Abstract
Kluyveromyces marxianus is homothallic hemiascomycete yeast frequently isolated from dairy environments. It possesses phenotypic traits such as enhanced thermotolerance, inulinase production, and rapid growth rate that distinguish it from its closest relative Kluyveromyces lactis. Certain of these traits, notably fermentation of lactose and inulin to ethanol, make this yeast attractive for industrial production of ethanol from inexpensive substrates. There is relatively little known, however, about the diversity in this species, at the genetic, metabolic or physiological levels. This study compared phenotypic traits of 13 K. marxianus strains sourced from two European Culture Collections. A wide variety of responses to thermo, osmotic, and cell wall stress were observed, with some strains showing multi-stress resistance. These traits generally appeared unlinked indicating that, as with other yeasts, multiple resistance/adaptation pathways are present in K. marxianus. The data indicate that it should be possible to identify the molecular basis of traits to facilitate selection or engineering of strains adapted for industrial environments. The loci responsible for mating were also identified by genome sequencing and PCR analysis. It was found that K. marxianus can exist as stable haploid or diploid cells, opening up additional prospects for future strain engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrom SU, Rine J (1998) Theme and variation among silencing proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces lactis. Genetics 148(3):1021–1029
Barnett JA, Entian KD (2005) A history of research on yeasts 9: regulation of sugar metabolism. Yeast 22(11):835–894
Barsoum E, Martinez P, Astrom SU (2010) Alpha 3, a transposable element that promoters host sexual reproduction. Genes Dev 24:33–44
Blank LM, Lehmbeck F, Sauer U (2005) Metabolic-flux and network analysis in fourteen hemiascomycetous yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res 5(6–7):545–558
Butler G, Kenny C, Fagan A, Kurischko C, Gaillardin C, Wolfe KH (2004) Evolution of the MAT locus and its Ho endonuclease in yeast species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(6):1632–1637
Christensen AD, Kadar Z, Oleskowicz-Popiel P, Thomsen MH (2011) Production of bioethanol from organic whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(2):283–289
Conant GC, Wolfe KH (2007) Increased glycolytic flux as an outcome of whole-genome duplication in yeast. Mol Syst Biol 3:129
Cubillos FA, Billi E, Zorgo E, Parts L, Fargier P, Omholt S, Blomberg A, Warringer J, Louis EJ, Liti G (2011) Assessing the complex architecture of polygenic traits in diverged yeast populations. Mol Ecol 20(7):1401–1413
Dujon B, Sherman D, Fischer G, Durrens P, Casaregola S, Lafontaine I, De Montigny J, Marck C, Neuveglise C, Talla E, Goffard N, Frangeul L, Aigle M, Anthouard V, Babour A, Barbe V, Barnay S, Blanchin S, Beckerich JM, Beyne E, Bleykasten C, Boisrame A, Boyer J, Cattolico L, Confanioleri F, De Daruvar A, Despons L, Fabre E, Fairhead C, Ferry-Dumazet H, Groppi A, Hantraye F, Hennequin C, Jauniaux N, Joyet P, Kachouri R, Kerrest A, Koszul R, Lemaire M, Lesur I, Ma L, Muller H, Nicaud JM, Nikolski M, Oztas S, Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O, Pellenz S, Potier S, Richard GF, Straub ML, Suleau A, Swennen D, Tekaia F, Wesolowski-Louvel M, Westhof E, Wirth B, Zeniou-Meyer M, Zivanovic I, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Thierry A, Bouchier C, Caudron B, Scarpelli C, Gaillardin C, Weissenbach J, Wincker P, Souciet JL (2004) Genome evolution in yeasts. Nature 430(6995):35–44
Fonseca GG, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Gombert AK (2008) The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and its biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(3):339–354
