Abstract
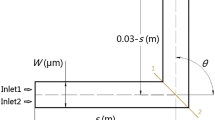
This paper discusses a flexible layout design method of passive micromixers based on the topology optimization of fluidic flows. Being different from the trial and error method, this method obtains the detailed layout of a passive micromixer according to the desired mixing performance by solving a topology optimization problem. Therefore, the dependence on the experience of the designer is weaken, when this method is used to design a passive micromixer with acceptable mixing performance. Several design disciplines for the passive micromixers are considered to demonstrate the flexibility of the layout design method for passive micromixers. These design disciplines include the approximation of the real 3D micromixer, the manufacturing feasibility, the spacial periodic design, and effects of the Péclet number and Reynolds number on the designs obtained by this layout design method. The capability of this design method is validated by several comparisons performed between the obtained layouts and the optimized designs in the recently published literatures, where the values of the mixing measurement is improved up to 40.4% for one cycle of the micromixer.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.S. Andreasen, A.R. Gersborg, O. Sigmund, Topology optimization of microfluidic mixers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 61, 498–513 (2009)
M.A. Ansari, K.Y. Kim, Shape optimization of a micromixer with staggered herringbone groove. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 6687–6695 (2007)
M.A. Ansari, K.Y. Kim, Evaluation of surrogate models for optimization of herringbone groove micromixer. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 22, 387–396 (2008)
T. Borrvall, J. Petersson, Topology optimization of fluid in Stokes flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 41, 77–107 (2003)
R.H. Byrd, P. Lu, J. Nocedal, A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 16, 1190–1208 (1995)
R. Choudhary, T. Bhakat, R.K. Singh, A. Ghubade, S. Mandal, A. Ghosh, A. Rammohan, A. Sharma, S. Bhattacharya, Bilayer staggered herringbone micro-mixers with symmetric and asymmetric geometries. Microfluid Nanofluid 10, 271–286 (2011)
C.K. Chung, T.R. Shih, Effect of geometry on fluid mixing of the rhombic micromixers. Microfluid Nanofluid 4, 419–425 (2008)
C.K. Chung, T.R. Shih, T.C. Chen, B.H. Wu, Mixing behavior of the rhombic micromixers over a wide Reynolds number range using Taguchi method and 3D numerical simulations. Biomed. Microdevices 10, 739–748 (2008)
C.A. Cortes-Quiroza, M. Zangeneh, A. Goto, On multi-objective optimization of geometry of staggered herringbone micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 7, 29–43 (2009)
C.A. Cortes-Quiroza, A. Azarbadegana, M. Zangeneha, A. Goto, Analysis and multi-criteria design optimization of geometric characteristics of grooved micromixer. Chem. Eng. J. 160, 852–864 (2010)
P. Danckwerts, The difinition and measurement of some characteristics of mixtures. Appl. Sci. Res. A3, 279–296 (1952)
Y. Deng, Z. Liu, P. Zhang, Y. Wu, J.G. Korvink, in Optimization of No-Moving Part Fluidic Resistance Microvalves with Low Reynolds Number. Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro MechanicalSystems (MEMS) (2010), pp. 67–70
Y. Deng, Y. Wu, M. Xuan, J.G. Korvink, Z. Liu, in Dynamic Optimization of Valveless Micropump. Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators, and Microsystems (Transducers) (2011), pp. 442–445
J. Donea, A. Hureta, Finite Element Methods for Flow Problems (Wiley, West Sussex, 2003)
