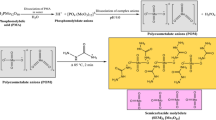
Abstract
In recent years, an increasing number of studies has demonstrated that redox polymers can be used in simple and effective electrochemical sensing platforms due to their fast electron transfer and electrocatalytic ability. To develop more sensitive and selective electrochemical (bio)sensors, the electrocatalytic properties of redox polymers and the electrical, mechanical, and catalytic properties of various nanomaterials are combined. This review aims to summarize and contribute to the development of (bio)sensors based on polyphenazine or polytriphenylmethane redox polymers combined with nanomaterials, including carbon-based nanomaterials, metal/metal oxide, and semiconductor nanoparticles. The synthesis, preparation, and modification of these nanocomposites is presented and the contribution of each material to the performance of (bio)sensor has been be examined. It is explained how the combined use of these redox polymers and nanomaterials as a sensing platform leads to improved analytical performance of the (bio)sensors. Finally, the analytical performance characteristics and practical applications of polyphenazine and polytriphenylmethane redox polymer/nanomaterial–based electrochemical (bio)sensors are compared and discussed.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruff A (2017) Redox polymers in bioelectrochemistry: common playgrounds and novel concepts. Curr Opin Electrochem 5:66–73
Yuan M, Minteer SD (2019) Redox polymers in electrochemical systems: from methods of mediation to energy storage. Curr Opin Electrochem 15:1–6
Barsan MM, Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2015) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: a review. Anal Chim Acta 881:1–23
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE, Schmidt HL (1999) Electropolymerized azines: a new group of electroactive polymers. Electroanal 11(3):149–155
Ameer Q, Adeloju SB (2009) Development of a potentiometric catechol biosensor by entrapment of tyrosinase within polypyrrole film. Sens Actuat B-Chem 140:5–11
Shrivastava S, Jadon N, Jain R (2016) Next-generation polymer nanocomposite-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 82:55–67
Aydemir N, Malmström J, Travas-Sejdic J (2016) Conducting polymer based electrochemical biosensors. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(12):8264–8277
El-Said WA, Abdeslhakour M, Choi JH, Choi JW (2020) Application of conducting polymer nanostructures to electrochemical biosensors. Molecules 25(2):307
Lakard B (2020) Electrochemical biosensors based on conducting polymers: a review. Appl Sci 10(18):6614
El Rhazi M, Majid S, Elbasri M, Salih FE, Oularbi L, Lafdi K (2018) Recent progress in nanocomposites based on conducting polymer: application as electrochemical sensors. Int Nano Lett 8(2):79–99
Gholivand MB, Ahmadi E, Haseli M (2017) A novel voltammetric sensor for nevirapine, based on modified graphite electrode by MWCNs/poly(methylene blue)/gold nanoparticle. Anal Biochem 527:4–12
da Silva W, Brett CMA (2020) Novel biosensor for acetylcholine based on acetylcholinesterase/poly (neutral red)–deep eutectic solvent/Fe2O3 nanoparticle modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 872:114050
Liu C, Huang J, Wang L (2018) Electrochemical synthesis of a nanocomposite consisting of carboxy-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes, polythionine and platinum nanoparticles for simultaneous voltammetric determination of myricetin and rutin. Microchim Acta 185(9):414
Pauliukaite R, Ghica ME, Barsan MM, Brett CMA (2010) Phenazines and polyphenazines in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Lett 43(10–11):1588–1608
Ganesh PS, Swamy BK (2015) Sodium dodecyl sulphate/poly (brilliant blue)/multi walled carbon nanotube modified carbon paste electrode for the voltammetric resolution of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. J Anal Bioanal Tech 6(6):1
da Silva W, Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2019) Novel nanocomposite film modified electrode based on poly(brilliant cresyl blue)-deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotubes and its biosensing applications. Electrochim Acta 317:766–777
Ding M, Zhou Y, Liang X, Zou H, Wang Z, Wang M, Ma J (2016) An electrochemical sensor based on graphene/poly(brilliant cresyl blue) nanocomposite for determination of epinephrine. J Electroanal Chem 763:25–31
da Silva W, Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2019) Choline oxidase inhibition biosensor based on poly (brilliant cresyl blue)–deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube modified electrode for dichlorvos organophosphorus pesticide. Sens Actuat B-Chem 298:126862