Fukuhara H (2003) The Kluyver effect revisited. FEMS Yeast Res 3(4):327–331
Fukuhara H (2006) Kluyveromyces lactis—a retrospective. FEMS Yeast Res 6(3):323–324
Hoffman CS, Winston F (1987) A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene 57(2–3):267–272
Hohmann S (2002) Osmotic stress signaling and osmoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(2):300–372
Hohmann S (2009) Control of high osmolarity signalling in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 583(24):4025–4029
Hohmann S, Krantz M, Nordlander B (2007) Yeast osmoregulation. Methods Enzymol 428:29–45
Hood-Degrenier JK (2011) Identification of phosphatase 2A-like Sit4-mediated signalling and ubiquitin-dependent protein sorting as modulators of caffeine sensitivity in S. cerevisiae. Yeast 28(3):189–204. doi:10.1002/yea.1830
Kawasaki L, Castaneda-Bueno M, Sanchez-Paredes E, Velazquez-Zavala N, Torres-Quiroz F, Ongay-Larios L, Coria R (2008) Protein kinases involved in mating and osmotic stress in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Eukaryot Cell 7(1):78–85
Kummel A, Ewald JC, Fendt SM, Jol SJ, Picotti P, Aebersold R, Sauer U, Zamboni N, Heinemann M (2010) Differential glucose repression in common yeast strains in response to HXK2 deletion. FEMS Yeast Res 10(3):322–332
Kurtzman CP (2003) Phylogenetic circumscription of Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces and other members of the Saccharomycetaceae, and the proposal of the new genera Lachancea, Nakaseomyces, Naumovia, Vanderwaltozyma and Zygotorulaspora. FEMS Yeast Res 4(3):233–245
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73(4):331–371
Lachance MA (2007) Current status of Kluyveromyces systematics. FEMS Yeast Res 7(5):642–645
Lane MM, Morrissey JP (2010) Kluyveromyces marxianus: a yeast emerging from its sister’s shadow. Fungal Biol Rev 24:17–26
Li H, Johnson AD (2010) Evolution of transcription networks–lessons from yeasts. Curr Biol 20(17):R746–R753
Llorente B, Malpertuy A, Blandin G, Artiguenave F, Wincker P, Dujon B (2000) Genomic exploration of the hemiascomycetous yeasts: 12 Kluyveromyces marxianus var. marxianus. FEBS Lett 487(1):71–75
Merico A, Sulo P, Piskur J, Compagno C (2007) Fermentative lifestyle in yeasts belonging to the Saccharomyces complex. FEBS J 274(4):976–989
Merico A, Galafassi S, Piskur J, Compagno C (2009) The oxygen level determines the fermentation pattern in Kluyveromyces lactis. FEMS Yeast Res 9(5):749–756
O’Donnell K (1993) Fusarium and its near relatives. In: Reynolds RR, Taylor JWW (eds) The fungal holomorph: mitotic, meiotic and pleomorphic speciation in fungal systematic. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Pang ZW, Liang JJ, Qin XJ, Wang JR, Feng JX, Huang RB (2010) Multiple induced mutagenesis for improvement of ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol Lett 32(12):1847–1851
Piskur J, Rozpedowska E, Polakova S, Merico A, Compagno C (2006) How did Saccharomyces evolve to become a good brewer? Trends Genet 22(4):183–186
Porro D, Branduardi P (2009) Yeast cell factory: fishing for the best one or engineering it? Microb Cell Fact 8:51
Qian J, Qin X, Yin Q, Chu J, Wang Y (2010) Cloning and characterization of Kluyveromyces marxianus HOG1 gene. Biotechnol Lett 33(3):571–575
Ram AF, Klis FM (2006) Identification of fungal cell wall mutants using susceptibility assays based on Calcofluor white and Congo red. Nat Protoc 1(5):2253–2256
Rodicio R, Heinisch JJ (2010) Together we are strong–cell wall integrity sensors in yeasts. Yeast 27(8):531–540
Rodicio R, Buchwald U, Schmitz HP, Heinisch JJ (2008) Dissecting sensor functions in cell wall integrity signaling in Kluyveromyces lactis. Fungal Genet Biol 45(4):422–435
Rodriguez-Pena JM, Garcia R, Nombela C, Arroyo J (2010) The high-osmolarity glycerol (HOG) and cell wall integrity (CWI) signalling pathways interplay: a yeast dialogue between MAPK routes. Yeast 27(8):495–502