Y. Du, Z. Zhang, C.H. Yim, M. Lin, X. Cao, A simplified design of the staggered herringbone micromixer for practical applications. Biomicrofluidics 4, 024105 (2010)
A. Gersborg-Hansen, O. Sigmund, R.B. Haber, Topology optimization of channel flow problems. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 29, 1–12 (2005)
I. Glasgow, N. Aubry, Enhancement of microfluidic mixing using time pulsing. Lab Chip. 3, 114–120 (2003)
M. Hinze, R. Pinnau, M. Ulbrich, S. Ulbrich, Optimization with PDE constraints (Springer, 2009)
S. Hossain, A. Husain, K.Y. Kim, Shape optimization of a micromixer with staggered-herringbone grooves patterned on opposite walls. Chem. Eng. J. 162, 730–737 (2010)
P.B. Howell, Jr., D.R. Mott, F.S. Ligler, J.P. Golden, C.R. Kaplan, E.S. Oran, A combinatorial approach to microfluidic mixing. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 18, 115019, 7 pp (2008)
M.Z. Huang, R.J. Yang, C.H. Tai, C.H. Tsai, L.M. Fu, Application of electrokinetic instability flow for enhanced micromixing in cross-shaped microchannel. Biomed. Microdevices 8, 309–315 (2006)
A. Jameson, in Optimum Aerodynamic Design Using Control Theory. CFD Review (Wiley, 1995)
G.S. Jeong, S. Chung, C.B. Kim, S.H. Lee, Applications of micromixing technology. Analyst 135, 460–473 (2010)
T.G. Kang, M.K. Singh, T.H. Kwon, P.D. Anderson, Chaotic mixing using periodic and aperiodic sequences of mixing protocols in a micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 4, 589–599 (2008)
T.G. Kang, M.K. Singh, P.D. Anderson, H.E.H. Meijer, A chaotic serpentine mixer efficient in the creeping flow regime: from design concept to optimization. Microfluid Nanofluid 7, 783–794 (2009)
G. Karniadakis, A. Beskok, N. Aluru, Microflows and Nanoflows: Fundamentals and Simulation (Springer, 2005)
S.P. Kee, A. Gavriilidis, Design and characterisation of the staggered herringbone mixer. Chem. Eng. J. 142, 109–121 (2008)
D.H. Kelley, N.T. Ouellette, Separating stretching from folding in fluid mixing. Nat. Phys. 7, 477–480 (2011)
H.Y. Lee, J. Voldman, Optimizing micromixer design for enhancing dielectrophoretic microconcentrator performance. Anal. Chem. 79, 1833–1839 (2007)
C.Y. Lee, C.L. Chang, Y.N. Wang, L.M. Fu, Microfluidic mixing: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 3263–3287 (2011)
D. Li, Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics (Springer, 2007)
C.H. Lin, L.M. Fu, Y.S. Chien, Microfluidic T-form mixer utilizing switching electroosmotic flow. Anal. Chem. 76, 5265–5276 (2004)
C.H. Lin, C.H. Tsai, C.W. Pan, L.M. Fu, Rapid circular microfluidic mixer utilizing unbalanced driving force. Biomed. Microdevices 9, 43–50 (2007)
R.H. Liu, M.A. Stremler, K.V. Sharp, M.G. Olsen, J.G. Santiago, R.J. Adrian, H. Aref, D.J. Beebe, Passive mixing in a three-dimensional serpentine microchannel. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 9, 190–197 (2000)
Y.Z. Liu, B.J. Kim, H.J. Sung, Two-fluid mixing in a microchannel. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 25, 986–995 (2004)
Z. Liu, Y. Deng, S. Lin, M. Xuan, Optimization of micro Venturi diode in steady flow at low Reynolds number. Eng. Optim. (2012). doi:10.1080/0305215X.2011.652100
N.S. Lynn, D.S. Dandy, Geometrical optimization of helical flow in grooved micromixers. Lab Chip 7, 580–587 (2007)
K. Malecha, L.J. Golonka, J. Baldyga, M. Jasińska, P. Sobieszuk, Serpentine microfluidic mixer made in LTCC. Sens. Actuators B 143, 400–413 (2009)
D.R. Mott, P.B. Howell, Jr., J.P. Golden, C.R. Kaplan, F.S. Ligler, E.S. Oran, Toolbox for the design of optimized microfluidic components. Lab Chip 6, 540–549 (2006)
