Abstract
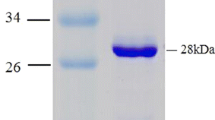
A novel alkylsulfatase gene, sdsAP, was cloned from a newly isolated bacterium Pseudomonas sp. S9. It encoded a protein of 675 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 74.9 kDa. The protein contained a typical N-terminal signal peptide of 41 amino acid residues, followed by a metallo-β-lactamase like domain at the N-terminus and a SCP-2-like domain at the C-terminus. This domain organization mode suggested that it belonged to the type III sulfatase. The mature alkylsulfatase was overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The optimal temperature and pH of the recombinant SdsAP were 70°C and 9.0, respectively. Notably, at optimal conditions, the purified recombinant SdsAP had a high specific activity of 23.25 μmol min−1 mg−1, a K m (app) of 264.3 μmol, and a V max (app) of 33.8 μmol min−1 mg−1 for SDS. Additionally, it still retained more than 90% activity after incubation at 65°C for 1 h, which was much different from other alkylsulfatases reported. The recombinant enzyme hydrolyzed the primary alkyl sulfate such as sodium octyl sulfate and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). It was a Zn2+-containing and Ca2+ activated alkylsulfatase. This is the first report to explore the various characteristics of the heterologous recombinant alkylsulfatase in details. These favorable properties could make SdsAP attractive to be useful in the degradation of SDS-containing waste.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud MM, Khleifat KM, Batarseh M, Tarawneha KA, Al-Mustafa A, Al-Madadhah M (2007) Different optimization conditions required for enhancing the biodegradation of linear alkylbenzosulfonate and sodium dodecyl sulfate surfactants by novel consortium of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Pantoea agglomerans. Enzyme Microbial Technol 41:432–439
Arunasri K, Sasikala C, Ramana CV, Süling J, Imhoff JF (2005) Marichromatium indicum sp. nov., a novel purple sulfur gammaproteobacterium from mangrove soil of Goa, India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:673–679
Bartholomew B, Dodgson KS, Gorham SD (1978) Purification and properties of the S1 secondary alkylsulphohydrolase of the detergent-degrading microorganism, Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J 169:659–667
Bateman TJ, Dodgson KS, White GF (1986) Primary alkylsulphatase activities of the detergent-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J 236:401–408
Berteau O, Guillot A, Benjdia A, Rabot S (2006) A new type of bacterial sulfatase reveals a novel maturation pathway in prokaryotes. J Biol Chem 281(32):22464–22470
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bryant RG, Jarvis J, Janda JM (1987) Use of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polymyxin B-sucrose medium for isolation of Vibrio vulnificus from shellfish. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(7):1556–1559
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
Claperon C, Rozenfeld R, Iturrioz X, Inguimbert N, Okada M, Roques B, Maigret B, Llorens-Cortes C (2008) Asp218 participates with Asp213 to bind a Ca2+ atom into the S1 subsite of aminopeptidase A: a key element for substrate specificity. Biochem J 416:37–46
Cloves JM, Dodgson KS, White GF, Fitzgerald JW (1980a) Specificity of P2 primary alkylsulphohydrolase induction in the detergent degrading bacterium Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J 185(1):13–21
Cloves JM, Dodgson KS, White GF, Fitzgerald JW (1980b) Purification and properties of the P2 primary alkylsulphohydrolase of the detergent-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J 185(1):23–31
Cserháti T, Forgács E, Oros G (2002) Biological activity and environmental impact of anionic surfactants. Environ Int 28:337–348
Danielsen EM, Noren O, Sjostrom H, Ingram J, Kenny AJ (1980) Aspartate aminopeptidase: purification by immunoadsorbent chromatography and properties of the detergent- and proteinase-solubilized forms. Biochem J 189:591–603
Davison J, Brunel F, Phanopoulos A, Prozzi D, Terpstra P (1992) Cloning and sequencing of Pseudomonas genes determining sodium dodecyl sulfate biodegradation. Gene 114:19–24
Dhouib A, Hamad N, Hassairi I, Sayadi S (2003) Degradation of anionic surfactants by Citrobacter braakii. Process Biochem 38:1245–1250
Dodgson KS, White GF (1983) Some microbial enzymes involved in the biodegradation of sulphated surfactants. Top Enzyme Ferment Biotechnol 7:90–155
Dodgson KS, Fitzgerald JW, Payne WJ (1974) Chemically defined inducers of alkylsulphatases present in Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J 138:53–62
Gao ZM, Ruan LW, Chen XL, Zhang YZ, Xu X (2010) A novel salt-tolerant endo-beta-1,4-glucanase Cel5A in Vibrio sp. G21 isolated from mangrove soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(4):1373–1382
Goto Y, Hattori A, Mizutani S, Tsujimoto M (2007) Aspartic acid 221 is critical in the calcium-induced modulation of the enzymatic activity of human aminopeptidase A. J Biol Chem 282:37074–37081
Hagelueken G, Adams TM, Wiehlmann L, Widow U, Kolmar H, Tümmler B, Heinz DW, Schubert W (2006) The crystal structure of SdsA1, an alkylsulfatase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, defines a third class of sulfatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(20):7631–7636
Jiang YX, Zheng TL, Tian Y (2006) Research on mangrove soil microorganisms: past, present and future. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 46(5):848–851