Rozpedowska E, Galafassi S, Johansson L, Hagman A, Piskur J, Compagno C (2011) Candida albicans—a pre-whole genome duplication yeast— is predominantly aerobic and a poor ethanol producer. FEMS Yeast Res 11(3):285–291
Rubio-Texeira M (2006) Endless versatility in the biotechnological applications of Kluyveromyces LAC genes. Biotechnol Adv 24(2):212–225
Salvado Z, Arroyo-Lopez FN, Guillamon JM, Salazar G, Querol A, Barrio E (2011) Temperature adaptation markedly determines evolution within the Saccharomyces genus. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2292–2302
Schaffrath R, Breunig KD (2000) Genetics and molecular physiology of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Fungal Genet Biol 30(3):173–190
Smith DA, Morgan BA, Quinn J (2010) Stress signalling to fungal stress-activated protein kinase pathways. FEMS Microbiol Lett 306(1):1–8
Suleau A, Jacques N, Reitz-Ausseur J, Casaregola S (2005) Intraspecific gene expression variability in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis revealed by micro-array analysis. FEMS Yeast Res 5(6–7):595–604
Winzeler EA, Shoemaker DD, Astromoff A, Liang H, Anderson K, Andre B, Bangham R, Benito R, Boeke JD, Bussey H, Chu AM, Connelly C, Davis K, Dietrich F, Dow SW, El Bakkoury M, Foury F, Friend SH, Gentalen E, Giaever G, Hegemann JH, Jones T, Laub M, Liao H, Liebundguth N, Lockhart DJ, Lucau-Danila A, Lussier M, M’Rabet N, Menard P, Mittmann M, Pai C, Rebischung C, Revuelta JL, Riles L, Roberts CJ, Ross-MacDonald P, Scherens B, Snyder M, Sookhai-Mahadeo S, Storms RK, Veronneau S, Voet M, Volckaert G, Ward TR, Wysocki R, Yen GS, Yu K, Zimmermann K, Philippsen P, Johnston M, Davis RW (1999) Functional characterization of the S cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285(5429):901–906
Wolfe KH, Shields DC (1997) Molecular evidence for an ancient duplication of the entire yeast genome. Nature 387(6634):708–713
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in parts by grants awarded by the Science Foundation of Ireland (08/RFP/GEN1295; 07/IN1/B911); the Irish Department of Agriculture FIRM programme (06RDC459; 06RDC506) and Enterprise Ireland (IP/2008/0559). We thank Michael McCarthy and Olan Burke, Carbery Group, Ballineen, West Cork for supporting aspects of this research. The technical help of Pat Higgins, Dan Walsh, Paddy Reilly, and Laura Casey is also appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supp Fig. 1.Alignment of 26S LSU D1_D2 sequences of strains used in this study.
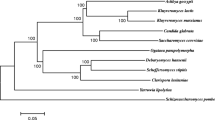
Sequences of the D1/D2 region of the LSU (26S) rDNA were retrieved from the CBS database for strains CBS 397, CBS 745, CBS 608, NCYC 2791 (CBS 712), NCYC 970 (CBS 2762), NCYC 2597 (CBS 6556) and NCYC 1424 (CBS 5795). The corresponding sequence from strains CBS 7858, NCYC 100, NCYC 111, NCYC 179, NCYC 587 and NCYC 2887 was generated de novo using the NL1 and NL4 primers as sequence of these strains was not available in databases. Reference sequence of type strains of K. marxianus (U94924) and K. lactis (U94922) were obtained from Genbank and used as standards. Sequences were trimmed to similar lengths and aligned using ClustalW on the EBI website (www.ebi.ac.uk). Alignments were displayed using Jalview and assembled to show the complete alignment of this region. The reference sequences show the G/A polymorphism (at position 100 in this alignment) that distinguishes K. lactis and K. marxianus. This alignment demonstrates that all the strains used in this study were correctly classified as K. marxianus isolates. (PPTX 551 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lane, M.M., Burke, N., Karreman, R. et al. Physiological and metabolic diversity in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 100, 507–519 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9606-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9606-x