D.R. Mott, P.B. Howell, Jr., K.S. Obenschain, E.S. Oran, The numerical toolbox: an approach for modeling and optimizing microfluidic components. Mech. Res. Commun. 36, 104–109 (2009)
P.E. Neerincx, R.P.J. Denteneer, S. Peelen, H.E.H. Meijer, Compact mixing using multiple splitting, stretching, and recombining flows. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 296, 349–361 (2011)
W.Y. Ng, S. Goh, Y.C. Lam, C. Yang, I. Rodriguez, DC-biased AC-electroosmotic and AC-electrothermal flow mixing in microchannels. Lab Chip 9, 802–809 (2009)
N.T. Nguyen, Micromixer: Fundamentals, Design and Fabrication (William Andrew, 2008)
N.T. Nguyen, Z. Wu, Micromixers—a review. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 15, 1–16 (2005)
J. Nocedal, S.J. Wright, Numerical Optimization (Springer, 1998)
F. Okkels, H. Bruus, in Design of Micro-Fluidic Bio-Reactors Using Topology Optimization. ECCOMAS CFD (2006)
L.H. Olesen, F. Okkels, H. Bruus, A high-level programming-language implementation of topology optimization applied to steady-state Navier–Stokes flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 65, 975–1001 (2006)
J.M. Park, T.H. Kwon, Numerical characterization of three-dimensional serpentine micromixers. AIChE J. 54, 1999–2008 (2008)
J.M. Park, D.S. Kim, T.G. Kang, T.H. Kwon, Improved serpentine laminating micromixer with enhanced local advection. Microfluid Nanofluid 4, 513–523 (2008)
E. Schall, Y.L. Guer, S. Gibout, in An Anisotropic Unstructured Meshes Mapping Method (AUM3) to Optimize Mixing in Laminar Periodic Flows. Proceedings of PSFVIP-4, Chamonix, France, 3–5 June 2003
O. Sigmund, Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 33, 401–424 (2007)
M.K. Singh, T.G. Kang, H.E.H. Meijer, P.D. Anderson, The mapping method as a toolbox to analyze, design, and optimize micromixers. Microfluid Nanofluid 5, 313–325 (2008)
M.K. Singh, T.G. Kang, P.D. Anderson, H.E.H. Meijer, A.N. Hrymak, Analysis and optimization of low-pressure drop static mixers. AIChE J. 55, 2208–2216 (2009)
H. Song, X.Z. Yin, D.J. Bennett, Optimization analysis of the staggered herringbone micromixer based on the slip-driven method. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 86, 883–891 (2008)
H. Song, Z. Cai, H. Noh, D. Bennett, Lab Chip 10, 734–740 (2010)
A.D. Stroock, S.K.W. Dertinger, A. Ajdari, I. Mezić, H.A. Stone, G.M. Whitesides, Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295, 647 (2002)
A.P. Sudarsan, V.M. Ugaz, Multivortex micromixing. PNAS 103, 7228–7233 (2006)
M.S. Williams, K.J. Longmuirb, P. Yager, A practical guide to the staggered herringbone mixer. Lab Chip 8, 1121–1129 (2008)
C.H. Wu, R.J. Yang, Improving the mixing performance of side channel type micromixers using an optimal voltage control model. Biomed. Microdevices 8, 119–131 (2006)
Z. Xu, C. Li, D. Vadilloc, X. Ruanb, X. Fu, Numerical simulation on fluid mixing by effects of geometry in staggered oriented ridges micromixers. Sens. Actuators B, Chem. 153, 284–292 (2011)
C. Zhu, R.H. Byrd, J. Nocedal, L-BFGS-B: algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B, FORTRAN routines for large scale bound constrained optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 23, 550–560 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50975272, No. 11034007), the 863 Program (No.2012AA040503) and the hundred talent project in Chinese Academy of Sciences. The authors are also grateful to the reviewers’ kind attention and valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, P. et al. A flexible layout design method for passive micromixers. Biomed Microdevices 14, 929–945 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9672-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9672-5