Abstract
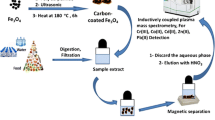
The authors show that the fungus Boletus edulis loaded with γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles is a viable sorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of trace levels of Co(II) and Sn(II). The surface structure of immobilized magnetized B. edulis was characterized by FT-IR, SEM and EDX. Experimental parameters were optimized. Following elution with 1 M HCl, the ions were quantified by ICP-OES. The limits of detection are 21 pg·mL−1 for Co(II), and 19 pg·mL−1 for Sn(II). The preconcentration factors are 100 for both ions. The sorption capacities of the sorbent are 35.8 mg·g−1 for Co(II) and 29.6 mg·g−1 for Sn(II). The method was applied to the analysis of certificated reference materials and gave ≥95% recoveries with low RSDs. It was also successfully applied to the quantification of Co(II) and Sn(II) in spiked environmental and food samples.

The fungus Boletus edulis loaded with γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles is a viable biosorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of trace levels of Co(II) and Sn(II). The surface structure of immobilized magnetized B. edulis was characterized by FT-IR, SEM and EDX. Experimental parameters were optimized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ataro A, McCrindle RI, Botha BM, McCrindle CME, Ndibewu PP (2008) Quantification of trace elements in raw cow’s milk by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chem 111(1):243–248
Elatrash S, Atoweir N (2014) Determination of lead and cadmium in raw cow’s milk by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy. Int J Chem Sci 12:92–100
Ozdemir S, Kilinc E, Poli A, Nicolaus B, Guven K (2012) Cd, cu, Ni, Mn and Zn resistance and bioaccumulation by thermophilic bacteria. Geobacillus toebii subsp. decanicus and Geobacillus thermoleovorans subsp. stromboliensis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:155–163
Ozcan SG, Satiroglu N, Soylak M (2010) Column solid phase extraction of iron(III), copper(II), manganese(II) and lead(II) ions food and water samples on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem Toxicol 48(8–9):2401–2406
Ozdemir S, Okumuş V, Dundar A, Kilinc E (2013) Preconcentration of metal ions using microbacteria. Microchim Acta 180:719–739
Vojoudi H, Badiei A, Bahar S, Ziarani GM, Faridbod F, Ganjali MR (2017) A new nano-sorbent for fast and efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions based on modification of magnetic mesoporous silica nanospheres. J Magn Magn Mater 441:193–203
Kazi TG, Khan S, Baig JA, Kolachi NF, Afridi HI, Kandhro GA, Kumar S, Shah AQ (2009) Separation and preconcentration of aluminum in parenteral solutions and bottled mineral water using different analytical techniques. J Hazard Mater 172:780–785
Salarian M, Ghanbarpour A, Behbahani M, Bagheri S, Bagheri A (2014) A metal-organic frame work sustained by a nano sized Ag12 cuboctahedral node for solid-phase extraction of ultra traces of lead(II) ions. Microchim Acta 181:999–1007
Vojoudi H, Badiedi A, Banaei A, Bahar S, Karimi S, Ziarani GM, Ganjali MR (2017) Extraction of gold, palladium and silver ions using organically modified silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles and silica gel as a sorbent. Microchim Acta 184:3859–3866
Kilinc E (2016a) γ-Fe2O3 magnetik nanoparticle functionalized with carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotube: synthesis, characterization, analytical and biomedical application. J Magn Magn Mater 401:949–955
Kilinc E (2016b) Fullerene C60 functionalized γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticle: synthesis, characterization, and biomedical applications. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:298–304
Ozdemir S, Okumus V, Dundar A, Kilinc E (2014) The use of fungal biomass Agaricus bisporus immobilized on Amberlite XAD-4 resin for the solid phase preconcentration of thorium. Bioremediation Journal 18:35–45
Ozdemir S, Kilinc E, Celik KS, Okumus V, Soylak M (2017) Simultaneous preconcentrations of Co2+, Cr6+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ ions by Bacillus altitudinis immobilized nanodiamond prior to their determinations in food samples by ICP-OES. Food Chem 215:447–453
Ozdemir S, Okumus V, Dundar A, Kilinc E (2013) Preconcentration of metal ions using microbacteria. Microchim Acta 180:719–739
Mahmoud ME, Abdoua AEH, Mohamed SMS, Osman MM (2016) Engineered staphylococcus aureus via immobilization on magnetic Fe3O4-phthalate nanoparticles for biosorption of divalent ions from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3810–3824
Mahmoud ME (2002) Study of the selectivity characteristics incorporated into physically adsorbed alumina phases. II. Mercaptonicotinic acid and potential applications as selective stationary phases for separation extraction, and preconcentration of lead(II) and copper(II). J Liquid Chromatogr Relat Technol 25:1187–1199
