Abstract
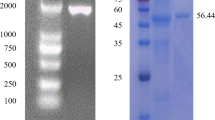
Although cellulases have been isolated from various microorganisms, no functional cellulase gene has been reported in the Vibrio genus until now. In this report, a novel endo-β-1,4-glucanase gene, cel5A, 1,362 bp in length, was cloned from a newly isolated bacterium, Vibrio sp. G21. The deduced protein of cel5A contains a catalytic domain of glycosyl hydrolase family 5 (GH5), followed by a cellulose binding domain (CBM2). The GH5 domain shows the highest sequence similarity (69%) to the bifunctional beta 1,4-endoglucanase/cellobiohydrolase from Teredinibacter turnerae T7902. The mature Cel5A enzyme was overexpressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity. The optimal pH and temperature of the recombinant enzyme were determined to be 6.5–7.5 and 50°C, respectively. Cel5A was stable over a wide range of pH and retained more than 90% of total activity even after treatment in pH 5.5–10.5 for 1 h, indicating high alkali resistance. Moreover, the enzyme was activated after pretreatment with mild alkali, a novel characteristic that has not been previously reported in other cellulases. Cel5A also showed a high level of salt tolerance. Its activity rose to 1.6-fold in 0.5 M NaCl and remained elevated even in 4 M NaCl. Further experimentation demonstrated that the thermostability of Cel5A was improved in 0.4 M NaCl. In addition, Cel5A showed specific activity towards β-1,4-linkage of amorphous region of lignocellulose, and the main final hydrolysis product of carboxymethylcellulose sodium and cellooligosaccharides was cellobiose. As an alkali-activated and salt-tolerant enzyme, Cel5A is an ideal candidate for further research and industrial applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunasri K, Sasikala C, Ramana CV, Süling J, Imhoff JF (2005) Marichromatium indicum sp. nov., a novel purple sulfur gammaproteobacterium from mangrove soil of Goa, India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:673–679
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:233–238
Ekborg NA, Morrill W, Burgoyne AM, Li L, Distel DL (2007) CelAB, a multifunctional cellulase encoded by Teredinibacter turnerae T7902, a culturable symbiont isolated from the wood-boring marine bivalve Lyrodus pedicallatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(23):7785–7788
Feng Y, Duan CJ, Pang H, Mo XC, Wu CF, Yu Y, Hu YL, Wei J, Tang JL, Feng JX (2007) Cloning and identification of novel cellulase genes from uncultured microorganisms in rabbit cecum and characterization of the expressed cellulases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(2):319–328
Gomes J, Steiner W (2004) The biocatalytic potential of extremophiles and extremozymes. Food Tech Biotechnol 42(4):223–235
Hakamada Y, Koike K, Yoshimatsu T, Mori H, Kobayashi T, Ito S (1997) Thermostable alkaline cellulase from an alkaliphilic isolate, Bacillus sp. KSM-S237. Extremophiles 1(3):151–156
Hirasawa K, Uchimura K, Kashiwa M, Grant WD, Ito S, Kobayashi T, Horikoshi K (2006) Salt-activated endoglucanase of a strain of alkaliphilic Bacillus agaradhaerens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 89(2):211–219
Hong K, Yan B (2008) Uncultured microorganisms in Hainan mangrove soil: diversity and functional genes. In: Liu SJ, Drake HL (eds) Microbes and the environment: perspective and challenges. Beijing, China, pp 52–58
Hyde KD, Lee SY (1995) Ecology of mangrove fungi and their role in nutrient cycling: what gaps occur in our knowledge? Hydrobiologia 295:107–118
Ito S (1997) Alkaline cellulases from alkaliphilic Bacillus: enzymatic properties, genetics, and application to detergents. Extremophiles 1(2):61–66
Ito S, Kobayashi T, Ara K, Ozaki K, Kawai S, Hatada Y (1998) Alkaline detergent enzymes from alkaliphiles: enzymatic properties, genetics, and structures. Extremophiles 2(3):185–190
Jiang YX, Zheng TL, Tian Y (2006) Research on mangrove soil microorganisms: past, present and future. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 46(5):848–851