Barsan MM, Pifferi V, Falciola L, Brett CMA (2016) New CNT/poly (brilliant green) and CNT/poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) based electrochemical enzyme biosensors. Anal Chim Acta 927:35–45
da Silva W, Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2020) Biotoxic trace metal ion detection by enzymatic inhibition of a glucose biosensor based on a poly (brilliant green)–deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube modified electrode. Talanta 208:120427
He S, He P, Zhang X, Zhang X, Li C, Dong F, Leia H, Liu D (2017) Poly (bromocresol green)/carbon quantum dots modified electrode for the simultaneous electrochemical determination of guanine and adenine. J Electroanal Chem 806:158–165
Shrestha S, Mascarenhas RJ, D’Souza OJ, Satpati AK, Mekhalif Z, Dhason A, Martis P (2016) Amperometric sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotube and poly (bromocresol purple) modified carbon paste electrode for the sensitive determination of L-tyrosine in food and biological samples. J Electroanal Chem 778:32–40
Hosu O, Barsan MM, Cristea C, Săndulescu R, Brett CMA (2017) Nanocomposites based on carbon nanotubes and redox-active polymers synthesized in a deep eutectic solvent as a new electrochemical sensing platform. Microchim Acta 184(10):3919–3927
Gorle DB, Kulandainathan MA (2016) Electrochemical sensing of dopamine at the surface of a dopamine grafted graphene oxide/poly(methylene blue) composite modified electrode. RSC Adv 6(24):19982–19991
Barsan MM, Toledo CT, Brett CMA (2015) New electrode architectures based on poly(methylene green) and functionalized carbon nanotubes: characterization and application to detection of acetaminophen and pyridoxine. J Electroanal Chem 736:8–15
Lin KC, Syu JJ, Chen SM (2015) A hybrid nanocomposite of poly(neutral red) and hemoglobin codeposited on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for determination of hydrogen peroxide. Int J Electrochem Sci 10:6886–6899
Shervedani RK, Amini A (2015) Preparation of graphene/Nile blue nanocomposite: application for oxygen reduction reaction and biosensing. Electrochim Acta 173:354–363
Yang S, Ding S, Li L, Sun Q, Yang J, Cao Q (2017) Hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on graphene-toluidine blue/HRP-poly (toluidine blue). Int J Electrochem Sci 12:10838–10849
Khan AAP, Khan A, Alam MM, Asiri AM, Uddin J, Rahman MM (2019) SDBS-functionalized MWCNT/poly (o-toluidine) nanowires modified glassy carbon electrode as a selective sensing platform for Ce3+ in real samples. J Mol Liq 279:392–399
Wang F, Gong W, Wang L, Chen Z (2015) Enhanced amperometric response of a glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase based bienzyme glucose biosensor modified with a film of polymerized toluidine blue containing reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 182(11–12):1949–1956
Dai J, Deng D, Yuan Y, Zhang J, Deng F, He S (2016) Amperometric nitrite sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and poly (toluidine blue). Microchim Acta 183(5):1553–1561
Palakollu VN, Karpoormath R (2018) Enhanced electrochemical sensing of dopamine based on carboxylic acid functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly (toluidine blue) composite. Synth Met 245:87–95
Li X, Kan X (2019) A boronic acid carbon nanodots/poly (thionine) sensing platform for the accurate and reliable detection of NADH. Bioelectrochem 130:107344
Ghica ME, Ferreira GM, Brett CMA (2015) Poly (thionine)-carbon nanotube modified carbon film electrodes and application to the simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and dipyrone. J Solid State Electrochem 19(9):2869–2881
Pandey SK, Sachan S, Singh SK (2019) Electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified with electrodeposited thionine and horseradish peroxidase for hydrogen peroxide sensing and inhibitive measurement of chromium. Mater Sci Technol 2(3):676–686
Liu Y, Song N, Ma Z, Zhou K, Gan Z, Gao Y, Tang S, Chen C (2019) Synthesis of a poly (N-methylthionine)/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for the detection of hydroquinone. Mater Chem Phys 223:548–556
Dalkıran B, Fernandes IPG, David M, Brett CMA (2020) Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of poly(thionine)-deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube–modified electrodes and application to electrochemical sensing. Microchim Acta 187(11):1–11
Mittal G, Dhand V, Rhee KY, Park SJ, Lee WR (2015) A review on carbon nanotubes and graphene as fillers in reinforced polymer nanocomposites. J Ind Eng Chem 21:11–25
Esumi K, Ishigami M, Nakajima A, Sawada K, Honda H (1996) Chemical treatment of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 34:279–281
Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2010) The influence of carbon nanotubes and polyazine redox mediators on the performance of amperometric enzyme biosensors. Microchim Acta 170:257–265