Porter SK, Scheckel KG, Impellitteri CA, Ryan JA (2004) Toxic metals in the environment: thermodynamic considerations for possible immobilization strategies for Pb, cd, as, and hg. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 34:495–604
Kilinc E, Dündar A, Ozdemir S, Okumus V (2013a) Preconcentration of Sn in real water samples by solid phase extraction based on the use of Helvella leucopus as a fungal biomass prior to its determination by ICP-OES. At Spectrosc 34(4):133–139
Mousavi AZ, Aibaghi-Esfahani B, Arjmandi A (2009) Solid phase extraction of lead(II) by sorption on grinded eucalyptus stem and determination with flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Chin Chem Soc 56:974–980
Karatepe A, Soylak M (2014) Sea sponge as a low cost biosorbent for solid phase extraction of some heavy metal ions and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J AOAC Int 97(6):1689–1695
Cho DH, Yoo MH, Kim EY (2004) Biosorption of lead (Pb2+) from aqueous solution by Rhodotorula Aurantiaca. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14(2):250–255
Kilinc E, Dundar A, Ozdemir S, Okumus V (2013b) Solid phase extraction based on the use of Agaricus arvensis as a fungal biomass for the preconcentrations of Pb and al prior to their determination in vegetables by ICP-OES. At Spectrosc 34:78–88
Tuzen M, Saygi KO, Soylak M (2008) Solid phase extraction of heavy metal ions in environmental samples on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 152:632–639
Oral EV, Ozdemir S, Dolak I, Okumuş V, Dündar A, Ziyadanoğulları B, Aksoy Z, Onat R (2015) Anoxybacillus sp. SO B1 immobilized Amberlite XAD-16 for solid phase preconcentration of cu(II), Pb(II) and their determinations by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Bioremediation Journal 19:139–150
Ozdemir S, Kilinc E, Okumuş V, Poli A, Nicolaus B, Romano I (2016) Thermophilic Geobacillus galactosidasius sp nov. loaded γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticle for the preconcentrations of Pb and cd. Bioresour Technol 201:269–275
Bakircioglu D, Ucar G, Bakircioglu Kurtulus Y (2011) Coliform bacteria immobilized on titanium dioxide nanoparticles as a biosorbent for trace lead preconcentration followed by atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Microchim Acta 174:367–374
Shegefti S, Mehdinia A, Shemirani F (2016) Preconcentration of cobalt(II) using polythionine-coated Fe3O4 nanocomposite prior its determination by AAS. Microchim Acta 183:1963–1970
Ozdemir S, Kilinc E, Erdogan S (2010) Bacillus sp. immobilized on Amberlite XAD-4 resin as a biosorbent for solid phase extraction of thorium prior to UV-vis spectrometry determinationin. Microchim Acta 171:275–281
Tuzen M, Uluozlu OD, Usta C, Soylak M (2007) Biosorption of copper(II), lead(II), iron(III) and cobalt(II) on Bacillus sphaericus-loaded Diaion SP-850 resin. Anal Chim Acta 581:241–246
Sacmacı S, Yılmaz Y, Kartal S, Kaya M, Duman F (2014) Resting eggs as new biosorbent for Preconcentration of trace elements in various samples prior to their determination by FAAS. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:254–262
Zheng H, Jia B, Zhu Z, Tang Z, Hu S (2014) Determination of trace amounts of Pb, cd, Ni and co by wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry after preconcentration with dithizone functionalized graphene. Anal Methods 6:8569–8576
Mohammadi SZ, Afzali D, Fallahi Z, Mehrabia A, Moslemia S (2015) Ligand-less in situ surfactant-based solid phase extraction for Preconcentration of cobalt, nickel and zinc from water samples prior to their FAAS determination. J Braz Chem Soc 26(1):51–56
Amjadi M, Manzoori JL, Hamedpour V (2013) Optimized ultrasound-assisted temperature-controlled ionic liquid microextraction coupled with FAAS for determination of tin in canned foods. Food Anal Methods 6:1657–1664
Uluozlu OD, Tuzen M (2015) Carrier element-free coprecipitation and speciation of inorganic tin in beverage samples and total tin in food samples using N-benzoyl-N,Ndiisobutylthiourea and its determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. LWT - Food Sci Technol 63:1091–1096
Vassileva E, Furuta N (2001) Application of high-surface-area ZrO2 in preconcentration and determination of 18 elements by on-line flow injection with inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 370:52–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1922 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir, S., Serkan Yalcin, M., Kilinc, E. et al. Boletus edulis loaded with γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as a magnetic sorbent for preconcentration of Co(II) and Sn(II) prior to their determination by ICP-OES. Microchim Acta 185, 73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2605-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2605-5