Johnson KG, Lanthier PH, Gochnauer MB (1986) Studies of two strains of Actinopolyspora halophilia, an extremely halophilic actinomycete. Arch Microbiol 143:370–378
Jung ED, Lao G, Irwin D, Barr BK, Benjamin A, Wilson DB (1993) DNA sequences and expression in Streptomyces lividans of an exoglucanase gene and an endoglucanase gene from Thermomonospora fusca. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(9):3032–3043
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li YC, Irwin D, Wilson DB (2007) Processivity, substrate binding, and mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis by Thermobifida fusca Cel9A. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(10):3165–3172
Li X, Dong X, Zhao C, Chen Z, Chen F (2003) Isolation and some properties of cellulose-degrading Vibrio sp. LX-3 with agar-liquefying from soil. World J Micobiol Biotechnol 19:375–379
Liebl W, Ruile P, Bronnenmeier K, Riedel K, Lottspeich F, Greif I (1996) Analysis of a Thermotoga maritima DNA fragment encoding two similar thermostable cellulases, CelA and CelB, and characterization of the recombinant enzymes. Microbiology 142(9):2533–2542
Lin Y, Wu X, Deng Z, Wang J, Zhou S, Vrijmoed LL, Jones EB (2002) The metabolites of the mangrove fungus Verruculina enalia No. 2606 from a salt lake in the Bahamas. Phytochemistry 59:469–471
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(3):506–577
Ma XD, Ke T, Xiong L, Yan H, Ma LX (2007) A new plate method for screening of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes and their producing microorganisms. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 47(6):1102–1104
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Ruby EG, Urbanowski M, Campbell J, Dunn A, Faini M, Gunsalus R, Lostroh P, Lupp C, McCann J, Millikan D, Schaefer A, Stabb E, Stevens A, Visick K, Whistler C, Greenberg EP (2005) Complete genome sequence of Vibrio fischeri: a symbiotic bacterium with pathogenic congeners. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:3004–3009
Pointing SB, Buswell JA, Jones EBG, Vrijmoed LLP (1999) Extracellular cellulolytic enzyme profiles of five lignicolous mangrove fungi. Mycol Res 103:696–700
Syn CK, Swarup S (2000) A scalable protocol for the isolation of large-sized genome DNA within an hour from several bacteria. Anal Biochem 278:86–90
Takeuchi M, Hatano K (1998) Gordonia rhizosphera sp. nov. isolated from the mangrove rhizosphere. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:907–912
Teather RM, Wood PJ (1982) Use of Congo-red polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:777–782
Thompson FL, Gevers D, Thompson CC, Dawyndt P, Naser S, Hoste B, Munn CB, Swings J (2005) Phylogeny and molecular identification of Vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5107–5115
Voget S, Steele HL, Streit WR (2006) Characterization of a metagenome-derived halotolerant cellulose. J Biotechnol 126:26–36
Vreeland RH, Piselli AF Jr, McDonnough S, Meyers SS (1998) Distribution and diversity of halophilic bactria in a subsurface salt formation. Extremophiles 2:321–331
Watson BJ, Zhang HT, Longmire AG (2009) Processive endoglucanase mediate degradation of cellulose by Saccharophagus degradans. J Bacteriol 191(18):5697–5705
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wood TM (1988) Preparation of crystalline, amorphous, and dyed cellulase substrates. Mthods Enzymol 160:19–25
Yan B, Hong K, Yu Z (2006) Archaeal communities in mangrove soil characterized by 16S rRNA gene colones. J Microbiol 44:566–571
Yang ZY, Chen RZ, Yang F, Xu X (2001) Cloning and DNA sequencing of Bacillus pumilus endo-1, 4-beta-glucanase gene. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 41:76–81
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of State Oceanic Administration HE 09302(1)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Ruan, L., Chen, X. et al. A novel salt-tolerant endo-β-1,4-glucanase Cel5A in Vibrio sp. G21 isolated from mangrove soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87, 1373–1382 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2554-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2554-y