Narang J, Malhotra N, Singhal C, Bhatia R, Kathuria V, Jain M (2017) Graphene nanoflakes on transparent glass electrode sensor for electrochemical sensing of anti-diabetic drug. Bioproc Biosystems Eng 40(4):537–548
Iijima S (2002) Carbon nanotubes: past, present, and future. Phys B Condens Matter 323(1–4):1–5
Zaporotskova IV, Boroznina NP, Parkhomenko YN, Kozhitov LV (2016) Carbon nanotubes: sensor properties. Mod Electron Mater 2(4):95–105
Ke Q, Wang J (2016) Graphene-based materials for supercapacitor electrodes–a review. J Mater 2(1):37–54
Suvarnaphaet P, Pechprasarn S (2017) Graphene-based materials for biosensors: a review. Sensors 17(10):2161
Salavagione HJ, Díez-Pascual AM, Lázaro E, Vera S, Gómez-Fatou MA (2014) Chemical sensors based on polymer composites with carbon nanotubes and graphene: the role of the polymer. J Mater Chem A 2(35):14289–14328
Shareena TPD, McShan D, Dasmahapatra AK, Tchounwou PB (2018) A review on graphene-based nanomaterials in biomedical applications and risks in environment and health. Nano-Micro Lett 10(3):53
Li H, Kang Z, Liu Y, Lee ST (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22(46):24230–24253
Xu XY, Ray R, Gu YL, Ploehn HJ, Gearheart L, Raker K, Scrivens WA (2014) Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc 126:12736–12737
Bairagi PK, Verma N (2018) Electrochemically deposited dendritic poly (methyl orange) nanofilm on metal-carbon-polymer nanocomposite: a novel non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor for cholesterol. J Electroanal Chem 814:134–143
Pandey I, Bairagi PK, Verma N (2018) Electrochemically grown polymethylene blue nanofilm on copper-carbon nanofiber nanocomposite: an electrochemical sensor for creatinine. Sens Actuat B-Chem 277:562–570
Tomé LIN, Brett CMA (2019) Polymer/iron oxide nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrodes for the enhanced detection of epinephrine. Electroanal 31(4):704–710
Liu T, Luo Y, Wang W, Kong L, Zhu J, Tan L (2015) Non-enzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide based on Fenton-type reaction on poly(azure A)-chitosan/Cu modified electrode. Electrochim Acta 182:742–750
Liu T, Luo Y, Zhu J, Kong L, Wang W, Tan L (2016) Non-enzymatic detection of glucose using poly (azure A)-nickel modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 156:134–140
Jimenez-Perez R, Gonzalez-Rodriguez J, González-Sánchez MI, Gómez-Monedero B, Valero E (2019) Highly sensitive H2O2 sensor based on poly (azure A)-platinum nanoparticles deposited on activated screen printed carbon electrodes. Sens Actuat B-Chem 298:126878
Ahammad AS, Shaikh AA, Jessy NJ, Akter T, Al Mamun A, Bakshi PK (2015) Hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase onto a gold nanoparticles-adsorbed poly (brilliant cresyl blue) film. J Electrochem Soc 162(3):B52–B56
Sangeetha NS, Narayanan SS (2019) Amperometric H2O2 sensor based on gold nanoparticles/poly(celestine blue) nanohybrid film. SN Appl Sci 1(7):732
Koyun O, Sahin Y (2018) Voltammetric determination of nitrite with gold nanoparticles/poly (methylene blue)-modified pencil graphite electrode: application in food and water samples. Ionics 24(10):3187–3197
Saritha D, Gupta VK, Reddy AVB, Agarwal S, Moniruzzaman M, Anitha K, Madhavi G (2019) Development of a simple, selective, stable and ultrasensitive poly (safranine/nano NiO) modified carbon paste electrode for selective detection of rutin in buckwheat and green tea samples. Int J Electrochem Sci 14:10093–10110
Chai R, Kan X (2019) Au-polythionine nanocomposites: a novel mediator for bisphenol A dual-signal assay based on imprinted electrochemical sensor. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(17):3839–3847
Huang Q, Zhao Z, Nie D, Jiang K, Guo W, Fan K, Zhang Z, Meng J, Wu Y, Han Z (2019) Molecularly imprinted poly (thionine)-based electrochemical sensing platform for fast and selective ultratrace determination of patulin. Anal Chem 91(6):4116–4123
Yang S, Bai C, Teng Y, Zhang J, Peng J, Fang Z, Xu W (2019) Study of horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide bi-analyte sensor with boronate affinity-based molecularly imprinted film. Can J Chem 97(12):833–839
Huang J, Xu W, Gong Y, Weng S, Lin X (2016) Selective and reliable electrochemical sensor based on polythionine/AuNPs composites for epinephrine detection in serum. Int J Electrochem Sci 11(10):8193–8203
Chen B, Zhang Y, Lin L, Chen H, Zhao M (2020) Au nanoparticles@ metal organic framework/polythionine loaded with molecularly imprinted polymer sensor: preparation, characterization, and electrochemical detection of tyrosine. J Electroanal Chem 863:114052
Zhao C, Jiang Z, Cai X, Lin L, Lin X, Weng S (2015) Ultrasensitive and reliable dopamine sensor based on polythionine/AuNPs composites. J Electroanal Chem 748:16–22
