Abstract
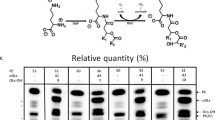
Thermo-tolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus is able to utilize a wide range of substrates, including xylose; however, the xylose fermentation ability is weak because of the redox imbalance under oxygen-limited conditions. Alleviating the intracellular redox imbalance through engineering the coenzyme specificity of NADPH-preferring xylose reductase (XR) and improving the expression of XR should promote xylose consumption and fermentation. In this study, the native xylose reductase gene (Kmxyl1) of the K. marxianus strain was substituted with XR or its mutant genes from Pichia stipitis (Scheffersomyces stipitis). The ability of the resultant recombinant strains to assimilate xylose to produce xylitol and ethanol at elevated temperature was greatly improved. The strain YZB014 expressing mutant PsXR N272D, which has a higher activity with both NADPH and NADH as the coenzyme, achieved the best results, and produced 3.55 g l−1 ethanol and 11.32 g l−1 xylitol—an increase of 12.24- and 2.70-fold in product at 42 °C, respectively. A 3.94-fold increase of xylose consumption was observed compared with the K. marxianus YHJ010 harboring KmXyl1. However, the strain YZB015 expressing a mutant PsXR K21A/N272D, with which co-enzyme preference was completely reversed from NADPH to NADH, failed to ferment due to the low expression. So in order to improve xylose consumption and fermentation in K. marxianus, both higher activity and co-enzyme specificity change are necessary.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Banat BMA, Nonklang S, Hoshida H, Akada R (2010) Random and targeted gene integrations through the control of non-homologous end joining in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Yeast 27:29–39
Banat IM, Marchant R (1995) Characterization and potential industrial applications of 5 novel, thermotolerant, fermentative, yeast strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:304–306
Banat IM, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) The use of a thermotolerant fermentative Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB3 yeast strain for ethanol production. Acta Biotechnol 16:215–223
Carter P (1986) Site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J 237:1–7
Cheng KK, Zhang JA, Chavez E, Li JP (2010) Integrated production of xylitol and ethanol using corncob. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:411–417
Ding X, Xia L (2006) Effect of aeration rate on production of xylitol from corncob hemicellulose hydrolysate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 133:263–270
Dmytruk OV, Dmytruk KV, Abbas CA, Voronovsky AY, Sibirny AA (2008) Engineering of xylose reductase and overexpression of xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase improves xylose alcoholic fermentation in the thermotolerant yeast Hansenula polymorpha. Microb Cell Fact 7:21
Fonseca GG, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Gombert AK (2008) The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and its biotechnological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:339–354
Hinman ND, Schell DJ, Riley CJ, Bergeron PW, Walter PJ (1992) Preliminary estimate of the cost of ethanol-production for Ssf technology. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 34–5:639–649
Hong J, Tamaki H, Akiba S, Yamamoto K, Kumagai H (2001) Cloning of a gene encoding a highly stable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Aspergillus niger and its expression in yeast. J Biosci Bioeng 92:434–441
Hong J, Wang Y, Kumagai H, Tamaki H (2007) Construction of thermotolerant yeast expressing thermostable cellulase genes. J Biotechnol 130:114–123
Jeffries TW, Jin YS (2004) Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:495–509
Jeppsson M, Bengtsson O, Franke K, Lee H, Hahn-Hagerdal R, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2006) The expression of a Pichia stipitis xylose reductase mutant with higher Km for NADPH increases ethanol production from xylose in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:665–673
Jin YS, Alper H, Yang YT, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Improvement of xylose uptake and ethanol production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae through an inverse metabolic engineering approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8249–8256
Karhumaa K, Fromanger R, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) High activity of xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase improves xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1039–1046
Karhumaa K, Garcia Sanchez R, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Comparison of the xylose reductase-xylitol dehydrogenase and the xylose isomerase pathways for xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 6:5
Katahira S, Ito M, Takema H, Fujita Y, Tanino T, Tanaka T, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2008) Improvement of ethanol productivity during xylose and glucose co-fermentation by xylose-assimilating S. cerevisiae via expression of glucose transporter Sut1. Enzym Microb Technol 43:115–119
Kim DM, Choi SH, Ko BS, Jeong GY, Jang HB, Han JG, Jeong KH, Lee HY, Won Y, Kim IC (2012) Reduction of PDC1 expression in S. cerevisiae with xylose isomerase on xylose medium. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:183–189
Kotter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Kumar S, Singh SP, Mishra IM, Adhikari DK (2009) Ethanol and xylitol production from glucose and xylose at high temperature by Kluyveromyces sp IIPE453. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1483–1489
