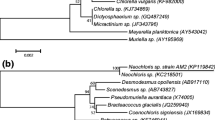
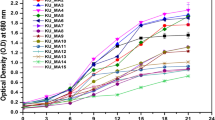
Abstract
The extremophile green alga Coccomyxa melkonianii SCCA 048 was investigated to evaluate its ability to grow in culture media with different pH. Specifically, Coccomyxa melkonianii was sampled in the Rio Irvi river (Sardinia, Italy) which is severely polluted by heavy metals as a result of abandoned mining activities. In this study, the strain was cultivated in growth media where the pH was kept fixed at the values of 4.0, 6.8 and 8.0, respectively. During the investigation, a significant phenotypic plasticity of this strain was observed. The strain grew well in the pH range 4.0–8.0, while the optimal value for its growth was 6.8. Furthermore, maximum lipid contents of about 24 and 22 %wt were achieved at the end of cultivation when using pH 4.0 and 8.0, respectively. Finally, the analysis of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) highlights the presence of suitable amounts of compounds which can be profitably exploited in the food, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industry. This aspect, coupled with the possibility of cultivating Coccomyxa melkonianii under extreme pH conditions in economic open ponds, makes this strain an interesting candidate for several biotechnological applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Hattori H, Hirano M (2007) Accumulation and antioxidant activity of secondary carotenoids in the aerial microalga Coelastrella striolata var. multistriata. Food Chem 100:656–661
An M, Mou S, Zhang X et al (2013) Temperature regulates fatty acid desaturases at a transcriptional level and modulates the fatty acid profile in the Antarctic microalga Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L. Bioresource Technology 134:151–157
Anitori RP (2012) Extremophiles: microbiology and biotechnology. Caister Academic Press, Poole
Azov Y (1982) Effect of pH on inorganic carbon uptake in algal cultures inorganic carbon uptake in algal cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:1300–1306
Barcytė D, Nedbalová L (2017) Coccomyxa: a dominant planktic alga in two acid lakes of different origin. Extremophiles 21:245–257
Bermejo E, Ruiz-Domínguez MC, Cuaresma M et al (2018) Production of lutein, and polyunsaturated fatty acids by the acidophilic eukaryotic microalga Coccomyxa onubensis under abiotic stress by salt or ultraviolet light. J Biosci Bioeng 125:669–675
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological Studies IV. Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species. University of Texas Publicatin No. 6318, Austin, pp 1–95
Bux F (2013) Biotechnological applications of microalgae: biodiesel and value-added products. CRC Press, Boca Ratón
Concas A, Ardau C, Cristini A et al (2006) Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site. Chemosphere 63:244–253
Concas A, Pisu M, Cao G (2014) Engineering aspects related to the use of microalgae for biofuel production and CO2 capture from flue gases. In: Cao G, Orrù R (eds) Current environmental issues and challenges. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 73–111
Concas A, Pisu M, Cao G (2015) Disruption of microalgal cells for lipid extraction through Fenton reaction: modeling of experiments and remarks on its effect on lipids composition. Chem Eng J 263:392–401
Concas A, Malavasi V, Costelli C et al. (2016) Autotrophic growth and lipid production of Chlorella sorokiniana in lab batch and BIOCOIL photobioreactors: experiments and modeling. Biores Technol 211:327–338
Cuaresma M, Garbayo I, Vega JM, Vílchez C (2006) Growth and photosynthetic utilization of inorganic carbon of the microalga Chlamydomonas acidophila isolated from Tinto river. Enzyme Microbial Technol 40:158–162
D’Alessandro EB, Antoniosi Filho NR (2016) Concepts and studies on lipid and pigments of microalgae: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 58:832–841
Darienko T, Gustavs L, Eggert A et al. (2015) Evaluating the species boundaries of green microalgae (Coccomyxa, Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) using integrative taxonomy and DNA barcoding with further implications for the species identification in environmental samples. PLoS One 10:1–31