da Silva W, Queiroz AC, Brett CMA (2020) Nanostructured poly(phenazine)/Fe2O3 nanoparticle film modified electrodes formed by electropolymerization in ethaline-deep eutectic solvent. Microscopic and electrochemical characterization. Electrochim Acta:347–136284
da Silva W, Queiroz AC, Brett CMA (2020) Poly (methylene green)-Ethaline deep eutectic solvent/Fe2O3 nanoparticle modified electrode electrochemical sensor for the antibiotic dapsone. Sens Actuat B-Chem 128747
Dalkiran B, Brett CMA (2021) A novel nanostructured poly(thionine)-deep eutectic solvent/CuO nanoparticle film modified disposable pencil graphite electrode for determination of acetaminophen in the presence of ascorbic acid. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:1149–1157
Zeng S, Yong KT, Roy I, Dinh XQ, Yu X, Luan F (2011) A review on functionalized gold nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Plasmonics 6(3):491–506
El-Zahry MR, Ali MF (2019) Enhancement effect of reduced graphene oxide and silver nanocomposite supported on poly brilliant blue platform for ultra-trace voltammetric analysis of rosuvastatin in tablets and human plasma. RSC Adv 9(13):7136–7146
Bollella P, Sharma S, Cass AEG, Antiochia R (2019) Microneedle-based biosensor for minimally-invasive lactate detection. Biosens Bioelectron 123:152–159
Topçu E, Dağcı K, Alanyalıoğlu M (2016) Free-standing graphene/poly (methylene blue)/AgNPs composite paper for electrochemical sensing of NADH. Electroanal 28(9):2058–2069
Bollella P, Sharma S, Cass AEG, Antiochia R (2019) Minimally-invasive microneedle-based biosensor array for simultaneous lactate and glucose monitoring in artificial interstitial fluid. Electroanal 31(2):374–382
Sahin M, Ayranci E (2015) Electrooxidation of NADH on modified screen-printed electrodes: effects of conducting polymer and nanomaterials. Electrochim Acta 166:261–270
Devi CL, Narayanan SS (2019) Poly(amido amine) dendrimer/silver nanoparticles/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly (neutral red)-modified electrode for electrochemical determination of paracetamol. Ionics 25(5):2323–2335
Bilgi M, Ayranci E (2018) Development of amperometric biosensors using screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with conducting polymer and nanomaterials for the analysis of ethanol, methanol and their mixtures. J Electroanal Chem 823:588–592
Mazar FM, Alijanianzadeh M, Molaeirad A, Heydari P (2017) Development of novel glucose oxidase immobilization on graphene/gold nanoparticles/poly neutral red modified electrode. Process Biochem 56:71–80
Chang Z, Gao Z (2018) Study of the enzyme-free glucose biosensor based on Ni2+@ poly (neutral red) hybrid nanocomposites (Ni2+@PNR HN)/MWCNTs/Nafion modified electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:1754–1772
George JM, Antony A, Mathew B (2018) Metal oxide nanoparticles in electrochemical sensing and biosensing: a review. Microchim Acta 185(7):358
Zhang H, Han J, Yang B (2010) Structural fabrication and functional modulation of nanoparticle–polymer composites. Adv Funct Mater 20(10):1533–1550
Ravi Shankaran D, Uehara N, Kato T (2003) A metal dispersed sol-gel biocomposite amperometric glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 18:721–728
Dalkiran B, Erden PE, Kiliç E (2017) Amperometric biosensors based on carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes-metal oxide nanoparticles-7, 7, 8, 8-tetracyanoquinodimethane composite for the determination of xanthine. Talanta 167:286–295
Ran G, Chen X, Xia Y (2017) Electrochemical detection of serotonin based on a poly (bromocresol green) film and Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a chitosan matrix. RSC Adv 7(4):1847–1851
Tomé LIN, Baião V, da Silva W, Brett CMA (2018) Deep eutectic solvents for the production and application of new materials. Appl Mater Today 10:30–50
Abad-Gil L, Procopio JR, Brett CMA (2021) Binary and ternary deep eutectic solvent mixtures: influence on methylene blue electropolymerisation. Electrochem Commun 124:106967
Acknowledgements
B. Dalkiran thankfully acknowledges the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK 2219) for a postdoctoral fellowship.
Funding
The authors thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), Portugal, project PTDC/QEQ-QAN/2201/2014, in the framework of Project 3599-PPCDT, co-financed by the European Community Fund FEDER), and CEMMPRE, project UIDB/EMS/00285/2020 by FEDER funds through the program COMPETE – Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade, and by national funds through FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalkiran, B., Brett, C.M.A. Polyphenazine and polytriphenylmethane redox polymer/nanomaterial–based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Microchim Acta 188, 178 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04821-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04821-1