Kuyper M, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2004) Minimal metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic xylose fermentation: a proof of principle. FEMS Yeast Res 4:655–664
Latif F, Rajoka MI (2001) Production of ethanol and xylitol from corn cobs by yeasts. Bioresour Technol 77:57–63
Lee SM, Jellison T, Alper HS (2012) Directed evolution of xylose isomerase for improved xylose catabolism and fermentation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5708–5716
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lulu L, Ling Z, Dongmei W, Xiaolian G, Hisanori T, Hidehiko K, Jiong H (2013) Identification of a Xylitol Dehydrogenase Gene from Kluyveromyces marxianus NBRC1777. Mol Biotechnol 53:159–169
Margaritis A, Bajpai P (1982) Direct Fermentation of d-Xylose to Ethanol by Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1039–1041
Matsumoto T, Takahashi S, Ueda M, Tanaka A, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2002) Preparation of high activity yeast whole cell bioctalysts by optimization of intracellular production of recombinant Rhizopus oryzae lipase. J Mol Cata B Enzym 17:143–149
Olofsson K, Runquist D, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Liden G (2011) A mutated xylose reductase increases bioethanol production more than a glucose/xylose facilitator in simultaneous fermentation and co-fermentation of wheat straw. AMB Express 1:4
Parachin NS, Bergdahl B, van Niel EW, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2011) Kinetic modelling reveals current limitations in the production of ethanol from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 13:508–517
Rodrigues RC, Kenealy WR, Jeffries TW (2011) Xylitol production from DEO hydrolysate of corn stover by Pichia stipitis YS-30. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1649–1655
Rodrussamee N, Lertwattanasakul N, Hirata K, Suprayogi, Limtong S, Kosaka T, Yamada M (2011) Growth and ethanol fermentation ability on hexose and pentose sugars and glucose effect under various conditions in thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(4):1573–1586. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3218-2
Sasaki M, Jojima T, Inui M, Yukawa H (2010) Xylitol production by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum under oxygen deprivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1057–1066
Shi R, Chiang VL (2005) Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. Biotechniques 39:519–525
Tantirungkij M, Nakashima N, Seki T, Yoshida T (1993) Construction of xylose assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 75:83–88
van Maris AJ, Winkler AA, Kuyper M, de Laat WT, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2007) Development of efficient xylose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: xylose isomerase as a key component. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:179–204
Watanabe S, Abu Saleh A, Pack SP, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein-engineered NADH-preferring xylose reductase from Pichia stipitis. Microbiology Sgm 153:3044–3054
Watanabe S, Pack SP, Saleh AA, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) The positive effect of the decreased NADPH-preferring activity of xylose reductase from Pichia stipitis on ethanol production using xylose-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1365–1369
Wilkins MR, Mueller M, Eichling S, Banat IM (2008) Fermentation of xylose by the thermotolerant yeast strains Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB2, IMB4, and IMB5 under anaerobic conditions. Process Biochem 43:346–350
Winer J, Jung CK, Shackel I, Williams PM (1999) Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal Biochem 270:41–49
Yanase S, Hasunuma T, Yamada R, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2010) Direct ethanol production from cellulosic materials at high temperature using the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus displaying cellulolytic enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:381–388
Zeng QK, Du HL, Wang JF, Wei DQ, Wang XN, Li YX, Lin Y (2009) Reversal of coenzyme specificity and improvement of catalytic efficiency of Pichia stipitis xylose reductase by rational site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechnol Lett 31:1025–1029
Zhang B, Zhang L, Wang D, Gao X, Hong J (2011) Identification of a xylose reductase gene in the xylose metabolic pathway of Kluyveromyces marxianus NBRC1777. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:2001–2010
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Tamaki Hisanori from Kagoshima University and Kumagai Hidehiko from Ishikawa Prefectural University for providing the K. marxianus YHJ010 and plasmids. We also thank Professor Sun Lianhong for all the useful discussions. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070028), the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CBA00801), and the Project-sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (WF2070000010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Li, L., Zhang, J. et al. Improving ethanol and xylitol fermentation at elevated temperature through substitution of xylose reductase in Kluyveromyces marxianus . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 305–316 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1230-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1230-5