Dixon C, Wilken LR (2018) Green microalgae biomolecule separations and recovery. Bioresour Bioprocess 5:14
Eibl JK, Corcoran JD, Senhorinho GNA et al (2014) Bioprospecting for acidophilic lipid-rich green microalgae isolated from abandoned mine site water bodies. AMB Express 4(4):7
Frau F, Medas D, Da Pelo S et al (2015) Environmental effects on the aquatic system and metal discharge to the mediterranean sea from a near-neutral zinc-ferrous sulfate mine drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:55
Frau F, Da Pelo S, Atzori R, Cidu R (2017) Impact on streams and sea water of a near-neutral drainage from a flooded mine in Sardinia, Italy. Proc Earth Planet Sci 17:213–216
Fuentes JL, Huss VAR, Montero Z et al (2016) Phylogenetic characterization and morphological and physiological aspects of a novel acidotolerant and halotolerant microalga Coccomyxa onubensis sp. nov. (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae). J Appl Phycol 28:3281–3282
Gensemer RW, Smith REH, Duthie HC, Schiff SL (1993) pH tolerance and metal toxicity in populations of the planktonic diatom Asterionella—influences of synthetic and natural dissolved organic carbon. Can J Fish and Aquat Sci 50:121–132
Gerloff-elias A, Spijkerman E, Pröschold T (2005) Effect of external pH on the growth, photosynthesis and photosynthetic electron transport of Chlamydomonas acidophila Negoro, isolated from an extremely acidic lake (pH 2.6). Plant Cell Environ 28:1218–1229
Ghozzi K, Zemzem M, Ben Dhiab R et al (2013) Screening of thermophilic microalgae and cyanobacteria from Tunisian geothermal sources. J Arid Environ 97:14–17
Gross W (2000) Ecophysiology of algae living in highly acidic environments. Hydrobiologia 433:31–37
Hargreaves JW, Whitton BA (1976) Effect of ph on growth of acid stream algae. Br Phycol J 11:215–223
Hirooka S, Higuchi S, Uzuka A et al (2014) Acidophilic green alga Pseudochlorella sp. YKT1 accumulates high amount of lipid droplets under a nitrogen-depleted condition at a low-pH. PLoS One 9:3–9
Hosikian A, Lim S, Halim R, Danquah MK (2010) Chlorophyll extraction from microalgae: a review on the process engineering aspects. Int J Chem Eng. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/391632
Iribar V (2004) Origin of neutral mine water in flooded underground mines: an appraisal using geochemical and hydrogeological methodologies. In: Proceedings, international mine water association symposium, Newcastle upon Tyne (University of Newcastle), pp 169–178
Khanra S, Mondal M, Halder G et al (2018) Downstream processing of microalgae for pigments, protein and carbohydrate in industrial application: a review. Food Bioprod Process 110:60–84
Kisková J, Perháčová Z, Vlčko L et al (2018) The bacterial population of neutral mine drainage water of Elizabeth’s Shaft (Slovinky, Slovakia). Curr Microbiol 75:988–996
Lane AE, Burris JE (1981) Effects of environmental pH on the internal pH of Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Scenedesmus quadricauda and Euglena mutabilis. Plant Physiol 68:439–442
Malavasi V, Cao G (2015) The Sardinian Culture Collection of Algae (SCCA): ex situ conservation of biodiversity and future technological applications. Nova Hedwig 101:273–283
Malavasi V, Škaloud P, Rindi F et al (2016) DNA-based taxonomy in ecologically versatile microalgae: a re-evaluation of the species concept within the coccoid green algal genus Coccomyxa (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta). PLoS One 11:1–25
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:217–232
Mishra SK, Suh WI, Farooq W et al (2014) Rapid quantification of microalgal lipids in aqueous medium by a simple colorimetric method. Biores Technol 155:330–333
Moser M, Weisse T (2011) Combined stress effect of pH and temperature narrows the niche width of flagellates in acid mining lakes. J Plankton Res 33:1023–1032
Navarro F, Forjàn E, Vàzquez M et al (2016) Microalgae as a safe food source for animals: nutritional characteristics of the acidophilic microalga Coccomyxa onubensis. Food Nutr Res 60:1–10
Navarro F, Forján E, Vázquez M et al (2017) Antimicrobial activity of the acidophilic eukaryotic microalga Coccomyxa onubensis. Phycol Res 65:38–43
