulose derived from bamboo pulp. Cellulose 26(3):1683–1701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2146-z
Saito T, Kuramae R, Wohlert J, Berglund LA, Isogai A (2013) An ultrastrong nanofibrillar biomaterial: the strength of single cellulose nanofibrils revealed via sonication-induced fragmentation. Biomacromolecules 14(1):248–253. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm301674e
Sanchez-Salvador JL, Balea A, Monte MC, Negro C, Miller M, Olson J, Blanco A (2020) Comparison of mechanical and chemical nanocellulose as additives to reinforce recycled cardboard. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-60507-3
Sehaqui H, Allais M, Zhou Q, Berglund L (2011) Wood cellulose biocomposites with fibrous structures at micro-and nanoscale. Compos Sci Technol 71(3):382–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.12.007
Sehaqui H, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2013) Nanofibrillated cellulose for enhancement of strength in high-density paper structures. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 28(2):182–189. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2013-28-02-p182-189
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak J (2010) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: water interactions and physical properties for packaging applications. Cellulose 17(4):835–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9424-8
Su J, Mosse WK, Sharman S, Batchelor WJ, Garnier G (2013) Effect of tethered and free microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) on the properties of paper composites. Cellulose 20(4):1925–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9955-x
Su J, Zhang L, Batchelor W, Garnier G (2014) Paper engineered with cellulosic additives: effect of length scale. Cellulose 21(4):2901–2911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0298-z
Subramanian R, Hiltunen E, Gane PA (2011) Potential use of micro-and nanofibrillated cellulose composites exemplified by paper. In: Kalia S (ed) Cellulose fibers: bio-and nano-polymer composites. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–152
Syverud K, Gregersen Ø, Chinga-Carrasco G, Eriksen Ø (2009) The influence of microfibrillated cellulose, MFC, on paper strength and surface properties. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 899–930. https://doi.org/10.15376/frc.2009.2.899
Taipale T, Österberg M, Nykänen A, Ruokolainen J, Laine J (2010) Effect of microfibrillated cellulose and fines on the drainage of kraft pulp suspension and paper strength. Cellulose 17(5):1005–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9431-9
Tajik M, Torshizi HJ, Resalati H, Hamzeh Y (2018) Effects of cationic starch in the presence of cellulose nanofibrils on structural, optical and strength properties of paper from soda bagasse pulp. Carbohydr Polym 194:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.026
Tarrés Q, Saguer E, Pèlach M, Alcalà M, Delgado-Aguilar M, Mutjé P (2016) The feasibility of incorporating cellulose micro/nanofibers in papermaking processes: the relevance of enzymatic hydrolysis. Cellulose 23(2):1433–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0889-y
Tozluoglu A, Poyraz B (2016) Effects of cellulose micro/nanofibers as paper additives in kraft and kraft-NaBH4pulps. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 31(4):561–572. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2016-31-04-p561-572
Vallejos ME, Felissia FE, Area MC, Ehman NV, Tarrés Q, Mutjé P (2016) Nanofibrillated cellulose (CNF) from eucalyptus sawdust as a dry strength agent of unrefined eucalyptus handsheets. Carbohydr Polym 139:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.12.004
Zambrano F, Starkey H, Wang Y, De Assis CA, Venditti R, Pal L, Jameel H, Hubbe MA, Rojas OJ, Gonzalez R (2020) Using micro-and nanofibrillated cellulose as a means to reduce weight of paper products: a review. BioResources 15(2):4553–4590. https://doi.org/10.15376/BIORES.15.2.4553-4590
Zeng J, Liu L, Li J, Dong J, Cheng Z (2020) Properties of cellulose nanofibril produced from wet ball milling after enzymatic treatment versus mechanical grinding of bleached softwood kraft fibers. BioResources 15(2):3809–3820. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.2.3809-3820
Zeng J, Zeng Z, Cheng Z, Wang Y, Wang X, Wang B, Gao W (2021) Cellulose nanofibrils manufactured by various methods with application as paper strength additives. Sci Rep 11(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91420-y
Zimmermann T, Pöhler E, Geiger T (2004) Cellulose fibrils for polymer reinforcement. Adv Eng Mater 6(9):754–761. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200400097
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, South Africa Biorefinery Industry Development Facility for supporting this work as part of the literature review of a MSc project. The authors would like to thank the Department of Science and Innovation for financial support via the General Budget Support (GBS) programme.
Funding
This review was supported by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Biorefinery Industry Development Facility, Durban, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TBJ had the idea for the article, TBJ performed the literature search and drafted, the manuscript whereas PL and BS critically revised the drafts and approved the review for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of this review.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jele, T.B., Lekha, P. & Sithole, B. Role of cellulose nanofibrils in improving the strength properties of paper: a review. Cellulose 29, 55–81 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04294-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04294-8