Jovcic B, Venturi V, Davison J, Topisirovic L, Kojic M (2010) Regulation of the sdsA alkyl sulfatase of Pseudomonas sp. ATCC19151 and its involvement in degradation of anionic surfactants. J Appl Microbiol 109:1076–1083
Kahnert A, Kertesz MA (2000) Characterization of a sulfur-regulated oxygenative alkylsulfatase from Pseudomonas putida S-313. J Biol Chem 275(41):31661–31667
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larsen KS, Auld DS (1989) Carboxypeptidase A: mechanism of zinc inhibition. Biochemistry 28:9620–9625
Lillis V, Dodgson KS, White GF, Payne WJ (1983) Initiation of activation of a preemergent herbicide by a novel alkylsulfatase of Pseudomonas putida FLA. Appl Environ Microbiol 46(5):988–994
Lin Y, Wu X, Deng Z, Wang J, Zhou S, Vrijmoed LL, Jones EB (2002) The metabolites of the mangrove fungus Verruculina enalia No. 2606 from a salt lake in the Bahamas. Phytochemistry 59:469–471
Marquordt C, Fang QH, Will E, Peng JH, Figura K, Dierks T (2003) Posttranslational modification of serine to formylglycine in bacterial sulfatases. J Biol Chem 278(4):2212–2218
Mikoulinskaia GV, Odinokova IV, Zimin AA, Lysanskaya VY, Feofanov SA, Stepnaya OA (2009) Identification and characterization of the metal ion-dependent l-alanoyl-d-glutamate peptidase encoded by bacteriophage T5. FEBS J 276:7329–7342
Pogorevc M, Faber K (2003) Purification and characterization of an inverting stereo- and enantioselective sec-alkylsulfatase from the gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus ruber DSM 44541. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(5):2810–2815
Rusconi F, Valton E, Nguyen R, Dufourc E (2001) Quantification of sodium dodecyl sulfate in microliter-volume biochemical samples by visible light spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 295:31–37
Shukor MY, Husin WSW, Rahman MFA, Shamaan NA, Syed MA (2009) Isolation and characterization of an SDS-degrading Klebsiella oxytoca. J Environ Biol 30(1):129–134
Singh KL, Kumar A, Kumar A (1998) Short communication: Bacillus cereus capable of degrading SDS shows growth with a variety of detergents. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 14(5):777–779
Syn CK, Swarup S (2000) A scalable protocol for the isolation of large-sized genomic DNA within an hour from several bacteria. Anal Biochem 278:86–90
Takeuchi M, Hatano K (1998) Gordonia rhizosphera sp. nov. isolated from the mangrove rhizosphere. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:907–912
Tsujimoto M, Goto Y, Maruyama M, Hattori A (2008) Biochemical and enzymatic properties of the M1 family of aminopeptidases involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Heart Fail Rev 13:285–291
Tuteja R (2005) Type I signal peptidase: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 441(2):107–111
Wang J, Cooper MD (1993) Histidine residue in the zinc-binding motif of aminopeptidase A is critical for enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1222–1226
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
White GF (1991) Enantiometric enrichment of R(−)-alkan-2-ols using a stereospecific alkylsulphatase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35(3):312–316
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of No. 200805050 from the Marine Scientific Research Special Foundation for Public Sector Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by T. Matsunaga.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
792_2011_357_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Fig. S1 Determination of the molecular weight of SdsAP. Standard proteins: (1) Catalase (206 kDa), (2) Adolase (177 kDa), (3) Albumin (63.5 kDa), (4) Ovalbumin (48 kDa). The arrow indicates the elution volume of SdsAP. Gel filtration was performed on a column (1 cm × 100 cm) of Sepharose G-150. 0.1 M NaH2PO4-Na2HPO4 buffer (pH 7.0) was used as the elution buffer. (DOC 39 kb)
792_2011_357_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Supplementary Fig. S2 Effect of temperature and pH on stability of SDS. (A) Temperature effect on the stability of SDS. (B) pH effect on the stability of SDS. Temperature stability was determined by measuring the residual amount of 500 μl of 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 9.0) containing SDS with a final concentration of 0.01% (w/v) at different temperatures (30–90°C) for 1 h. pH stability was determined by measuring the residual amount of 500 μl of different pHs (pH 4.0-11.0) containing SDS with a final concentration of 0.01% (w/v) at 70°C for 1 h. pH profiles were mearsured in 50 mM of different buffers: acetic acid buffer (pH 4.0-5.0), sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.0-7.0), Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0 and pH 9.0), and glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.0-11.0). The relative activity was defined as the percentage of amount determined with respect to that measured 500 μl distilled water containing SDS with a final concentration of 0.01% (w/v) at room temperature for 1 h. (DOC 122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, M., Ruan, L., Li, F. et al. Heterologous expression and characterization of a recombinant thermostable alkylsulfatase (sdsAP). Extremophiles 15, 293–301 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0357-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0357-4