Olaizola M (2003) Commercial development of microalgal biotechnology: from the test tube to the marketplace. Biomol Eng 20:459–466
Pasqualetti M, Tempesta S, Malavasi V et al (2015) Lutein production by Coccomyxa sp. SCCA048 isolated from a heavy metal-polluted river in Sardinia (Italy). J Environ Prot Ecol 16:1262–1272
Pulz O, Gross W (2004) Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:635–648
Rampelotto PH (2013) Extremophiles and extreme environments. Life 3:482–485
Richmond A, Hu Q (2013) Handbook of microalgal culture: biotechnology and applied phycology, 2nd edn. Wiley Blackwell, Oxford, pp 1–736
Ruiz-Domínguez MC, Vaquero I, Obregón V et al (2015) Lipid accumulation and antioxidant activity in the eukaryotic acidophilic microalga Coccomyxa sp. (strain onubensis) under nutrient starvation. J Appl Phycol 27:1099–1108
Sahu A, Pancha I, Jain D et al (2013) Fatty acids as biomarkers of microalgae. Phytochemistry 89:53–58
Scharer JM, Pettit CM, Kirkaldy JL, Bolduc L, Halbert BE, Chambers DB, Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration (2000) Leaching of metals from sulphide mine wastes at neutral pH. ICARD 2000 Proceedings from the fifth international conference on acid rock drainage, vol I. The Society, Littleton, Colo, pp 191–201
Schneider RDCDS, de de Moura Lima M, Hoeltz M et al (2018) Life cycle assessment of microalgae production in a raceway pond with alternative culture media. Algal Res 32:280–292
Skorupa DJ, Castenholz RW, Mazurie A et al (2014) In situ gene expression profiling of the thermoacidophilic alga Cyanidioschyzon in relation to visible and ultraviolet irradiance. Environ Microbiol 16:1627–1641
Slocombe SP, Zhang Q, Ross M et al (2015) Unlocking nature’s treasure-chest: screening for oleaginous algae. Sci Rep 5:1–17
Souza LS, Simioni C, Bouzon ZL et al (2017) Morphological and ultrastructural characterization of the acidophilic and lipid-producer strain Chlamydomonas acidophila LAFIC-004 (Chlorophyta) under different culture conditions. Protoplasma 254:1385–1398
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng 101:87–96
Steriti A, Rossi R, Concas A, Cao G (2014) A novel cell disruption technique to enhance lipid extraction from microalgae. Biores Technol 164:70–77
Talebi AF, Mohtashami SK, Tabatabaei M et al (2013) Fatty acids profiling: a selective criterion for screening microalgae strains for biodiesel production. Algal Res 2:258–267
Teoh ML, Phang SM, Chu WL (2012) Response of Antarctic, temperate, and tropical microalgae to temperature stress. J Appl Phycol 25:285–297
Vaquero I, Vázquez M, Ruiz-Domínguez MC, Vílchez C (2014) Enhanced production of a lutein-rich acidic environment microalga. J Appl Microbiol 116:839–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12428
Varshney P, Mikulic P, Vonshak A et al (2015) Extremophilic micro-algae and their potential contribution in biotechnology. Biores Technol 184:363–372
Verma V, Bhatti S, Huss VA, Colman B (2009) Photosynthetic inorganic carbon acquisition in an acid-tolerant, free-living species of Coccomyxa (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 45(4):847–854
Yun HS, Lee H, Park YT et al (2014) Isolation of novel microalgae from acid mine drainage and its potential application for biodiesel production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:2054–2064
Acknowledgments
The financial support of the COMISAR project (POR FESR 2014/2020 - Asse prioritario I “ricerca scientifica, sviluppo tecnologico e innovazione” Regione Autonoma della Sardegna, Italy) is gratefully acknowledged. One of us S.S. acknowledges the financial support obtained from the University of Cagliari during her Ph.D. program in Innovation Sciences and Technologies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Atomi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soru, S., Malavasi, V., Caboni, P. et al. Behavior of the extremophile green alga Coccomyxa melkonianii SCCA 048 in terms of lipids production and morphology at different pH values. Extremophiles 23, 79–89 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1062-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1062-3